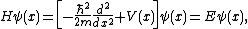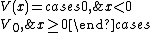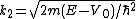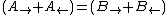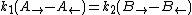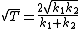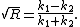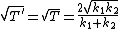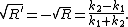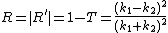- Calculation Schrödinger equation and potential function Solution Boundary conditions
- Transmission and reflection
- Analysis of the expressions Energy less than step height (E < V0) Energy greater than step height (E > V0)
- Classical limit
- Relativistic calculation
- Applications
- See also
- References
- Sources
- Further reading
In quantum mechanics and scattering theory, the one-dimensional step potential is an idealized system used to model incident, reflected and transmitted matter waves. The problem consists of solving the time-independent Schrödinger equation for a particle with a step-like potential in one dimension. Typically, the potential is modelled as a Heaviside step function.
Calculation
Schrödinger equation and potential function
The time-independent Schrödinger equation for the wave function 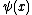 is
is
where H is the Hamiltonian, ħ is the reduced Planck constant, m is the mass, E the energy of the particle. The step potential is simply the product of V0, the height of the barrier, and the Heaviside step function:
The barrier is positioned at x = 0, though any position x0 may be chosen without changing the results, simply by shifting position of the step by −x0.
The first term in the Hamiltonian, 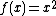 is the kinetic energy of the particle.
is the kinetic energy of the particle.
Solution
The step divides space in two parts: x < 0 and x > 0. In any of these parts the potential is constant, meaning the particle is quasi-free, and the solution of the Schrödinger equation can be written as a superposition of left and right moving waves (see free particle)
,
where subscripts 1 and 2 denote the regions x < 0 and x > 0 respectively, the subscripts (→) and (←) on the amplitudes A and B denote the direction of the particle's velocity vector: right and left respectively.
The coefficients 1/√k1 and 1/√k2 are normalization constants. The wave vectors in the respective regions being
,
both of which have the same form as the De Broglie relation (in one dimension)
.
Boundary conditions
The coefficients A, B have to be found from the boundary conditions of the wave function at x = 0. The wave function and its derivative have to be continuous everywhere, so:
,
.
Inserting the wave functions, the boundary conditions give the following restrictions on the coefficients
Transmission and reflection
It is useful to compare the situation to the classical case. In both cases, the particle behaves as a free particle outside of the barrier region. A classical particle with energy E larger than the barrier height V0 will be slowed down but never reflected by the barrier, while a classical particle with E < V0 incident on the barrier from the left would always be reflected. Once we have found the quantum-mechanical result we will return to the question of how to recover the classical limit.
To study the quantum case, let us consider the following situation: a particle incident on the barrier from the left side A→. It may be reflected (A←) or transmitted (B→). Here and in the following assume E > V0.
To find the amplitudes for reflection and transmission for incidence from the left, we set in the above equations A→ = 1 (incoming particle), A← = {{radic|R}} (reflection), B← = 0 (no incoming particle from the right) and B→ = {{radic|Tk1/k2}} (transmission). We then solve for T and R.
The result is:
The model is symmetric with respect to a parity transformation and at the same time interchange k1 and k2. For incidence from the right we have therefore the amplitudes for transmission and reflection
Analysis of the expressions
Energy less than step height (E < V0)
For energies E < V0, the wave function to the right of the step is exponentially decaying over a distance 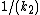 .
.
Energy greater than step height (E > V0)
In this energy range the transmission and reflection coefficient differ from the classical case. They are the same for incidence from the left and right:
In the limit of large energies E ≫ V0, we have k1 ≈ k2 and the classical result T = 1, R = 0 is recovered.
Thus there is a finite probability for a particle with an energy larger than the step height to be reflected.
Classical limit
The result obtained for R depends only on the ratio E/V0. This seems superficially to violate the correspondence principle, since we obtain a finite probability of reflection regardless of the value of Planck's constant or the mass of the particle. For example, we seem to predict that when a marble rolls to the edge of a table, there can be a large probability that it is reflected back rather than falling off. Consistency with classical mechanics is restored by eliminating the unphysical assumption that the step potential is discontinuous. When the step function is replaced with a ramp that spans some finite distance w, the probability of reflection approaches zero in the limit 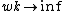 , where k is the wavenumber of the particle.[1]
, where k is the wavenumber of the particle.[1]
Relativistic calculation
The relativistic calculation of a free particle colliding with a step potential can be obtained using relativistic quantum mechanics. For the case of 1/2 fermions, like electrons and neutrinos, the solutions of the Dirac equation for high energy barriers produce transmission and reflection coefficients that are not bounded. This phenomenon is known as the Klein paradox. The apparent paradox disappears in the context of quantum field theory.
Applications
The Heaviside step potential mainly serves as an exercise in introductory quantum mechanics, as the solution requires understanding of a variety of quantum mechanical concepts: wavefunction normalization, continuity, incident/reflection/transmission amplitudes, and probabilities.
A similar problem to the one considered appears in the physics of normal-metal superconductor interfaces. Quasiparticles are scattered at the pair potential which in the simplest model may be assumed to have a step-like shape. The solution of the Bogoliubov-de Gennes equation resembles that of the discussed Heaviside-step potential. In the superconductor normal-metal case this gives rise to Andreev reflection.
See also
- Rectangular potential barrier
- Finite potential well
- Infinite potential well
- Delta potential barrier (QM)
- Finite potential barrier (QM)
References
Sources
- Quantum Mechanics Demystified, D. McMahon, Mc Graw Hill (USA), 2006, {{ISBN|0-07-145546 9}}
- Quantum Physics of Atoms, Molecules, Solids, Nuclei, and Particles (2nd Edition), R. Eisberg, R. Resnick, John Wiley & Sons, 1985, {{ISBN|978-0-471-87373-0}}
- Quantum Mechanics, E. Abers, Pearson Ed., Addison Wesley, Prentice Hall Inc, 2004, {{ISBN|978-0-13-146100-0}}
- Elementary Quantum Mechanics, N.F. Mott, Wykeham Science, Wykeham Press (Taylor & Francis Group), 1972, {{ISBN|0-85109-270-5}}
- Stationary States, A. Holden, College Physics Monographs (USA), Oxford University Press, 1971, {{ISBN|0-19-851121-3}}
- Quantum mechanics, E. Zaarur, Y. Peleg, R. Pnini, Schaum’s Oulines, Mc Graw Hill (USA), 1998, {{ISBN|007-0540187}}
Further reading
- The New Quantum Universe, T.Hey, P.Walters, Cambridge University Press, 2009, {{ISBN|978-0-521-56457-1}}.
- Quantum Field Theory, D. McMahon, Mc Graw Hill (USA), 2008, {{ISBN|978-0-07-154382-8}}
- Quantum mechanics, E. Zaarur, Y. Peleg, R. Pnini, Schaum’s Easy Outlines Crash Course, Mc Graw Hill (USA), 2006, {{ISBN|007-145533-7}} {{ISBN|978-007-145533-6}}
- Johanni Mbuna
- Johannine
- Johannine comma
- Johannine works
- Johann I, Prince of Liechtenstein
- Johannis
- Johannisberger wine
- Johannis Browall
- Johannisburger Heide
- Johannis Cossiers
- Johannis de Lublin
- Johannis de Rijke
- Johannis Dogete
- Johannishogl
- Johannishus
- Johannishus Castle
- Johannishögl
- Johanniskirche, Lueneburg
- Johanniskirche, Luneburg
- Johannis L. Van Alen Farm
- Johannism
- Johan Nissen
- Johannisthal (Berlin)
- Johannisthal (disambiguation)
- Johannite