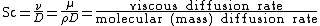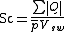- Turbulent Schmidt Number
- Stirling engines
- References
- Notes
Schmidt number (Sc) is a dimensionless number defined as the ratio of momentum diffusivity (kinematic viscosity) and mass diffusivity, and is used to characterize fluid flows in which there are simultaneous momentum and mass diffusion convection processes. It was named after the German engineer Ernst Heinrich Wilhelm Schmidt (1892–1975).
The Schmidt number is the ratio of the shear component for diffusivity viscosity/density to the diffusivity for mass transfer D. It physically relates the relative thickness of the hydrodynamic layer and mass-transfer boundary layer. Its analysis has engendered many extensions in various fields of physics.[1]
It is defined[2] as:
where:
-
 is the kinematic viscosity or (
is the kinematic viscosity or (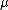 /
/ ) in units of (m2/s)
) in units of (m2/s) -
 is the mass diffusivity (m2/s).
is the mass diffusivity (m2/s). -
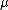 is the dynamic viscosity of the fluid (Pa·s or N·s/m² or kg/m·s)
is the dynamic viscosity of the fluid (Pa·s or N·s/m² or kg/m·s) -
 is the density of the fluid (kg/m³).
is the density of the fluid (kg/m³).
The heat transfer analog of the Schmidt number is the Prandtl number (Pr). The ratio of thermal diffusivity to mass diffusivity is the Lewis number (Le).
Turbulent Schmidt Number
The turbulent Schmidt number is commonly used in turbulence research and is defined as:[3]
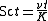
where:
-
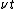 is the eddy viscosity in units of (m2/s)
is the eddy viscosity in units of (m2/s) -
 is the eddy diffusivity (m2/s).
is the eddy diffusivity (m2/s).
The turbulent Schmidt number describes the ratio between the rates of turbulent transport of momentum and the turbulent transport of mass (or any passive scalar). It is related to the turbulent Prandtl number which is concerned with turbulent heat transfer rather than turbulent mass transfer. It is useful for solving the mass transfer problem of turbulent boundary layer flows. The simplest model for Sct is the Reynolds analogy, which yields a turbulent Schmidt number of 1. From experimental data and CFD simulations, Sct ranges from 0.4 to 3.5.
Stirling engines
For Stirling engines, the Schmidt number is related to the specific power.
Gustav Schmidt of the German Polytechnic Institute of Prague published an analysis in 1871 for the now-famous closed-form solution for an idealized isothermal Stirling engine model.[4][5]
where,
-
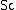 is the Schmidt number
is the Schmidt number -
 is the heat transferred into the working fluid
is the heat transferred into the working fluid -
 is the mean pressure of the working fluid
is the mean pressure of the working fluid -
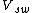 is the volume swept by the piston.
is the volume swept by the piston.
References
2. ^{{Citation | last1 = Incropera | first1 = Frank P. | last2 = DeWitt | first2 = David P. | title = Fundamentals of Heat and Mass Transfer | edition = 3rd | publisher = John Wiley & Sons | year = 1990 | pages = 345 | isbn = 978-0-471-51729-0 }} Eq. 6.71.
3. ^{{cite journal|last=Brethouwer|first=G.|title=The effect of rotation on rapidly sheared homogeneous turbulence and passive scalar transport. Linear theory and direct numerical simulation|journal=J. Fluid Mech.|year=2005|volume=542|pages=305–342|doi=10.1017/s0022112005006427|bibcode = 2005JFM...542..305B }}
4. ^Schmidt Analysis (updated 12/05/07) {{webarchive|url=https://web.archive.org/web/20080518073519/http://www.ent.ohiou.edu/~urieli/stirling/isothermal/Schmidt.html |date=2008-05-18 }}
5. ^http://mac6.ma.psu.edu/stirling/simulations/isothermal/schmidt.html
}}
Notes
{{NonDimFluMech}}- County Route 14A (Cattaraugus County, New York)
- County Route 14 (Albany County, New York)
- County Route 14 (Allegany County, New York)
- County Route 14 (Cayuga County, New York)
- County Route 14 (Chemung County, New York)
- County Route 14 (Delaware County, New York)
- County Route 14 (Greene County, New York)
- County Route 14 (Orange County, New York)
- County Route 14 (Oswego County, New York)
- County Route 14 (Saratoga County, New York)
- County Route 14 (Schoharie County, New York)
- County Route 14 (Steuben County, New York)
- County Route 14 (St. Lawrence County, New York)
- County Route 14 (Sullivan County, New York)
- County Route 14 (Tioga County, New York)
- County Route 150 (Cortland County, New York)
- County Route 150 (Fulton County, New York)
- County Route 150 (Onondaga County, New York)
- County Route 151 (Albany County, New York)
- County Route 151 (Cortland County, New York)
- County Route 151 (Randolph and Upshur Counties, West Virginia)
- County Route 151 (Randolph County, West Virginia)
- County Route 151 (Schenectady County, New York)
- County Route 151 (Upshur County, West Virginia)
- County Route 152A (Cortland County, New York)