- References
In the study of zero sum games, Glicksberg's theorem (also Glicksberg's existence theorem) is a result that shows certain games have a minimax value
.[1]
If A and B are compact sets, and K is an upper semicontinuous or lower semicontinuous function on 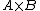 , then
, then
where f and g run over Borel probability measures on A and B.
The theorem is useful if f and g are interpreted as mixed strategies of two players in the context of a continuous game. If the payoff function K is upper semicontinuous, then the game has a value.
The continuity condition may not be dropped: see example of a game with no value.
References
1. ^{{citation | chapter = On a game without a value | first1 = Maurice | last1 = Sion | first2 = Phillip | last2 = Wolfe | pages = 299-306 | title = Contributions to the Theory of Games III | editor1-first = M. | editor1-last = Dresher | editor2-first = A. W. | editor2-last = Tucker | editor3-first = P. | editor3-last = Wolfe | year = 1957 | isbn = 9780691079363 | publisher = Princeton University Press | series = Annals of Mathematics Studies 39}}
{{DEFAULTSORT:Glicksberg's Theorem}}{{gametheory-stub}} 1 : Game theory
- James River Parks system
- James River Parks System
- James River Park System
- James Rivers
- James River Steam Brewery Cellars
- James River Subdivision
- James River (Texas)
- James Rivett-Carnac (Royal Navy officer)
- James R. Jacks
- James R. Jarmusch
- James R. Kass
- James R. Kelley (Pennsylvania legislator)
- James R. Laidler
- James R. Law Jr.
- James R. Lawson
- James R. Leininger
- James R. Lewis (disambiguation)
- James R. L. Macdonald
- James R. Ludlow School
- James R. Lupski
- James R. MacDonnell
- James R. McCartney
- James R. Mead (pioneer)
- James R. Miceli
- James R. Milkey
