- Nomenclature
- Homologues
- Structure
- Reaction
- Mechanism
- Broader significance
- Open questions
- References
- Further reading
| Name = polyneuridine-aldehyde esterase
| EC_number = 3.1.1.78
| CAS_number = 87041-55-2
| IUBMB_EC_number = 3/1/1/78
| GO_code = 0050529
| image = File:Enzyme Polyneuridine Aldehyde Esterase.png
| width =
| caption = Polyneuridine-Aldehyde Esterase 3D Rendering
}}
In enzymology, a polyneuridine-aldehyde esterase ({{EC number|3.1.1.78}}) is an enzyme that catalyzes the chemical reaction:
polyneuridine aldehyde + H2O16-epivellosimine + CO2 + methanol
Thus, the two substrates of this enzyme are polyneuridine aldehyde and H2O, whereas its three products are 16-epivellosimine, CO2, and methanol.[1]
This enzyme participates in indole and ipecac alkaloid biosynthesis.
Nomenclature
This enzyme belongs to the family of hydrolases, specifically those acting on carboxylic ester bonds. The systematic name of this enzyme class is polyneuridine aldehyde hydrolase (decarboxylating). Other names in common use include:
- polyneuridine aldehyde esterase
- PNAE
Homologues
This enzyme is found in various forms in plant species such as Arabidopsis thaliana, Glycine max (soybean), Vitis vinifera (wine grape), and Solanum lycopersicum (tomato) among others.
Polyneuridine-aldehyde esterase also appears in select bacteria including Enterobacter cloacae.
Structure
The secondary structure of this enzyme consists mainly of alpha helices. In its native form, this enzyme has a tertiary structure that includes two main lobes (as depicted above in the blue 3D representation on the top right).
Reaction
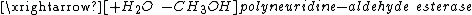 |  |
Polyneuridine-aldehyde esterase catalyzes the hydrolysis of the methyl ester in polyneuridine aldehyde to form polyneuridine β-aldehydoacid and methanol. The carboxylic acid in the product spontaneously undergoes decarboxylation, yielding 16-epivellosimine and carbon dioxide.[1]
Mechanism
The mechanism of hydrolysis performed by polyneuridine-aldehyde esterase is not known. It has been suggested that the enzyme utilizes a catalytic triad composed of Ser-87, Asp-216 and His-244.[3] The catalytic amino acid order is the same as the order of enzymes that are part of the α/β hydrolase family. Thus polyneuridine-aldehyde esterase may be a novel member of the α/β hydrolase group.[4]
Broader significance
This enzyme is a part of the pathway of indole alkaloid biosynthesis. The indole alkaloids that result from this metabolic pathway are used by many plant species as a defense against herbivores and parasites.
Open questions
The precise mechanisms by which this enzyme performs its function is still unknown. As noted above, researchers are formulating suggestions as to how polyneuridine-aldehyde esterase catalyses the decomposition of polyneuridine-aldehyde, but a mechanism has not yet been affirmed with absolute certainty. Due to the lack of complete understanding of polyneuridine-aldehyde esterase's precise mechanism, this enzyme cannot be grouped into a family of enzymes. Based on mechanism theories, suggestions can be made as to how this enzyme should be categorized, and some parallels can be drawn between polyneuridine-aldehyde esterase and other enzymes.
References
2. ^{{PDB|3GZJ}}; {{cite journal |vauthors=Yang L, Hill M, Wang M, Panjikar S, Stöckigt J | title = Structural basis and enzymatic mechanism of the biosynthesis of C9- from C10-monoterpenoid indole alkaloids | journal = Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. Engl. | volume = 48 | issue = 28 | pages = 5211–3 | year = 2009 | pmid = 19496101 | doi = 10.1002/anie.200900150 }}
3. ^{{cite journal |vauthors=Mattern-Dogru E, Ma X, Hartmann J, Decker H, Stöckigt J | title = Potential active-site residues in polyneuridine aldehyde esterase, a central enzyme of indole alkaloid biosynthesis, by modelling and site-directed mutagenesis | journal = Eur. J. Biochem. | volume = 269 | issue = 12 | pages = 2889–96 |date=June 2002 | pmid = 12071952 | doi = 10.1046/j.1432-1033.2002.02956.x }}
4. ^{{cite journal |vauthors=Dogru E, Warzecha H, Seibel F, Haebel S, Lottspeich F, Stöckigt J | title = The gene encoding polyneuridine aldehyde esterase of monoterpenoid indole alkaloid biosynthesis in plants is an ortholog of the alpha/betahydrolase super family | journal = Eur. J. Biochem. | volume = 267 | issue = 5 | pages = 1397–406 |date=March 2000 | pmid = 10691977 | doi = 10.1046/j.1432-1327.2000.01136.x }}
Further reading
{{refbegin}}- {{cite journal |vauthors=Pfitzner A, Stockigt J| year = 1983 | title = Polyneuridine aldehyde esterase: an unusual specific enzyme involved in the biosynthesis of sarpagine type alkaloids | journal = J. Chem. Soc. Chem. | volume = Commun. | issue = 8 | pages = 459–460 | doi = 10.1039/C39830000459 }}
- Modern Family season 5
- Modern Family (season 6)
- Modern family season 6
- Modern Family (season 7)
- Modern Farmer
- Modern Farmer (disambiguation)
- Modern Farmer (magazine)
- Modern Farmer (TV series)
- Modern feminism
- Modern Fiction (essay)
- Modern Fishing with Jared Jeffries
- Modern Flat Earth societies
- Modern flute
- Modern Folk Trio
- Modern Folk Uclusu
- Modern Folk Üçlüsü
- Modern (font)
- Modern Food Industries
- Modern Food Industries (India) Ltd
- Modern Gallery
- Modern Gallery (disambiguation)
- Modern Gallery in Zagreb
- Modern Game chicken
- Modern Game fowl
- Modern Game Fowl