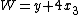- Mathematical definition
- Non-currency examples
- Methods of solving Simple dynamic programming Optimal substructure Implementation Dynamic programming with the probabilistic convolution tree Greedy method
- Related problems
- See also
- References
- Further reading
The change-making problem addresses the question of finding the minimum number of coins (of certain denominations) that add up to a given amount of money. It is a special case of the integer knapsack problem, and has applications wider than just currency.
It is also the most common variation of the coin change problem, a general case of partition in which, given the available denominations of an infinite set of coins, the objective is to find out the number of possible ways of making a change for a specific amount of money, without considering the order of the coins.
It is weakly NP-hard, but may be solved optimally in pseudo-polynomial time by dynamic programming.[1][2]
Mathematical definition
Coin values can be modeled by a set of {{mvar|n}} distinct positive integer values (whole numbers), arranged in increasing order as {{math|w1 {{=}} 1}} through {{math|wn}}. The problem is: given an amount {{mvar|W}}, also a positive integer, to find a set of non-negative (positive or zero) integers {{math|{x1, x2, ..., xn}}}, with each {{math|xj}} representing how often the coin with value {{math|wj}} is used, which minimize the total number of coins {{math|f(W)}}
subject to
Non-currency examples
An application of change-making problem can be found in computing the ways one can make a nine dart finish in a game of darts.
Another application is computing the possible atomic (or isotopic) composition of a given mass/charge peak in mass spectrometry.
Methods of solving
Simple dynamic programming
A classic dynamic programming strategy works upward by finding the combinations of all smaller values that would sum to the current threshold.[3] Thus, at each threshold, all previous thresholds are potentially considered to work upward to the goal amount W. For this reason, this dynamic programming approach may require a number of steps that is at least quadratic in the goal amount W.
Optimal substructure
Since the problem exhibits optimal substructure, dynamic programming strategy can be applied to reach a solution as follows:
Firstly, given that  is the optimal solution that contains exactly
is the optimal solution that contains exactly  coins, hence
coins, hence  . It may seem as if
. It may seem as if  , is the optimal solution for the sub-problem that contains exactly
, is the optimal solution for the sub-problem that contains exactly  coins.
coins.
However,  does not contain
does not contain  coins, and is not optimal, therefore the solution is known as
coins, and is not optimal, therefore the solution is known as  , hence
, hence 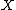 becomes the optimal solution, since it must contain fewer coins than
becomes the optimal solution, since it must contain fewer coins than  .
.
Finally, combining 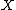 with
with  achieves the optimal solution that contains exactly
achieves the optimal solution that contains exactly  coins, while contradicting any assumptions that
coins, while contradicting any assumptions that  is the optimal solution for the original problem.
is the optimal solution for the original problem.
Implementation
The following is a dynamic programming implementation (with Python 3) which uses a matrix to keep track of the optimal solutions to sub-problems, and returns the minimum number of coins. A second matrix may be used to obtain the set of coins for the optimal solution.
def _get_change_making_matrix(set_of_coins, r):
m = [[0 for _ in range(r + 1)] for _ in range(len(set_of_coins) + 1)] for i in range(r + 1): m[0][i] = i return m
def change_making(coins, n):
"""This function assumes that all coins are available infinitely. n is the number to obtain with the fewest coins. coins is a list or tuple with the available denominations.""" m = _get_change_making_matrix(coins, n) for c in range(1, len(coins) + 1): for r in range(1, n + 1): # Just use the coin coins[c - 1]. if coins[c - 1] == r: m[c][r] = 1 # coins[c - 1] cannot be included. # Use the previous solution for making r, # excluding coins[c - 1]. elif coins[c - 1] > r: m[c][r] = m[c - 1][r] # coins[c - 1] can be used. # Decide which one of the following solutions is the best: # 1. Using the previous solution for making r (without using coins[c - 1]). # 2. Using the previous solution for making r - coins[c - 1] (without # using coins[c - 1]) plus this 1 extra coin. else: m[c][r] = min(m[c - 1][r], 1 + m[c][r - coins[c - 1]]) return m[-1][-1]
Dynamic programming with the probabilistic convolution tree
The probabilistic convolution tree[4] can also be used as a more efficient dynamic programming approach. The probabilistic convolution tree merges pairs of coins to produce all amounts which can be created by that pair of coins (with neither coin present, only the first coin present, only the second coin present, and both coins present), and then subsequently merging pairs of these merged outcomes in the same manner. This process is repeated until the final two collections of outcomes are merged into one, leading to a balanced binary tree with W log(W) such merge operations. Furthermore, by discretizing the coin values, each of these merge operations can be performed via convolution, which can often be performed more efficiently with the fast Fourier transform (FFT). In this manner, the probabilistic convolution tree may be used to achieve a solution in sub-quadratic number of steps: each convolution can be performed in n log(n), and the initial (more numerous) merge operations use a smaller n, while the later (less numerous) operations require n on the order of W.
