- Algorithm
- Example
- Example implementations
- References
- External links
Shanks's square forms factorization is a method for integer factorization devised by Daniel Shanks as an improvement on Fermat's factorization method.
The success of Fermat's method depends on finding integers  and
and  such that
such that 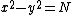 , where
, where  is the integer to be factored. An improvement (noticed by Kraitchik) is to look for integers
is the integer to be factored. An improvement (noticed by Kraitchik) is to look for integers  and
and  such that
such that 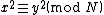 . Finding a suitable pair
. Finding a suitable pair  does not guarantee a factorization of
does not guarantee a factorization of  , but it implies that
, but it implies that  is a factor of
is a factor of 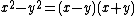 , and there is a good chance that the prime divisors of
, and there is a good chance that the prime divisors of  are distributed between these two factors, so that calculation of the greatest common divisor of
are distributed between these two factors, so that calculation of the greatest common divisor of  and
and  will give a non-trivial factor of
will give a non-trivial factor of  .
.
A practical algorithm for finding pairs  which satisfy
which satisfy 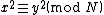 was developed by Shanks, who named it Square Forms Factorization or SQUFOF. The algorithm can be expressed in terms of continued fractions or in terms of quadratic forms. Although there are now much more efficient factorization methods available, SQUFOF has the advantage that it is small enough to be implemented on a programmable calculator.
was developed by Shanks, who named it Square Forms Factorization or SQUFOF. The algorithm can be expressed in terms of continued fractions or in terms of quadratic forms. Although there are now much more efficient factorization methods available, SQUFOF has the advantage that it is small enough to be implemented on a programmable calculator.
Algorithm
Input:  , the integer to be factored, which must be neither a prime number nor a perfect square, and a small multiplier
, the integer to be factored, which must be neither a prime number nor a perfect square, and a small multiplier  .
.
Output: a non-trivial factor of  .
.
Initialize 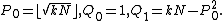
Repeat

until  is a perfect square at some even
is a perfect square at some even 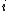 .
.
Initialize 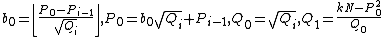
Repeat

until 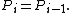
Then if 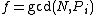 is not equal to
is not equal to  and not equal to
and not equal to  , then
, then  is a non-trivial factor of
is a non-trivial factor of  . Otherwise try another value of
. Otherwise try another value of  .
.
Shanks's method has time complexity 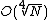 .
.
Stephen S. McMath wrote
a more detailed discussion of the mathematics of Shanks's method,
together with a proof of its correctness.[1]
Example
Let 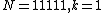
 | 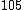 |  | |
 |  | 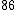 |  |
 | 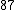 | 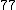 |  |
 | 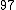 | 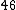 |  |
 | 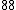 | 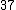 |  |
 | 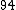 | 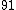 |  |
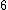 |  |
Here 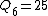 is a perfect square.
is a perfect square.
 | 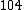 |  |  |
 | 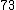 | 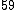 |  |
 |  | 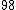 |  |
 | 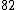 | 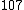 |  |
 | 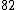 | 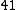 |  |
Here 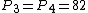 .
.
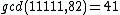 , which is a factor of
, which is a factor of 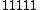 .
.
Thus, 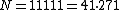
Example implementations
Below is an example of C function for performing SQUFOF factorization on unsigned integer not larger than 64 bits, without overflow of the transient operations. {{cn|date=May 2017}}
- include
- define nelems(x) (sizeof(x) / sizeof((x)[0]))
const int multiplier[] = {1, 3, 5, 7, 11, 3*5, 3*7, 3*11, 5*7, 5*11, 7*11, 3*5*7, 3*5*11, 3*7*11, 5*7*11, 3*5*7*11};
uint64_t SQUFOF( uint64_t N )
{ uint64_t D, Po, P, Pprev, Q, Qprev, q, b, r, s; uint32_t L, B, i; s = (uint64_t)(sqrtl(N)+0.5); if (s*s == N) return s; for (int k = 0; k < nelems(multiplier) && N <= UINT64_MAX/multiplier[k]; k++) { D = multiplier[k]*N; Po = Pprev = P = sqrtl(D); Qprev = 1; Q = D - Po*Po; L = 2 * sqrtl( 2*s ); B = 3 * L; for (i = 2 ; i < B ; i++) { b = (uint64_t)((Po + P)/Q); P = b*Q - P; q = Q; Q = Qprev + b*(Pprev - P); r = (uint64_t)(sqrtl(Q)+0.5); if (!(i & 1) && r*r == Q) break; Qprev = q; Pprev = P; }; if (i >= B) continue; b = (uint64_t)((Po - P)/r); Pprev = P = b*r + P; Qprev = r; Q = (D - Pprev*Pprev)/Qprev; i = 0; do { b = (uint64_t)((Po + P)/Q); Pprev = P; P = b*Q - P; q = Q; Q = Qprev + b*(Pprev - P); Qprev = q; i++; } while (P != Pprev); r = gcd(N, Qprev); if (r != 1 && r != N) return r; } return 0;}
References
- {{cite book
| author = D. A. Buell
| title = Binary Quadratic Forms
| publisher = Springer-Verlag
| year = 1989
| isbn=0-387-97037-1 }}
- {{cite book
| author = D. M. Bressoud|authorlink=David Bressoud
| title = Factorisation and Primality Testing
| publisher = Springer-Verlag
| year = 1989
| isbn=0-387-97040-1 }}
- {{cite book
| last=Riesel | first=Hans | authorlink=Hans Riesel
| title=Prime numbers and computer methods for factorization
| publisher=Birkhauser
|edition = 2nd
| year=1994
| isbn=0-8176-3743-5 }}
- {{cite book | author =Samuel S. Wagstaff, Jr. | title=The Joy of Factoring | publisher=American Mathematical Society | location=Providence, RI | year=2013 | isbn=978-1-4704-1048-3 |url=http://www.ams.org/bookpages/stml-68 |author-link=Samuel S. Wagstaff, Jr. |pages=163–168 }}
External links
- Daniel Shanks: Analysis and Improvement of the Continued Fraction Method of Factorization, (transcribed by S. McMath 2004)
- Daniel Shanks: SQUFOF Notes, (transcribed by S. McMath 2004)
- Stephen S. McMath: Parallel integer factorization using quadratic forms, 2005
- S. McMath, F. Crabbe, D. Joyner: Continued fractions and parallel SQUFOF, 2005
- Jason Gower, Samuel Wagstaff: Square Form Factorisation (Published)
- Shanks's SQUFOF Factoring Algorithm
- [https://github.com/TilmanNeumann/java-math-library java-math-library]
- Agesta Nuclear Plant
- Agesta Nuclear Power Plant
- Age Starheim
- Agestasjon
- Age Station
- Agestaverket
- Age Sten Nilsen
- A Gest of Robin Hood
- Age stratification
- Age structure
- Age-structured homosexuality
- Age structure diagram
- Ages (wine)
- A Get2Gether
- Agetas
- Age the wine
- AGETIP
- Age to age
- Age tofu
- Agetor
- Age to run for public office
- Age Tovan
- A Get Together to Tear It Apart
- Age UK
- A. Geulincx
 !
! !
!