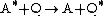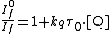- See also
- Sources and notes
The Stern–Volmer relationship, named after Otto Stern and Max Volmer,[1] allows us to explore the kinetics of a photophysical intermolecular deactivation process.
Processes such as fluorescence and phosphorescence are examples of intramolecular deactivation (quenching) processes. An intermolecular deactivation is where the presence of another chemical species can accelerate the decay rate of a chemical in its excited state. In general, this process can be represented by a simple equation:
or
where A is one chemical species, Q is another (known as a quencher) and * designates an excited state.
The kinetics of this process follows the Stern–Volmer relationship:
Where  is the intensity, or rate of fluorescence, without a quencher,
is the intensity, or rate of fluorescence, without a quencher,  is the intensity, or rate of fluorescence, with a quencher,
is the intensity, or rate of fluorescence, with a quencher,  is the quencher rate coefficient,
is the quencher rate coefficient,  is the lifetime of the emissive excited state of A, without a quencher present and
is the lifetime of the emissive excited state of A, without a quencher present and 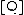 is the concentration of the quencher.[2]
is the concentration of the quencher.[2]
For diffusion-limited quenching (i.e., quenching in which the time for quencher particles to diffuse toward and collide with excited particles is the limiting factor, and almost all such collisions are effective), the quenching rate coefficient is given by 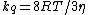 , where
, where  is the ideal gas constant,
is the ideal gas constant, 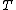 is temperature in kelvins and
is temperature in kelvins and  is the viscosity of the solution. This formula is derived from the Stokes–Einstein relation and is only useful in this form in the case of two spherical particles of identical radius that react every time they approach a distance R, which is equal to the sum of their two radii. The more general expression for the diffusion limited rate constant is
is the viscosity of the solution. This formula is derived from the Stokes–Einstein relation and is only useful in this form in the case of two spherical particles of identical radius that react every time they approach a distance R, which is equal to the sum of their two radii. The more general expression for the diffusion limited rate constant is

Where  and
and  are the radii of the two molecules and
are the radii of the two molecules and 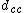 is an approach distance at which unity reaction efficiency is expected (this is an approximation).
is an approach distance at which unity reaction efficiency is expected (this is an approximation).
In reality, only a fraction of the collisions with the quencher are effective at quenching, so the true quenching rate coefficient must be determined experimentally.[3]
See also
Optode, a chemical sensor that makes use of this relationship
Sources and notes
2. ^Permyakov, Eugene A.. [Luminescent Spectroscopy of Proteins], CRC Press, 1993.
3. ^Fluorescence lifetimes and dynamic quenching
- Aram Safrastyan
- A Ram Sam Sam
- Aram Sargsian
- Aram Sargsyan (communist leader)
- Aram Sarkisov
- Aram Satian
- Aram's New Ground
- Aram-Sobah
- Aram Ter-Ghevondyan
- Aram Tigran
- Aramu
- Aramuna
- Aramuna lutosa
- Aramuna marginata
- Aramus, Armenia
- Aramus (disambiguation)
- Aramá River
- Aramäer
- Araméans
- Arana (disambiguation)
- Aranaes
- Aran, Aghjabadi
- Arana Hall
- Arana Hills
- Aranas