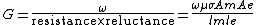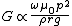- References
The goodness factor is a metric developed by Eric Laithwaite to determine the 'goodness' of an electric motor.[1][2] Using it he was able to develop efficient magnetic levitation induction motors.[3]
where
{{math|G}} is the goodness factor (factors above 1 are likely to be efficient)
{{math|Am}}, {{math|Ae}} are the cross sections of the magnetic and electric circuit
{{math|lm}}, {{math|le}} are the lengths of the magnetic and electric circuits
{{math|μ}} is the permeability of the core
{{math|ω}} is the angular frequency the motor is driven at
{{math|σ}} is the conductivity of the conductor
From this he showed that the most efficient motors are likely to be relatively large. However, the equation only directly relates to non-permanent magnet motors.
Laithwaite showed that for a simple induction motor this gave:
where {{math|p}} is the pole pitch arc length, {{math|ρr}} is the surface resistivity of the rotor and {{math|g}} is the air gap.
References
1. ^{{cite journal | author = ER Laithwaite | date = 1965 | title = The Goodness of a Machine | journal = Electronics and Power | volume = 11 | issue = 3 | pages = 101–103 | doi =10.1049/ep.1965.0071}}
2. ^{{cite journal |author1=DJ Patterson |author2=CW Brice |author3=RA Dougal |author4=D Kovuri | date = 2003 | title = The "Goodness" of Small Contemporary Permanent Magnet Electric Machines | url = http://vtb.engr.sc.edu/vtbwebsite/downloads/publications/IEMDCpaper.pdf | journal = Proceedings of the International Electric Machines and Drives Conference | volume = 2| issue = | pages = 1195–1200 | doi = 10.1109/IEMDC.2003.1210392}}
3. ^{{cite journal | author = ER Laithwaite | date = 1965 | title = Electromagnetic levitation | url = http://ieeexplore.ieee.org/stamp/stamp.jsp?tp=&arnumber=5176480 | journal = Electronics and Power | volume = 11 | issue = 12 | pages = 408–410 | doi = 10.1049/ep.1965.0312}}
2. ^{{cite journal |author1=DJ Patterson |author2=CW Brice |author3=RA Dougal |author4=D Kovuri | date = 2003 | title = The "Goodness" of Small Contemporary Permanent Magnet Electric Machines | url = http://vtb.engr.sc.edu/vtbwebsite/downloads/publications/IEMDCpaper.pdf | journal = Proceedings of the International Electric Machines and Drives Conference | volume = 2| issue = | pages = 1195–1200 | doi = 10.1109/IEMDC.2003.1210392}}
3. ^{{cite journal | author = ER Laithwaite | date = 1965 | title = Electromagnetic levitation | url = http://ieeexplore.ieee.org/stamp/stamp.jsp?tp=&arnumber=5176480 | journal = Electronics and Power | volume = 11 | issue = 12 | pages = 408–410 | doi = 10.1049/ep.1965.0312}}
3 : Induction motors|Dimensionless numbers|Magnetism
- Anil Film Director
- Anil Ganguly
- Anil Goonaratne
- Anil Goswami
- Anil Gote
- Anili
- Anilicus
- Aniline black
- Aniline N,N-dimethyl
- Aniline Violet
- Anilinomethane
- Anilio, Elis
- Anilio, Ioannina
- Anilite Bomb
- Anilite bomb
- Anil Jain (Indian politician)
- Anil Jain (Madhya Pradesh politician)
- Anil Jha Vats
- Anil Johnson
- Anil johnson
- Anil Joshi
- Anil Kadam
- Anil Kamath
- Anil Kapoor's filmography
- Anil K. Bera