- Turnover number of acetylcholinesterase
- See also
- References
Turnover number has two different meanings:
In enzymology, turnover number (also termed kcat) is defined as the maximum number of chemical conversions of substrate molecules per second that a single catalytic site will execute for a given enzyme concentration 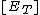 . It can be calculated from the maximum reaction rate
. It can be calculated from the maximum reaction rate  and catalyst site concentration
and catalyst site concentration 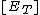 as follows:
as follows:
(See Michaelis-Menten kinetics).
For example, carbonic anhydrase has a turnover number of 400,000 to 600,000 s−1, which means that each carbonic anhydrase molecule can produce up to 600,000 molecules of product (bicarbonate ions) per second.[1]
In other chemical fields, such as organometallic catalysis, turnover number (abbreviated TON) has a different meaning: the number of moles of substrate that a mole of catalyst can convert before becoming inactivated. An ideal catalyst would have an infinite turnover number in this sense, because it wouldn't ever be consumed, but in actual practice one often sees turnover numbers which go from 100 up to 40 million for catalase. The term turnover frequency (abbreviated TOF) is used to refer to the turnover per unit time, as in enzymology. For most relevant industrial applications, the turnover frequency is in the range of 10−2 - 102 s−1 (enzymes 103 - 107 s−1).[1]
Turnover number of catalase is maximum i.e. 4 X 107 s−1.
Turnover number of acetylcholinesterase
{{See also|Diffusion limited enzyme}}Acetylcholinesterase (AChE) may be one of the fastest enzymes. It hydrolyzes acetylcholine to choline and an acetate group. One of the earliest values of the turnover number was 3 x 107 (molecules of acetylcholine) per minute per molecule of enzyme.[2] A more recent value at 25 °C, pH = 7.0, acetylcholine concentration of 2.5 x 10−3 M, was found to be 7.4 x 105 min−1.[3]There may be some 30 active centers per molecule.[4] AChE is a serine hydrolase that reacts with acetylcholine at close to the diffusion-controlled rate.[5]
See also
- Catalysis
References
2. ^{{ cite journal |vauthors=Rothenberg MA, Nachmansohn D |title= Studies on cholinesterase; purification of the enzyme from electric tissue by fractional ammonium sulfate precipitation.|journal=J Biol Chem |volume=168 |issue=1 |pages=223–31 |year=1947 |pmid=20291080 |url=http://www.jbc.org/content/168/1/223.full.pdf}}
3. ^{{ cite journal |vauthors=Wilson IB, Harrison MA |title=Turnover number of acetylcholinesterase |journal=J Biol Chem |date=Aug 1961 |volume=236 |issue=8 |pages=2292–5 |url=http://www.jbc.org/content/236/8/2292.full.pdf }}
4. ^{{ cite journal |author=Berry WK |title=The turnover number of cholinesterase |journal=Biochem. J. |date=Oct 1951 |volume=49 |issue=5 |pages=615–20 |pmid=14886354 |pmc=1197565 |url=http://www.biochemj.org/bj/049/0615/0490615.pdf }}
5. ^{{ cite journal |doi=10.1021/bi00349a019 |vauthors=Bazelyansky M, Robey E, Kirsch JF |title=Fractional diffusion-limited component of reactions catalyzed by acetylcholinesterase|journal=Biochemistry |month= |year=1986 |volume=25 |issue= 1|pages=125–30 |pmid=3954986 }}
- Shing-shen Chern
- Shing-Tung Yau
- Shing-tung Yau
- Shingu
- Shinguu
- Shinguu, Fukuoka
- Shingō, Aomori
- Shingō, Okayama
- Shingū, Ehime
- Shingū, Fukuoka
- Shingū, Hyōgo
- Shingū, Wakayama
- Shin Hae-chul
- Shinhan Financial Group
- Shin-hanga
- Shin (Hebrew)
- Shin Hirayama
- Shinhiroshima Telecasting
- Shinhwa
- Shin Hye-sung
- Shin'ichi Chiba
- Shinichi Chiba
- Shinichi Fujimura
- Shinichi Hoshi
- Shinichi Kitaoka