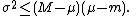- See also
- References
In mathematics, the Bhatia–Davis inequality, named after Rajendra Bhatia and Chandler Davis, is an upper bound on the variance σ2 of any bounded probability distribution on the real line.
Suppose a distribution has minimum m, maximum M, and expected value μ. Then the inequality says:
Equality holds precisely if all of the probability is concentrated at the endpoints m and M.
The Bhatia–Davis inequality is stronger than Popoviciu's inequality on variances.
See also
- Cramér–Rao bound
- Chapman–Robbins bound
References
1. ^Agarwal R P, Barnett N S, Cerone P and Dragomir S S (2005) "A survey on some inequalities for expectation and variance." Computers and mathematics with applications 49 (2005) 429–480
- {{cite journal
| doi = 10.2307/2589180
| last = Bhatia
| first = Rajendra
|author2=Davis, Chandler |authorlink2=Chandler Davis
|date=April 2000
| title = A Better Bound on the Variance
| journal = American Mathematical Monthly
| volume = 107
| issue = 4
| pages = 353–357
| publisher = Mathematical Association of America
| issn = 0002-9890
| jstor = 2589180
}}{{DEFAULTSORT:Bhatia-Davis Inequality}}{{probability-stub}}
2 : Statistical inequalities|Theory of probability distributions
- CARE Act of 1999
- CA-Realizer
- Care Alto
- Care Ambulance Service
- Care Australia
- CARE Australia
- Care (band)
- Carebear
- Care Bear cousin
- Care Bear cousins
- Carebears
- Care Bears: Adventures in Care-a-lot
- Care Bears: Adventures In Care-A-Lot
- Care Bears: Big Wish Movie
- Care Bears cousin
- Care Bears cousins
- Care Bears Gummi Bears
- Care Bears: Journey to Joke-a-lot (soundtrack)
- Care Bears Movie 2: A New Generation
- Care Bears Movie II
- Care Bears Nighty-Night
- Care Bears Nutcracker Suite
- Care Bears on Fire
- Care Bears On Fire
- Care Bears: Oopsy Does It!