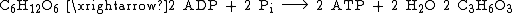- History
- Biochemistry Homofermentative process Heterofermentative process
- Applications Pickle Fermented fish Kimchi Sauerkraut Sour beer Yogurt Physiological
- Notes and references
If oxygen is present in the cell, many organisms will bypass fermentation and undergo cellular respiration; however, facultative anaerobic organisms will both ferment and undergo respiration in the presence of oxygen.[3] Sometimes even when oxygen is present and aerobic metabolism is happening in the mitochondria, if pyruvate is building up faster than it can be metabolized, the fermentation will happen anyway.
Lactate dehydrogenase catalyzes the interconversion of pyruvate and lactate with concomitant interconversion of NADH and NAD+.
In homolactic fermentation, one molecule of glucose is ultimately converted to two molecules of lactic acid. Heterolactic fermentation, in contrast, yields carbon dioxide and ethanol in addition to lactic acid, in a process called the phosphoketolase pathway.[1]
History
Several chemists discovered during the 19th century some fundamental concepts of the domain of organic chemistry. One of them for example was the French chemist Joseph Louis Gay-Lussac, who was especially interested in fermentation processes, and he passed this fascination to one of his best students, Justus von Liebig. With a difference of some years, each of them described, together with colleague, the chemical structure of the lactic acid molecule as we know it today. They had a purely chemical understanding of the fermentation process, which means that you can’t see it using a microscope, and that it can only be optimized by chemical catalyzers. It was then in 1857 when the French chemist Louis Pasteur first described the lactic acid as the product of a microbial fermentation. During this time, he worked at the university of Lille, where a local distillery asked him for advice concerning some fermentation problems. Per chance and with the badly equipped laboratory he had at that time, he was able to discover that in this distillery, two fermentations were taking place, a lactic acid one and an alcoholic one, both induced by some microorganisms. He then continued the research on these discoveries in Paris, where he also published his theories that presented a stable contradiction to the purely chemical version represented by Liebig and his followers. Even though Pasteur described some concepts that are still accepted nowadays, Liebig refused to accept them until his death in 1873. But even Pasteur himself wrote that he was “driven” to a completely new understanding of this chemical phenomenon. Even if Pasteur didn’t find every detail of this process, he still discovered the main mechanism of how the microbial lactic acid fermentation works. He was for example the first to describe fermentation as a “form of life without air."[4][5]
Even if this chemical process hasn’t been properly described before Pasteur’s work, people had been using microbial lactic acid fermentation for food production much earlier. Chemical analysis of archeological finds showed that milk fermentation uses predate the historical period, its first applications were probably a part of the Neolithic Revolution. Since milk naturally contains lactic acid bacteria, the discovery of the fermentation process was quite evident, since it happens spontaneously at an adequate temperature. The problem of these first farmers was that fresh milk is nearly not digestible by an adult, so they had an interest to discover this mechanism: in fact, lactic acid bacteria contain the needed enzymes to digest lactose, and their populations multiply strongly during the fermentation. Therefore, even short-fermented milk contains enough enzymes to digest the lactose molecules, once the milk is in the human body, which allowed also adults to consume it. Even safer was a longer fermentation, which was practiced for cheesemaking. This process was discovered a very long time ago too, which is proofed by recipes for cheese production on Cuneiform scripts, the first written documents that exist, and a bit later in Babylonian and Egyptian texts.
What is interesting is the theory of the competitive advantage of fermented milk products. The idea of this theory is that the women of these first settled farmer clans could shorten the time between two children thanks to the additional lactose uptake from milk consumption. This factor may have given them an important advantage to out-compete the hunter-gatherer societies.[6]
With the increasing consumption of milk products these societies developed a lactase persistence by epigenetic inheritance, which means that the milk-digesting enzyme lactase was present in their body during the whole lifetime, so they could drink unfermented milk as adults too. This early habituation to lactose consumption in the first settler societies can still be observed today on regional differences of this mutation’s concentration. It’s estimated that about 65% of world population still lacks it.[7] Since these first societies came from regions around eastern Turkey to central Europe, the gene appears more frequently there and in North America, as it was settled by Europeans. On the contrary, lactose intolerance is much more present in Asian countries.
Milk products and their fermentation have had an important influence on some cultures’ development. This is the case in Mongolia, where people often practice a pastoral form of agriculture. The milk that they produce and consume in these cultures is mainly mare milk and has a long tradition. But not every part or product of the fresh milk has the same meaning. For instance, the fattier part on the top, the “deež”, is seen as the most valuable part and is therefore often used to honor guests.
