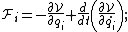- Mathematical definition
- See also
- References
In classical mechanics, a physical system is termed a monogenic system if the force acting on the system can be modelled in an especially convenient mathematical form (see mathematical definition below). In physics, among the most studied physical systems are monogenic systems.
In Lagrangian mechanics, the property of being monogenic is a necessary condition for the equivalence of different formulations of principle. If a physical system is both a holonomic system and a monogenic system, then it is possible to derive Lagrange's equations from d'Alembert's principle; it is also possible to derive Lagrange's equations from Hamilton's principle.[1]
The term was introduced by Cornelius Lanczos in his book The Variational Principles of Mechanics (1970).[2][3]
Monogenic systems have excellent mathematical characteristics and are well suited for mathematical analysis. Pedagogically, within the discipline of mechanics, it is considered a logical starting point for any serious physics endeavour.
Mathematical definition
In a physical system, if all forces, with the exception of the constraint forces, are derivable from the generalized scalar potential, and this generalized scalar potential is a function of generalized coordinates, generalized velocities, or time, then, this system is a monogenic system.
Expressed using equations, the exact relationship between generalized force 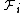 and generalized potential
and generalized potential  is as follows:
is as follows:
where  is generalized coordinate,
is generalized coordinate, 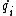 is generalized velocity, and
is generalized velocity, and  is time.
is time.
If the generalized potential in a monogenic system depends only on generalized coordinates, and not on generalized velocities and time, then, this system is a conservative system.The relationship between generalized force and generalized potential is as follows:
;
See also
- Lagrangian mechanics
- Hamiltonian mechanics
- Holonomic system
- Scleronomous
References
2. ^{{cite web|url=http://philsci-archive.pitt.edu/1937/1/BetLMLag.pdf|title=Between Laws and Models: Some Philosophical Morals of Lagrangian Mechanics|last1=J. |first1=Butterfield |date=3 September 2004 |website=PhilSci-Archive |accessdate=23 January 2015|pages=43}}
3. ^{{cite book |first1=Lanczos |last1=Cornelius |title=The Variational Principles of Mechanics |location= Toronto |publisher=University of Toronto Press |year=1970 |isbn=0-8020-1743-6 |pages=30}}
- Small Madagascar babul blue
- Small Madagascar Babul Blue
- Small Maf
- Small Magellanic Cloud in fiction
- Small magpie
- Small Main-Belt Asteroid Spectroscopic Survey
- Small Mallow
- Small mallow
- Smallman
- Smallman, David
- Smallman, William
- Small Maracanazo
- Small marbled bush brown
- Small marbled elf
- Small Marbled Elf
- Small, Mark
- Small Meadow White
- Small meadow white
- Small, Medium to Mid-size Enterprises
- Small meningeal arteries
- Small Metal Objects
- Small, Michael
- Small Miracle
- Small Miracles
- Small Miracles (film)