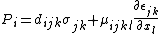- See also
- References
- External links
Flexoelectricity is a property of a dielectric material whereby it exhibits a spontaneous electrical polarization induced by a strain gradient. Flexoelectricity is closely related to piezoelectricity, but while piezoelectricity refers to polarization due to uniform strain, flexoelectricity refers specifically to polarization due to strain that changes from point to point in the material. This nonuniform strain breaks centrosymmetry, meaning that unlike in piezoelectiricty, flexoelectric effects can occur in centrosymmetric crystal structures.[1] Flexoelectricity is not the same as Ferroelasticity.
The electric polarization due to mechanical stress in a dielectric is given by
where the first term corresponds to the direct piezoelectric effect and the second term corresponds to the flexoelectric polarization induced by the strain gradient.
Here, the flexoelectric coefficient, 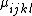 , is a fourth-rank polar tensor and
, is a fourth-rank polar tensor and 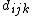 is the coefficient corresponding to the direct piezoelectric effect.
is the coefficient corresponding to the direct piezoelectric effect.
See also
- Piezoelectricity
- Ferroelectricity
- Ferroelasticity
References
External links
- Introduction to Flexoelectricity
- Jayam (2003 film)
- Jayamala
- Jayamala (actress)
- Jayamalini
- Jayamangali Blackbuck Reserve
- Jayamangali (Maidenahalli) Blackbuck Conservation Reserve
- Jayamant Mishra
- Jayamkondaan
- Jayamkondan
- Jayam Manadera
- Jayamohan
- Jayam Raja
- Jayam Ravi
- Jayananda Dasa
- Jayananda Prabhu
- Jayananda Warnaweera
- Jay Andrew Rabinowitz
- Jay Andrews
- Jay and Silent Bob Go Canadian, Eh?
- Jay and Silent Bob go Canadian, eh?
- Jay And Silent Bob Strike Back
- Jay and Silent Bob strike back
- Jay and the americans
- Jay and The Doctor
- Jay and the doctor