软腐病细菌ruanfubingxijun
引起白菜等多种蔬菜发生软腐病的细菌。主要的病原菌有两种,二者形态很相似,仅在生理上稍有不同。菌体均为短杆状,周围有2~8条鞭毛。在较老的培养中是单杆的,但在液体培养中可以连成链状。不生芽孢,革兰色染色阴性。平时只能在有机质中才能生活,病菌只能从白菜等植物体的伤口侵入,能产生分解细胞间隙中间层(果胶素)的酶,破坏植物组织。受害植株主要症状是呈 A、具鞭毛菌体 B、病组织内的细菌萎蔫状态,植株的柔软部分受病初期呈水浸透明状,渐次变为褐色和黑色,并腐烂而流出粘稠汁液,病部有臭味。植株较坚硬部分受病后先呈褐色,渐次腐烂。在田间一般在接近地面的部位先发病。软腐病不仅严重威胁白菜生产,同时也危害萝卜、胡萝卜、芹菜、菠菜、马铃薯、番茄等近30种蔬菜。该病害分布广,除田间为害外,并在运输、贮藏中给蔬菜生产带来重大损失。
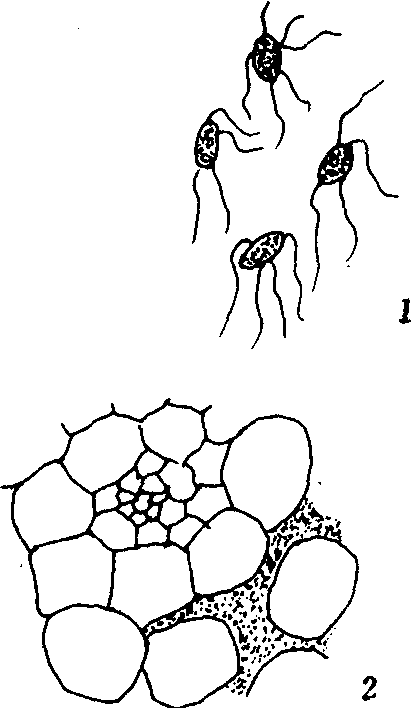
图73 白菜软腐病细菌