- Definition
- Mathematical detail
- See also
- References
- External links
In control theory the settling time of a dynamical system such as an amplifier or other output device is the time elapsed from the application of an ideal instantaneous step input to the time at which the amplifier output has entered and remained within a specified error band.
Settling time includes a propagation delay, plus the time required for the output to slew to the vicinity of the final value, recover from the overload condition associated with slew, and finally settle to within the specified error.
Systems with energy storage cannot respond instantaneously and will exhibit transient responses when they are subjected to inputs or disturbances.[1]
Definition
Tay, Mareels and Moore (1997) defined settling time as "the time required for the response curve to reach and stay within a range of certain percentage (usually 5% or 2%) of the final value."[2]
Mathematical detail
Settling time depends on the system response and natural frequency.
The settling time for a second order, underdamped system responding to a step response can be approximated if the damping ratio 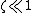 by
by
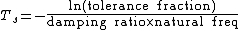
A general form is
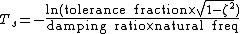
Thus, settling time to within 2% = 0.02 is:
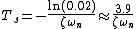
See also
- Rise time
- Time constant
References
2. ^{{Cite book| title = High performance control | last = Tay | first = Teng-Tiow |author2=Iven Mareels |author3=John B. Moore | publisher = Birkhäuser | year = 1997 | isbn = 978-0-8176-4004-0 | page = 93}}
External links
{{wikisourcehas|a paper on settling time measurements.|High accuracy settling time measurements}}- [https://web.archive.org/web/20040626102542/http://bass.gmu.edu/~gbeale/ece_421/second_order_04.html Second-Order System Example]
- Op Amp Settling Time
- [https://web.archive.org/web/20070705124107/http://www.facstaff.bucknell.edu/mastascu/eControlHTML/SysDyn/SysDyn5.html Graphical tutorial] of Settling time and Risetime
- MATLAB function for computing settling time, rise time, and other step response characteristics
- Shadaab Khan
- Shadab Kabir
- Shada Hassoon
- Shadal
- Shad Bagh
- Shad Barry
- Shad Bay, Nova Scotia
- Shad Beast Gaspard
- Shadbelly
- Shad berry
- Shadblow
- Shadblow Serviceberry
- Shad boat
- Shad Boat
- Shad-bush
- Shadbush serviceberry
- Shadchanim
- Shaddad
- Shaddadids
- Shaddah
- Shaddai (god)
- Shaddam
- Shaddam Corrino I
- Shadda palace
- Shaddapa You Face