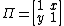- Mathematical definition
- Example
- Relation to solvency cone
- Notes
- References
The bid–ask matrix is a matrix with elements corresponding with exchange rates between the assets. These rates are in physical units (e.g. number of stocks) and not with respect to any numeraire. The  element of the matrix is the number of units of asset
element of the matrix is the number of units of asset 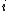 which can be exchanged for 1 unit of asset
which can be exchanged for 1 unit of asset  .
.
Mathematical definition
A  matrix
matrix 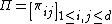 is a bid-ask matrix, if
is a bid-ask matrix, if
-
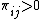 for
for  . Any trade has a positive exchange rate.
. Any trade has a positive exchange rate. -
 for
for 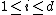 . Can always trade 1 unit with itself.
. Can always trade 1 unit with itself. -
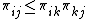 for
for 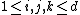 . A direct exchange is always at most as expensive as a chain of exchanges.&91;1&93;
. A direct exchange is always at most as expensive as a chain of exchanges.&91;1&93;
Example
Assume a market with 2 assets (A and B), such that  units of A can be exchanged for 1 unit of B, and
units of A can be exchanged for 1 unit of B, and  units of B can be exchanged for 1 unit of A. Then the bid–ask matrix
units of B can be exchanged for 1 unit of A. Then the bid–ask matrix  is:
is:
Relation to solvency cone
If given a bid–ask matrix  for
for  assets such that
assets such that 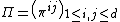 and
and 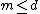 is the number of assets which with any non-negative quantity of them can be "discarded" (traditionally
is the number of assets which with any non-negative quantity of them can be "discarded" (traditionally 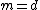 ). Then the solvency cone
). Then the solvency cone 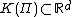 is the convex cone spanned by the unit vectors
is the convex cone spanned by the unit vectors 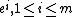 and the vectors
and the vectors 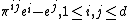 .[1]
.[1]
Similarly given a (constant) solvency cone it is possible to extract the bid–ask matrix from the bounding vectors.
Notes
- The bid–ask spread for pair
 is
is  .
. - If
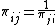 then that pair is frictionless.
then that pair is frictionless.
References
- Kalakaua Park
- Kalakauas
- Kalakaua Torah
- Kalake
- Kalakend
- Kalakeri
- Kalakhamb
- Kala Khel Masti Khan
- Kalaki (disambiguation)
- Kalakik
- Kalakkad S. Ramanarayana Iyer
- Kalakkad S Ramanarayana Iyer
- Kalakkura Chandru
- Kalakshetra Manipur
- Kalaktang Monpa language
- Kalakua
- Kalakua Kaheiheimaile
- Kalakua Kaheiheimalie
- Kalakua Kaheiheimālie
- Kalakundi, India
- Kalakut
- Kalalah
- Kalala Ilunga
- Kalalao
- Kalal clan