- References
The Grinold and Kroner Model is used to calculate expected returns for a stock, stock index or the market as whole. It is a part of a larger framework for making forecasts about market expectations.
The model states that:
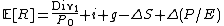 [1]
[1]Where
-
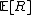 are the expected returns
are the expected returns -
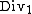 is the dividend in next period (period 1 assuming current t=0)
is the dividend in next period (period 1 assuming current t=0) -
 is the current price (price at time 0)
is the current price (price at time 0) -
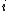 is the expected inflation rate
is the expected inflation rate -
 is the real growth rate in earnings (note that by adding real growth and inflation, this is basically identical to just adding nominal growth)
is the real growth rate in earnings (note that by adding real growth and inflation, this is basically identical to just adding nominal growth) -
 is the changes in shares outstanding (i.e. increases in shares outstanding decrease expected returns)
is the changes in shares outstanding (i.e. increases in shares outstanding decrease expected returns) -
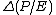 is the changes in P/E ratio (positive relationship between changes in P/e and expected returns).
is the changes in P/E ratio (positive relationship between changes in P/e and expected returns).
One offshoot of this discounted cash flow analysis is the Fed Model. Under the Fed model, the earnings yield is compared to the 10-year treasury bonds. If the earnings yield is lower than that of the bonds, the investor would shift their money into the less risky T-bonds.
Grinold, Kroner, and Siegel (2011) estimated the inputs to the Grinold and Kroner model and arrived at a then-current equity risk premium estimate between 3.5% and 4%.[2] The equity risk premium is the difference between the expected total return on a capitalization-weighted stock market index and the yield on a riskless government bond (in this case one with 10 years to maturity).
References
2. ^Richard Grinold, Kenneth Kroner, and Laurence Siegel, "A Supply Model of the Equity Premium," in B. Hammond, M. Leibowitz, and L. Siegel, eds., Rethinking the Equity Risk Premium, Charlottesville, VA: Research Foundation of CFA Institute, 2011.
- List of failed nominations to the Supreme Court of the United States
- List of Fairbanks-Morse locomotives
- List of Fairtrade settlements
- List of fairy and sprite characters
- List of fairy tales by alphabetical order
- List of Falklands War Victoria Cross recipients
- List of false scorpions
- List of Famicom accessories
- List of Family Computer Disk System games
- List of Family Computer games
- List of Family Guy Characters
- List of Family Guy characters
- List of Family Guy episodes
- List of Family Matters episodes
- List of family name affixes
- List of family trees
- List of famous African-Americans
- List of famous African Americans
- List of famous Albanian people
- List of famous Albanians
- List of famous American Houses
- List of famous archaeological sites
- List of famous archaeologists
- List of famous Austrian people
- List of famous Austrians