- References
In 1957 John Philip introduced the term sorptivity and defined it as a measure of the capacity of the medium to absorb or desorb liquid by capillarity.[1]
According to C Hall and W D Hoff, the sorptivity expresses the tendency of a material to absorb and transmit water and other liquids by capillarity.[2]
The sorptivity is widely used in characterizing soils and porous construction materials such as brick, stone and concrete.
Calculation of the true sorptivity required numerical iterative procedures dependent on soil water content and diffusivity.
John R. Philip (1969) showed that sorptivity can be determined from horizontal infiltration where water flow is mostly controlled by capillary absorption:
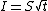
where S is sorptivity and I is the cumulative infiltration (i.e. distance) at time t. Its associated SI unit is m·s−1/2.
For vertical infiltration, Philip's solution is adapted using a parameter A1. This results in the following equations, which are valid for short times:
cumulative: 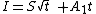
rate: 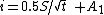
where the sorptivity S is defined (when a sharp wetting front Lf exists) as:

References
2. ^{{Cite book|last=Hall|first=Christopher|last2=Hoff|first2=William D|title=Water transport in brick, stone and concrete, 2nd edn|year=2012|publisher=Taylor and Francis|location=London and New York|url=http://www.routledge.com/books/details/9780415564670/}}