Very important with often a traditional meaning as well are fermentation products of mare milk, like for example the slightly-alcoholic yogurt kumis. Consumption of these peaks during cultural festivities such as the Mongolian lunar new year (in spring). The time of this celebration is called the “white month”, which indicates that milk products (called “white food” together with starchy vegetables, in comparison to meat products, called “black food”) are a central part of this tradition. The purpose of these festivities is to “close” the past year – clean the house or the yurt, honor the animals for having provided their food, and prepare everything for the coming summer season – to be ready to “open” the new year. Consuming white food in this festive context is a way to connect to the past and to a national identity, which is the great Mongolian empire personified by Genghis Khan. During the time of this empire, the fermented mare milk was the drink to honor and thank warriors and leading persons, it was not meant for everybody. Even though it can became a drink for normal people, it has kept its honorable meaning. Like many other traditions, this one feels the influence of the globalizing industry. Other products, coming mainly from China and western countries, like industrial yogurt, tend to replace it more and more, mainly in urban areas. However, in rural and poorer regions it’s still of great importance.[8]
Biochemistry
Homofermentative process
Overall, the homofermentative lactic acid fermentation converts a six-carbon sugar molecule to two lactic acid molecules, storing the released energy into two ATP molecules. The following equation describes this net result:
Heterofermentative process
Heterofermentative bacteria produce one mole of lactate from one mole of glucose as well as CO2 and acetic acid or ethanol. Examples include Leuconostoc mesenteroides, Lactobacillus bifermentous, and Leconostoc lactis.
Applications
Lactic acid fermentation is used in many areas of the world to produce foods that cannot be produced through other methods.[9][10] The most commercially important genus of lactic acid-fermenting bacteria is Lactobacillus, though other bacteria and even yeast are sometimes used.[9] Two of the most common applications of lactic acid fermentation are in the production of yogurt and sauerkraut.
Pickle
{{Main|Pickling}}A product prepared by lactic acid bacteria (LAB) fermentation of sugars present in the pieces of fruits and vegetables. The prepared product is rich in lactic acid, and only the beneficial bacteria that can tolerate lactic acid pH survive. It not only assures good quality of nutrients, but it is also a good source of probiotics.
Fermented fish
{{main|Fermented fish}}In some Asian cuisines, fish is traditionally fermented with rice to produce lactic acid that preserves the fish. Examples of these dishes include burong isda of the Philippines; narezushi of Japan; and pla ra of Thailand. The same process is also used for shrimp in the Philippines in the dish known as balao-balao.[11][12][13]
Kimchi
{{main article|Kimchi}}Kimchi also uses lactic acid fermentation.[14]Sauerkraut
{{main article|Sauerkraut}}Lactic acid fermentation is also used in the production of sauerkraut. The main type of bacteria used in the production of sauerkraut is of the genus Leuconostoc.[1][15]
As in yogurt, when the acidity rises due to lactic acid-fermenting organisms, many other pathogenic microorganisms are killed. The bacteria produce lactic acid, as well as simple alcohols and other hydrocarbons. These may then combine to form esters, contributing to the unique flavor of sauerkraut.[1]
Sour beer
{{main article|Lambic|Berliner Weisse}}Lactic acid is a component in the production of sour beers, including Lambics and Berliner Weisses.[16]
Yogurt
{{main article|Yogurt}}The main method of producing yogurt is through the lactic acid fermentation of milk with harmless bacteria.[9][17] The primary bacteria used are typically Lactobacillus bulgaricus and Streptococcus thermophilus, and United States as well as European law requires all yogurts to contain these two cultures (though others may be added as probiotic cultures).[17] These bacteria produce lactic acid in the milk culture, decreasing its pH and causing it to congeal. The bacteria also produce compounds that give yogurt its distinctive flavor. An additional effect of the lowered pH is the incompatibility of the acidic environment with many other types of harmful bacteria.[9][17]
For a probiotic yogurt, additional types of bacteria such as Lactobacillus acidophilus are also added to the culture.[17]
Physiological
Lactobacillus fermentation and accompanying production of acid provides a protective vaginal microbiome that protects against the proliferation of pathogenic organisms.[18]
Notes and references
