- History
- Definition
- Applications
- See also
- References
- Sources
Transfer learning is a research problem in machine learning that focuses on storing knowledge gained while solving one problem and applying it to a different but related problem.[1] For example, knowledge gained while learning to recognize cars could apply when trying to recognize trucks. This area of research bears some relation to the long history of psychological literature on transfer of learning, although formal ties between the two fields are limited.
History
The earliest cited work on transfer in machine learning is attributed to Lorien Pratt, who formulated the discriminability-based transfer (DBT) algorithm in 1993.[2]
In 1997, the journal Machine Learning published a special issue devoted to transfer learning,[3] and by 1998, the field had advanced to include multi-task learning,[4] along with a more formal analysis of its theoretical foundations.[5] Learning to Learn,{{sfn|Thrun|Pratt|2012}} edited by Pratt and Sebastian Thrun, is a 1998 review of the subject.
Transfer learning has also been applied in cognitive science, with the journal Connection Science
publishing a special issue on reuse of neural networks through transfer in 1996.[6]
Definition
The definition of transfer learning is given in terms of domain and task. The domain  consists of: a feature space
consists of: a feature space 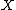 and a marginal probability distribution
and a marginal probability distribution  , where
, where  . Given a specific domain,
. Given a specific domain, 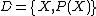 , a task consists of two components: a label space
, a task consists of two components: a label space  and an objective predictive function
and an objective predictive function  (denoted by
(denoted by  ), which is learned from the training data consisting of pairs , which consist of pairs
), which is learned from the training data consisting of pairs , which consist of pairs 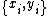 , where
, where  and
and  . The function
. The function  can be used to predict the corresponding label,
can be used to predict the corresponding label, , of a new instance
, of a new instance  .[7]
.[7]
Given a source domain  and learning task
and learning task 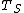 , a target domain
, a target domain  and learning task
and learning task  , transfer learning aims to help improve the learning of the target predictive function
, transfer learning aims to help improve the learning of the target predictive function  in
in  using the knowledge in
using the knowledge in  and
and 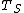 , where
, where 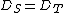 , or
, or 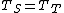 .[7]
.[7]
Applications
Algorithms are available for transfer learning in Markov logic networks[8] and Bayesian networks.[9] Transfer learning has also been applied to cancer subtype
discovery,[10] building utilization,[11][12] general game playing,[13] text classification[14][15] and spam filtering.[16]
See also
- Crossover (genetic algorithm)
- Domain adaptation
- General game playing
- Multi-task learning
- Multitask optimization
References
2. ^{{cite book|url={{google books|plainurl=y|id=6tGHlwEACAAJ|page=204}}|title=NIPS Conference: Advances in Neural Information Processing Systems 5|last=Pratt|first=L. Y.|publisher=Morgan Kaufmann Publishers|year=1993|pp=204–211|chapter=Discriminability-based transfer between neural networks|chapter-url=http://papers.nips.cc/paper/641-discriminability-based-transfer-between-neural-networks.pdf}}
3. ^{{Cite web|url=https://link.springer.com/journal/10994/28/1/page/1|title=Machine Learning - Special Issue on Inductive Transfer|last=Pratt|first=L. Y.|authorlink=|last2=Thrun|first2=Sebastian|date=July 1997|website=link.springer.com|publisher=Springer|access-date=2017-08-10|volume=28|issue=1}}
4. ^Caruana, R., "Multitask Learning", pp. 95-134 in {{Harvnb|Pratt|Thrun|1998}}
5. ^Baxter, J., "Theoretical Models of Learning to Learn", pp. 71-95 {{Harvnb|Pratt|Thrun|1998}}
6. ^{{Cite journal|url=http://www.tandfonline.com/toc/ccos20/8/2|title=Special Issue: Reuse of Neural Networks through Transfer|last=Pratt|first=L.|year=1996 |access-date=2017-08-10|journal=Connection Science|volume=8|issue=2}}
7. ^1 {{cite journal |last1=Lin |first1=Yuan-Pin |last2=Jung |first2=Tzyy-Ping |title=Improving EEG-Based Emotion Classification Using Conditional Transfer Learning |journal=Frontiers in Human Neuroscience |date=27 June 2017 |volume=11 |doi=10.3389/fnhum.2017.00334}} Material was copied from this source, which is available under a [https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/ Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International License].
