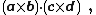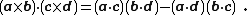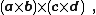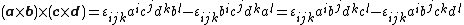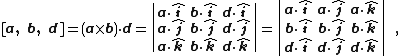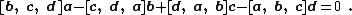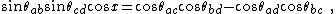- Scalar quadruple product
- Vector quadruple product
- Application
- Notes
- References
- See also
In mathematics, the quadruple product is a product of four vectors in three-dimensional Euclidean space. The name "quadruple product" is used for two different products,[1] the scalar-valued scalar quadruple product and the vector-valued vector quadruple product or vector product of four vectors .
Scalar quadruple product
The scalar quadruple product is defined as the dot product of two cross products:
where a, b, c, d are vectors in three-dimensional Euclidean space.[2] It can be evaluated using the identity:[2]
or using the determinant:
Vector quadruple product
The vector quadruple product is defined as the cross product of two cross products:
where a, b, c, d are vectors in three-dimensional Euclidean space.[3] It can be evaluated using the identity:[4]
This identity can also be written using tensor notation and the Einstein summation convention as follows:
using the notation for the triple product:
where the last two forms are determinants with 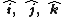 denoting unit vectors along three mutually orthogonal directions.
denoting unit vectors along three mutually orthogonal directions.
Equivalent forms can be obtained using the identity:[5]
Application
The quadruple products are useful for deriving various formulas in spherical and plane geometry.[3] For example, if four points are chosen on the unit sphere, A, B, C, D, and unit vectors drawn from the center of the sphere to the four points, a, b, c, d respectively, the identity:
in conjunction with the relation for the magnitude of the cross product:
and the dot product:
where a = b = 1 for the unit sphere, results in the identity among the angles attributed to Gauss:
where x is the angle between a × b and c × d, or equivalently, between the planes defined by these vectors.
Josiah Willard Gibbs's pioneering work on vector calculus provides several other examples.[3]Notes
2. ^1 {{harvnb|Gibbs|Wilson|1901|p=76}}
3. ^1 2 {{harvnb|Gibbs|Wilson|1901|pp=77 ff}}
4. ^{{harvnb|Gibbs|Wilson|1901|p=77}}
5. ^{{harvnb|Gibbs|Wilson|year=1901|loc=Equation 27, p. 77}}
References
- {{cite book |last1=Gibbs|last2=Wilson |first1=Josiah Willard |first2= Edwin Bidwell |title=Vector analysis: a text-book for the use of students of mathematics |url=https://archive.org/details/vectoranalysiste00gibbiala |publisher=Scribner |year=1901 |ref=harv}}
See also
- Binet–Cauchy identity
- Lagrange's identity