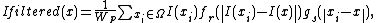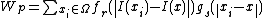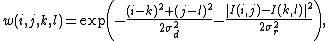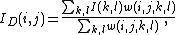- Definition
- Parameters
- Limitations
- Implementations
- Related models
- See also
- External links
- References
A bilateral filter is a non-linear, edge-preserving, and noise-reducing smoothing filter for images. It replaces the intensity of each pixel with a weighted average of intensity values from nearby pixels. This weight can be based on a Gaussian distribution. Crucially, the weights depend not only on Euclidean distance of pixels, but also on the radiometric differences (e.g., range differences, such as color intensity, depth distance, etc.). This preserves sharp edges.
Definition
The bilateral filter is defined as[1][2]
where the normalization term
ensures that the filter preserves image energy and
is the filtered image;
is the original input image to be filtered;
are the coordinates of the current pixel to be filtered;
is the window centered in
;
is the range kernel for smoothing differences in intensities (this function can be a Gaussian function);
is the spatial kernel for smoothing differences in coordinates (this function can be a Gaussian function).
As mentioned above, the weight 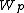 is assigned using the spatial closeness and the intensity difference.[2] Consider a pixel located at
is assigned using the spatial closeness and the intensity difference.[2] Consider a pixel located at  that needs to be denoised in image using its neighbouring pixels and one of its neighbouring pixels is located at
that needs to be denoised in image using its neighbouring pixels and one of its neighbouring pixels is located at 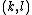 . Then, the weight assigned for pixel
. Then, the weight assigned for pixel 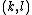 to denoise the pixel
to denoise the pixel  is given by
is given by
where σd and σr are smoothing parameters, and I(i, j) and I(k, l) are the intensity of pixels  and
and 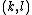 respectively.
respectively.
After calculating the weights, normalize them:
where 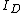 is the denoised intensity of pixel
is the denoised intensity of pixel  .
.
Parameters
- As the range parameter σr increases, the bilateral filter gradually approaches Gaussian convolution more closely because the range Gaussian widens and flattens, which means that it becomes nearly constant over the intensity interval of the image.
- As the spatial parameter σd increases, the larger features get smoothened.
Limitations
The bilateral filter in its direct form can introduce several types of image artifacts:
- Staircase effect – intensity plateaus that lead to images appearing like cartoons[3]
- Gradient reversal – introduction of false edges in the image.[4]
There exist several extensions to the filter that deal with these artifacts. Alternative filters, like the guided filter,[5] have also been proposed as an efficient alternative without these limitations.
Implementations
Adobe Photoshop implements a bilateral filter in its surface blur tool. GIMP implements a bilateral filter in its Filters-->Blur tools; and it is called Selective Gaussian Blur. The free G'MIC plugin Repair → Smooth [bilateral] for GIMP adds more control.[6]A simple trick to efficiently implement a bilateral filter is to exploit Poisson-disk subsampling.[1]
Related models
The bilateral filter has been shown to be an application of the short time kernel of the Beltrami flow
[7][8][9] that was introduced as an edge preserving selective smoothing mechanism before the bilateral filter.
Other edge-preserving smoothing filters include: anisotropic diffusion, weighted least squares,[10] edge-avoiding wavelets,[11] geodesic editing,[12] guided filtering,[13] and domain transforms.[14]
See also
- Gaussian filter
- Gaussian function
- Gaussian blur
- Convolution
External links
{{External links|date=May 2017}}- Kaiming He: Guided image filtering (faster than bilateral filter and avoids staircasing and gradient reversal artifacts)
- Haarith Devarajan, Harold Nyikal, Bilateral Filters, in: Image Scaling and Bilateral Filtering 2006 course
- Sylvain Paris, Pierre Kornprobst, Jack Tumblin, Frédo Durand, [https://dx.doi.org/10.1561/0600000020 Bilateral Filtering: Theory and Applications], preprint
- Sylvain Paris, Pierre Kornprobst, Jack Tumblin, Frédo Durand, A Gentle Introduction to Bilateral Filtering and its Applications, SIGGRAPH 2008 class
- Ben Weiss, Fast Median and Bilateral Filtering, SIGGRAPH 2006 preprint
