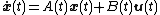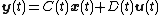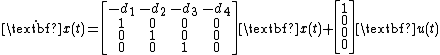- LTI System Canonical realizations
- General System D = 0
- System identification
- See also
- References
In systems theory, a realization of a state space model is an implementation of a given input-output behavior. That is, given an input-output relationship, a realization is a quadruple of (time-varying) matrices 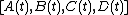 such that
such that
with 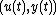 describing the input and output of the system at time
describing the input and output of the system at time  .
.
LTI System
For a linear time-invariant system specified by a transfer matrix,  , a realization is any quadruple of matrices
, a realization is any quadruple of matrices 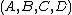 such that
such that  .
.
Canonical realizations
Any given transfer function which is strictly proper can easily be transferred into state-space by the following approach (this example is for a 4-dimensional, single-input, single-output system)):
Given a transfer function, expand it to reveal all coefficients in both the numerator and denominator. This should result in the following form:
.
The coefficients can now be inserted directly into the state-space model by the following approach:
.
This state-space realization is called controllable canonical form (also known as phase variable canonical form) because the resulting model is guaranteed to be controllable (i.e., because the control enters a chain of integrators, it has the ability to move every state).
The transfer function coefficients can also be used to construct another type of canonical form
.
This state-space realization is called observable canonical form because the resulting model is guaranteed to be observable (i.e., because the output exits from a chain of integrators, every state has an effect on the output).
General System
D = 0
If we have an input  , an output
, an output  , and a weighting pattern
, and a weighting pattern 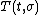 then a realization is any triple of matrices
then a realization is any triple of matrices 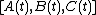 such that
such that 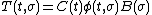 where
where  is the state-transition matrix associated with the realization.[1]
is the state-transition matrix associated with the realization.[1]
System identification
{{main|System identification}}System identification techniques take the experimental data from a system and output a realization. Such techniques can utilize both input and output data (e.g. eigensystem realization algorithm) or can only include the output data (e.g. frequency domain decomposition). Typically an input-output technique would be more accurate, but the input data is not always available.
See also
{{Portal|Mathematics}}- Grey box model
- Statistical Model
- System identification
References
- Ralph Pucci: The Art of the Mannequin
- Ralph Querfurth
- Ralph Raffles
- Ralph Raisbeck
- Ralph Reed (baseball)
- Ralph Reitan
- Ralph R. Frerichs
- Ralph, Richard
- Ralph Richardson (geologist)
- Ralph Richeson
- Ralph Richter
- Ralph Risk
- Ralph Roberts (athlete)
- Ralph Robert Shaw
- Ralph Robertson
- Ralph Robertson (soccer)
- Ralph Roberts (sailor)
- Ralph Robey
- Ralph Robinson (clergyman)
- Ralph Rodgerson (footballer, born 1913)
- Ralph Rokeby
- Ralph Rokeby (disambiguation)
- Ralph Rollins House
- Ralph Romano
- Ralph Ropp