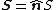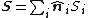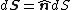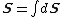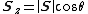- Projection of area onto planes
- See also
- Notes
In 3-dimensional geometry, for a finite planar surface of scalar area {{mvar|S}} and unit normal {{math|n̂}}, the vector area {{math|S}} is defined as the unit normal scaled by the area:
For an orientable surface {{mvar|S}} composed of a set {{mvar|Si}} of flat facet areas, the vector area of the surface is given by
where {{math|n̂i}} is the unit normal vector to the area {{mvar|Si}}.
For bounded, oriented curved surfaces that are sufficiently well-behaved, we can still define vector area. First, we split the surface into infinitesimal elements, each of which is effectively flat. For each infinitesimal element of area, we have an area vector, also infinitesimal.
where {{math|n̂}} is the local unit vector perpendicular to {{mvar|dS}}. Integrating gives the vector area for the surface.
For a curved or faceted surface, the vector area is smaller in magnitude than the area. As an extreme example, a closed surface can possess arbitrarily large area, but its vector area is necessarily zero.[1] Surfaces that share a boundary may have very different areas, but they must have the same vector area—the vector area is entirely determined by the boundary. These are consequences of Stokes' theorem.
The concept of an area vector simplifies the equation for determining the flux through the surface. Consider a planar surface in a uniform field. The flux can be written as the dot product of the field and area vector. This is much simpler than multiplying the field strength by the surface area and the cosine of the angle between the field and the surface normal.
Projection of area onto planes
The projected area onto (for example) the {{mvar|xy}}-plane is equivalent to the {{mvar|z}}-component of the vector area, and is given as
where {{mvar|θ}} is the angle between the plane normal and the {{mvar|z}}-axis.
See also
- Cross product
- Surface normal
- Surface integral
Notes
- Lukas Reimann (Swiss politician)
- Lukas Reiter
- Lukas Resetar
- Lukas Rifesser
- Lukas Rindos
- Lukas Ronald Rumkabu
- Lukas Rotpuller
- Lukas Rumkabu
- Lukas Rupp
- Lukas Rypl
- Lukas Sablik
- Lukas Schubert
- Lukas Schut
- Lukas Sebek
- Lukas Sembera
- Lukas Simonis
- Lukas Skovajsa
- Lukas Spalvis
- Lukas Spelda
- Lukas Spendlhofer
- Lukas Stadler
- Lukas Stetina
- Lukas Stratil
- Lukas Sutter
- Lukas Szabo