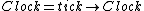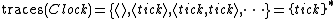- Definitions Rewriting Denotational semantics Concurrency theory
- See also
- Notes
- References
In computer science, a computation is said to diverge if it does not terminate or terminates in an (unobservable) exceptional state. Otherwise it is said to converge. In domains where computations are expected to be infinite, such as process calculi, a computation is said to diverge if it fails to be productive (always produces an action within a finite amount of time.)
Definitions
Various subfields of computer science use varying, but mathematically precise, definitions of what it means for a computation to converge or diverge.
Rewriting
In abstract rewriting, an abstract rewriting system is called convergent if it is both confluent and terminating.{{sfn|Baader|Nipkow|1998|p=9}}
The notation t ↓ n means that t reduces to normal form n in zero or more reductions, t↓ means t reduces to some normal form in zero or more reductions, and t↑ means t does not reduce to a normal form; the latter is impossible in a terminating rewriting system.
In the lambda calculus an expression is divergent if it has no normal form.{{sfn|Pierce|2002|p=65}}
Denotational semantics
In denotational semantics an object function f : A → B can be modelled as a mathematical function f : A ∪ {⊥} → B ∪ {⊥} where ⊥ (bottom) indicates that the object function or its argument diverges.
Concurrency theory
In the calculus of communicating sequential processes, divergence is a drastic situation where a process performs an endless series of hidden actions. For example, consider the following process, defined by CSP notation:
The traces of this process are defined as:
Now, consider the following process, which conceals the tick event of the Clock process:
By definition, P is called a divergent process.
See also
- Infinite loop
- Termination analysis
Notes
References
- {{cite book|first1=Franz|last1=Baader|authorlink1=Franz Baader|first2=Tobias|last2=Nipkow|authorlink2=Tobias Nipkow|title=Term Rewriting and All That|year=1998|publisher=Cambridge University Press|ref=harv|url=https://books.google.com/books?id=N7BvXVUCQk8C&printsec=frontcover#v=onepage&q=Divergent&f=false}}
- {{cite book|first=Benjamin C.|last=Pierce|authorlink=Benjamin C. Pierce|title=Types and Programming Languages|year=2002|publisher=MIT Press|ref=harv}}
- J. M. R. Martin and S. A. Jassim (1997). "How to Design Deadlock-Free Networks Using CSP and Verification Tools: A Tutorial Introduction" in Proceedings of the WoTUG-20.
- Look Me in the Heart
- Look mexico
- Look Mexico
- Look Model Agency
- LOOK Musical Theatre
- Look My Way
- Look My Way (Rosemary Clooney album)
- Look'n'feel
- Look North (East Yorkshire and Lincolnshire)
- Look North (North East and Cumbria)
- Look North (Yorkshire and North Midlands)
- Look Now Look Again
- Look Now (Smog song)
- Look of Love
- Look of Love (ABC song)
- Look of Love: The Very Best of ABC
- Look on the Floor
- Look on the Floor (Hypnotic Tango)
- Look Or The Lifestyle?
- Lookout
- Look-out
- Lookout Air Raids
- Look Out Below
- Lookout book
- Lookout (disambiguation)