8. ^{{citation|title=Learning Proceedings of the 22nd AAAI Conference on Artificial Intelligence (AAAI-2007)|date=July 2007|last1=Mihalkova|last2=Huynh|last3=Mooney|first1=Lilyana|first2=Tuyen|first3=Raymond J.|contribution=Mapping and Revising Markov Logic Networks for Transfer|contribution-url=http://www.cs.utexas.edu/users/ml/papers/mihalkova-aaai07.pdf|location=Vancouver, BC|accessdate=2007-08-05|pp=608–614}}
9. ^{{citation|last=Niculescu-Mizil|title=Proceedings of the Eleventh International Conference on Artificial Intelligence and Statistics (AISTATS 2007)|date=March 21–24, 2007|last2=Caruana|first1=Alexandru|first2=Rich|contribution=Inductive Transfer for Bayesian Network Structure Learning|contribution-url=http://www.stat.umn.edu/~aistat/proceedings/data/papers/043.pdf|access-date=2007-08-05}}
10. ^Hajiramezanali, E. & Dadaneh, S. Z. & Karbalayghareh, A. & Zhou, Z. & Qian, X. Bayesian multi-domain learning for cancer subtype discovery from next-generation sequencing count data. 32nd Conference on Neural Information Processing Systems (NeurIPS 2018), Montréal, Canada. https://arxiv.org/pdf/1810.09433.pdf
11. ^{{Cite conference|last=Arief-Ang|first=I.B.|last2=Salim|first2=F.D.|last3=Hamilton|first3=M.|date=2017-11-08|title=DA-HOC: semi-supervised domain adaptation for room occupancy prediction using CO2 sensor data|url=https://dl.acm.org/citation.cfm?id=3137146|conference=4th ACM International Conference on Systems for Energy-Efficient Built Environments (BuildSys)|location=Delft, Netherlands|pages=1–10|doi=10.1145/3137133.3137146|isbn=978-1-4503-5544-5}}
12. ^{{cite journal |last1=Arief-Ang |first1=I.B. |last2=Hamilton |first2=M. |last3=Salim |first3=F.D. |date=2018-12-01 |title=A Scalable Room Occupancy Prediction with Transferable Time Series Decomposition of CO2 Sensor Data |journal=ACM Transactions on Sensor Networks (TOSN) |volume=14 |issue=3–4 |pages=21:1–21:28 |doi=10.1145/3217214 }}
13. ^Banerjee, Bikramjit, and Peter Stone. "General Game Learning Using Knowledge Transfer." IJCAI. 2007.
14. ^{{cite conference|last1=Do|first1=Chuong B.|last2=Ng|first2=Andrew Y.|year=2005|title=Neural Information Processing Systems Foundation, NIPS*2005|url=http://papers.nips.cc/paper/2843-transfer-learning-for-text-classification.pdf|accessdate=2007-08-05|contribution=Transfer learning for text classification}}
15. ^{{cite conference|last1=Rajat|first1=Raina|last2=Ng|first2=Andrew Y.|last3=Koller|first3=Daphne|year=2006|title=Twenty-third International Conference on Machine Learning|url=http://ai.stanford.edu/~ang/papers/icml06-transferinformativepriors.pdf|accessdate=2007-08-05|contribution=Constructing Informative Priors using Transfer Learning}}
16. ^{{cite conference|last=Bickel|first=Steffen|year=2006|title=ECML-PKDD Discovery Challenge Workshop|url=http://www.ecmlpkdd2006.org/discovery_challenge2006_overview.pdf|accessdate=2007-08-05|contribution=ECML-PKDD Discovery Challenge 2006 Overview}}
Sources
- {{cite book|url={{google books|plainurl=y|id=X_jpBwAAQBAJ}}|title=Learning to Learn|last1=Thrun|first1=Sebastian|last2=Pratt|first2=Lorien|date=6 December 2012|publisher=Springer Science & Business Media|isbn=978-1-4615-5529-2|ref=harv}}
- Medium lift launch vehicle
- Medium octahedrite
- Medium power
- Medium pulse repetition frequency
- Medium-Range Forecast Model
- Medium Rare
- Medium Rare (album)
- Medium Rare (disambiguation)
- Medium Rare (film)
- Medium Rare (Foo Fighters album)
- Medium Raw
- Medium Raw (disambiguation)
- Medium Raw: Night of the Wolf
- Medium Scale Integration
- Medium school
- Medium-security
- Medium security prison
- Medium-sized congenital nevus
- Medium-sized seeds
- Mediums of exchange
- Mediums of instruction
- Medium speed rail
- Medium-speed rail
- Medium Speed Vehicle
- Medium speed vehicle