- Carlo Tomasi, Roberto Manduchi, Bilateral Filtering for Gray and Color Images (shorter HTML version), proceedings of the ICCV 1998
- Qingxiong Yang, Kar-Han Tan, Narendra Ahuja, Real-Time O(1) Bilateral Filtering
References
2. ^1 {{cite conference |url=http://www.cse.ucsc.edu/~manduchi/Papers/ICCV98.pdf |title= Bilateral filtering for gray and color images |first1=C|last1=Tomasi|first2=R|last2=Manduchi |author= |author-link= |date= |year=1998 |conference=Sixth International Conference on Computer Vision|conference-url= |editor= |others= |volume= |edition= |book-title= |publisher= |archive-url= |archive-date= |location=Bombay |pages=839–846 |format= |id= |isbn= |bibcode= |oclc= |doi=10.1109/ICCV.1998.710815 |access-date= |quote= |ref= |postscript= |language= |page= |at= |trans-title= }}
3. ^{{cite web|last1=Kornprobst|first1=Pierre|title=Limitations? - A Gentle Introductionto Bilateral Filteringand its Applications|url=http://people.csail.mit.edu/sparis/bf_course/slides/09_limitations.pdf|accessdate=7 May 2017|date=2007}}
4. ^{{cite web|last1=He|first1=Kaiming|last2=Sun|first2=Jian|last3=Tang|first3=Xiaoou|title=Guided Image Filtering|url=http://kaiminghe.com/eccv10/eccv10ppt.pdf|accessdate=7 May 2017}}
5. ^{{cite web|last1=He|first1=Kaiming|title=Guided Image Filtering|url=http://kaiminghe.com/eccv10/index.html|accessdate=7 May 2017}}
6. ^http://gmic.eu/gimp.shtml
7. ^R. Kimmel, R. Malladi, and N. Sochen. Images as embedding maps and minimal surfaces: Movies, color, and volumetric medical images. IEEE CVPR'97, pp. 350-355, Puerto Rico, June 17-19, 1997. http://www.cs.technion.ac.il/~ron/PAPERS/cvpr97.pdf
8. ^R. Kimmel, R. Malladi, and N. Sochen. Images as Embedded Maps and Minimal Surfaces: Movies, Color, Texture, and Volumetric Medical Images. International Journal of Computer Vision, 39(2):111-129, Sept. 2000. http://www.cs.technion.ac.il/~ron/PAPERS/KimMalSoc_IJCV2000.pdf
9. ^N. Sochen, R. Kimmel, and A.M. Bruckstein. Diffusions and confusions in signal and image processing, Journal of Mathematical Imaging and Vision, 14(3):195-209, 2001.http://www.cs.technion.ac.il/~ron/PAPERS/SocKimBru_JMIV2001.pdf
10. ^Farbman, Zeev, Raanan Fattal, Dani Lischinski, and Richard Szeliski. "Edge-preserving decompositions for multi-scale tone and detail manipulation." In ACM Transactions on Graphics, vol. 27, no. 3 (2008): 67. http://www.cs.huji.ac.il/~danix/epd/
11. ^Fattal, Raanan. "Edge-avoiding wavelets and their applications." In ACM Transactions on Graphics vol. 28, no. 3 (2009): 22. http://www.cs.huji.ac.il/~raananf/projects/eaw/
12. ^Criminisi, Antonio, Toby Sharp, Carsten Rother, and Patrick Pérez. "Geodesic image and video editing." In ACM Transactions on Graphphics (TOG), vol. 29, no. 5 (2010): 134. http://research.microsoft.com/apps/pubs/default.aspx?id=81528
13. ^He, Kaiming, Jian Sun, and Xiaoou Tang. "Guided image filtering." In Computer Vision–ECCV 2010, pp. 1-14. Springer Berlin Heidelberg, 2010. http://kaiminghe.com/eccv10/index.html
14. ^Gastal, Eduardo S. L., and Manuel M. Oliveira. "Domain transform for edge-aware image and video processing." In ACM Transactions on Graphics, vol. 30, no. 4 (2011): 69. http://inf.ufrgs.br/~eslgastal/DomainTransform/
- Solihull Metropolitan Borough Council election, 1973
- Solihull Metropolitan Borough Council election, 1984
- Solihull Metropolitan Borough Council election, 1986
- Solihull Metropolitan Borough Council election, 1987
- Solihull Metropolitan Borough Council election, 1988
- Solihull Metropolitan Borough Council election, 1990
- Solihull Metropolitan Borough Council election, 1991
- Solihull Metropolitan Borough Council election, 1992
- Solihull Metropolitan Borough Council election, 1994
- Solihull Metropolitan Borough Council election, 1995
- Solihull Metropolitan Borough Council election, 1996
- Solihull Metropolitan Borough Council election, 1998
- Solihull Metropolitan Borough Council election, 1999
- Solihull Metropolitan Borough Council election, 2000
- Solihull Metropolitan Borough Council election, 2002
- Solihull Metropolitan Borough Council election, 2003
- Solihull Metropolitan Borough Council election, 2004
- Solihull Metropolitan Borough Council election, 2006
- Solihull Metropolitan Borough Council election, 2007
- Solihull Metropolitan Borough Council election, 2008
- Solihull Metropolitan Borough Council election, 2010
- Solihull Metropolitan Borough Council election, 2011
- Solihull Metropolitan Borough Council election, 2012
- Solihull Metropolitan Borough Council election, 2014
- Solihull Metropolitan Borough Council election, 2015