2. ^{{cite web |url= http://www.mansfield.ohio-state.edu/~sabedon/biol1095.htm#lactic_acid_fermentation|title=Glycolysis and Fermentation |author=Ohio State University |date=1998-04-03 |accessdate=2010-01-12}}
3. ^1 {{cite book |last1 = Campbell |first1 = Neil |last2 = Reece |first2 = Jane |authorlink1 = Neil Campbell (scientist) |authorlink2 = Jane Reece |title = Biology, 7th Edition |publisher = Benjamin Cummings |year = 2005 |isbn = 0-8053-7146-X}}
4. ^{{cite book| last=Latour |first=Bruno |title=Les objets ont-ils une histoire? Rencontre de Pasteur et de Whitehead dans un bain d’acide lactique. in L’effet Whitehead, Vrin, Paris, pp.196-217 |year=1993 |isbn=978-2-7116-1216-1}}
5. ^{{cite book|last=Benninga |first=H. |title=A History of Lactic Acid Making: A Chapter in the History of Biotechnology, chapter 1 and 2 |year=1990 |isbn=978-0-7923-0625-2}}
6. ^{{cite book |last1=Shurtleff |first1=William |last2=Aoyagi |first2=Akiko |title=A Brief History of Fermentation, East and West. In History of Soybeans and Soyfoods, 1100 B.C. to the 1980s |year=2004 |isbn=1-58008336-6}}
7. ^{{cite book |last = Brüssow |first = Harald |title = Nutrition, population growth and disease: a short history of lactose. in Environmental Microbiology Volume 15, pages 2154-2161 |year = 2013 }}
8. ^{{cite book| last1=Ruhlmann |first1=Sandrine |last2=Gardelle |first2=Linda |title=Les dessus et les dessous du lait. Sociologie et politique du lait et de ses dérivés en Mongolie. in Études mongoles et sibériennes, centrasiatiques et tibétaines, n° 43-44|year=2013 }}
9. ^1 2 3 {{cite web|url=http://www.tempeh.info/fermentation/lactic-acid-fermentation.php |title=Lactic acid fermentation |accessdate=2010-01-09}}
10. ^{{cite web |url=http://www.microbiologyprocedure.com/industrial-microbiology/lactic-acid-fermentation.htm |title=Lactic acid fermentation |accessdate=2010-01-09 |deadurl=yes |archiveurl=https://web.archive.org/web/20090802172900/http://www.microbiologyprocedure.com/industrial-microbiology/lactic-acid-fermentation.htm |archivedate=2009-08-02 |df= }}
11. ^{{cite journal |last1=Kanno |first1=Tomomi |last2=Kuda |first2=Takashi |last3=An |first3=Choa |last4=Takahashi |first4=Hajime |last5=Kimura |first5=Bon |title=Radical scavenging capacities of saba-narezushi, Japanese fermented chub mackerel, and its lactic acid bacteria |journal=LWT - Food Science and Technology |date=2012 |volume=47 |issue=1 |pages=25-30 |doi=10.1016/j.lwt.2012.01.007 |url=https://www.sciencedirect.com/science/article/pii/S0023643812000096}}
12. ^{{cite book |last1=Olympia |first1=Minderva S.D. |chapter=Fermented Fish Products in the Philippines|title=Applications of Biotechnology to Traditional Fermented Foods: Report of an Ad Hoc Panel of the Board on Science and Technology for International Development |date=1992 |publisher=National Academy Press |pages=131-139 |url=https://books.google.com.ph/books?id=21IrAAAAYAAJ&lpg=PR1&pg=PA131#v=onepage&q&f=false}}
13. ^{{cite book|first1=Priscilla C.|last1= Sanchez|title =Philippine Fermented Foods: Principles and Technology|chapter =Lactic-Acid-Fermented Fish and Fishery Products|publisher =University of the Philippines Press|year =2008|page=264|isbn = 9789715425544|url =https://books.google.com.ph/books?id=smfr-KYgtWkC&lpg=PP1&pg=PT10#v=onepage&q&f=false}}
14. ^{{cite journal|url=http://www.springerlink.com/content/m474t54828022g3k/|title=Lactic acid fermentation in the production of foods from vegetables, cereals and legumes|year=1983|publisher=Antonie van Leeuwenhoek Journal|accessdate=2010-06-28|doi=10.1007/BF00399508|volume=49|issue=3|journal=Antonie van Leeuwenhoek|pages=337–348}}
15. ^{{cite web|url=http://www.jlindquist.net/generalmicro/324sauerkraut.html |title=Sauerkraut Fermentation |author= |year=1999 |publisher=University of Wisconsin–Madison |accessdate=2010-01-09}}
16. ^{{cite web|last=Nummer|first=Brian A.|title=Brewing With Lactic Acid Bacteria|url=http://morebeer.com/articles/brewing_with_lactic_acid_bacteria|publisher=MoreFlavor Inc.|accessdate=2 October 2013}}
17. ^1 2 3 {{cite web|url=http://www.milkfacts.info/Milk%20Processing/Yogurt%20Production.htm |title=Yogurt Production| date=2006-12-29 |accessdate=2010-01-09}}
18. ^{{cite journal|last1=Nardis|first1=C.|last2=Mastromarino|first2=P.|last3=Mosca|first3=L.|title=Vaginal microbiota and viral sexually transmitted diseases|journal=Annali di Igiene |date=September–October 2013 |volume=25|issue=5|pages=443–56|doi=10.7416/ai.2013.1946|pmid=24048183}}
- Purísima del Rincón
- Purús Province
- Purāṇa
- P:US
- P:USA
- Pusa
- Pusa (album)
- Pusa caspica
- Pusad
- Pusad (disambiguation)
- Pusadian series
- P:USAF
- Pusai
- PUSA Inc
- PUSA Inc.
- Pusa Institute
- Pusan Daewoo Royals
- Pusan Film Festival
- Pusan, Korea
- Pusanky
- Pusan National University
- Pusan National University of Technology
- Pusan Subway
- Pusapati Ananda Gajapati Raju
- Pusapati Rega