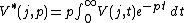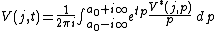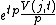- Definition
- See also
- References
In mathematics, the Laplace–Carson transform, named after Pierre Simon Laplace and John Renshaw Carson, is an integral transform with significant applications in the field of physics and engineering, particularly in the field of railway engineering.
Definition
Let 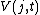 be a function and
be a function and  a complex variable. The Laplace–Carson transform is defined as:[1]
a complex variable. The Laplace–Carson transform is defined as:[1]
The inverse Laplace–Carson transform is:
where  is a real-valued constant,
is a real-valued constant, 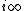 refers to the imaginary axis, which indicates the integral is carried out along a straight line parallel to the imaginary axis lying to the right of all the singularities of the following expression:
refers to the imaginary axis, which indicates the integral is carried out along a straight line parallel to the imaginary axis lying to the right of all the singularities of the following expression:
See also
- Laplace transform
References
1. ^{{cite book |title=Vibration of solids and structures under moving loads |last=Frýba|first= Ladislav|lccn=70-151037|year=1973}}
{{DEFAULTSORT:Laplace-Carson transform}}{{mathanalysis-stub}} 4 : Integral transforms|Differential equations|Fourier analysis|Transforms
- Ann Rachel Ratner
- Ann R. Chaintreuil
- Ann. R. Coll. Surg. Engl.
- Ann R Coll Surg Engl
- Ann. Rech. Vet.
- Ann. Rech. Vét.
- Ann Rech Vét
- Ann-Renee Desbiens
- Ann. Res. Hosp.
- Ann Res Hosp
- Ann Rice O'Hanlon
- Ann R. Miller
- Ann & Robert H Lurie Children's Hospital of Chicago
- Ann Robertson (silversmith)
- Ann Robinson (glass artist)
- Ann Rosalie David
- Ann Rosman
- Ann Rowles
- Ann. Royal Coll. Surg. Engl.
- Ann Royal Coll Surg Engl
- Ann. Roy. Coll. Surg. Engl.
- Ann Roy Coll Surg Engl
- Ann Run
- Ann Sabina
- Ann Salens