The probabilistic convolution tree-based dynamic programming method also efficiently solves the probabilistic generalization of the change-making problem, where uncertainty or fuzziness in the goal amount W makes it a discrete distribution rather than a fixed quantity, where the value of each coin is likewise permitted to be fuzzy (for instance, when an exchange rate is considered), and where different coins may be used with particular frequencies.
Greedy method
For the so-called canonical coin systems, like those used in the US and many other countries, a greedy algorithm of picking the largest denomination of coin which is not greater than the remaining amount to be made will produce the optimal result.[5] This is not the case for arbitrary coin systems, though: if the coin denominations were 1, 3 and 4, then to make 6, the greedy algorithm would choose three coins (4,1,1) whereas the optimal solution is two coins (3,3).
However, there is a modified version of greedy algorithm to solve this question. In our case, we have
where 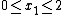 and
and 
since  and
and  .
.
Now let  . We can write
. We can write
where  .
.
For example, given  , we have
, we have 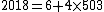 .
.
Hence  .
.
Therefore
where  denotes the largest integer less than or equal to
denotes the largest integer less than or equal to 
and  denotes the remainder of
denotes the remainder of  divided by 4.
divided by 4.
Related problems
The "optimal denomination problem"[6] is a problem for people who design entirely new currencies. It asks what denominations should be chosen for the coins in order to minimize the average cost of making change, that is, the average number of coins needed to make change? The version of this problem assumed that the people making change will use the minimum number of coins (from the denominations available). One variation of this problem assumes that the people making change will use the "greedy algorithm" for making change, even when that requires more than the minimum number of coins. Most current currencies use a 1-2-5 series, but some other set of denominations would require fewer denominations of coins or a smaller average number of coins to make change or both.
See also
- List of knapsack problems
- Coin problem
- The coin collector's problem
References
2. ^{{cite book | last1 = Goodrich | first1 = Michael T. | last2 = Tamassia | first2 = Roberto | at = Exercise A-12.1, p. 349 | publisher = Wiley | title = Algorithm Design and Applications | year = 2015}}
3. ^* {{cite journal |author=J.W.Wright |title=The Change-Making Problem |journal=Journal of the Association for Computing Machinery |volume=22 |issue=1 |year=1975 |pages=125-128 |doi=10.1145/321864.321874 }}
4. ^{{cite journal|last=Serang|first=O.|title=The Probabilistic Convolution Tree: Efficient Exact Bayesian Inference for Faster LC-MS/MS Protein Inference|journal=PLOS ONE|volume=9|year=2012|doi=10.1371/journal.pone.0091507|ref=harv|issue=3|pages=e91507|pmid=24626234|pmc=3953406|bibcode=2014PLoSO...991507S}}
5. ^{{cite journal |author=Xuan Cai |title=Canonical Coin Systems for CHANGE-MAKING Problems |journal=Proceedings of the Ninth International Conference on Hybrid Intelligent Systems |volume=1 |pages=499–504 |year=2009 |doi=10.1109/HIS.2009.103 |arxiv=0809.0400 }}
6. ^{{cite journal |author=J. Shallit |title=What this country needs is an 18c piece |journal=Mathematical Intelligencer |volume=25 |issue=2| year=2003 |pages=20–23 |doi=10.1007/BF02984830 |url=http://www.cs.uwaterloo.ca/~shallit/Papers/change2.pdf}}
Further reading
- {{cite journal |author=X. Cai |title=Canonical Coin Systems for Change-Making Problems |journal=Proceedings of the Ninth International Conference on Hybrid Intelligent Systems |year=2009 |pages=499–504 |doi=10.1109/HIS.2009.103 |arxiv=0809.0400|ref=Cai}}
- {{cite journal |author=M. Adamaszek, A. Niewiarowska |title=Combinatorics of the change-making problem |journal=European Journal of Combinatorics |volume=31 |issue=1 |year=2010 |pages=47–63 |doi=10.1016/j.ejc.2009.05.002 |arxiv=0801.0120}}
- {{cite journal |author=J.W.Wright |title=The Change-Making Problem |journal=Journal of the Association for Computing Machinery |volume=22 |issue=1 |year=1975 |pages=125-128 |doi=10.1145/321864.321874 }}
- Attila Szabo (Hungarian canoer)
- Attila Szabo (Slovak canoer)
- Attila Szabó
- Attila Szabó (athlete)
- Attila Szabó (Hungarian canoeist)
- Attila Szabó (Slovak canoeist)
- Attila Szeki
- Attila Szili
- Attila Széki
- Attila Sánta
- Attila the Hun
- Attila The Hun (pinball)
- Attila Toekoeli
- Attila Tokoli
- Attila Toth
- Attila Tóth
- Attila Vadkerti
- Attila Vari
- Attila Verestoy
- Attila Verestóy
- Attila Végh (canoeist)
- Attila Zabos
- Attila-Zoltan Cseke
- Attila Zoltan Cseke
- Attila-Zoltán Cseke