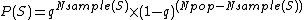- Mathematical formulation
- An example of a sampling design
- Sample design for managerial research
- See also
- Further reading
- References
In the theory of finite population sampling, a sampling design specifies for every possible sample its probability of being drawn.
Mathematical formulation
Mathematically, a sampling design is denoted by the function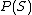 which gives the probability of drawing a sample
which gives the probability of drawing a sample 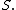
An example of a sampling design
During Bernoulli sampling, 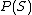 is given by
is given by
where for each element  is the probability of being included in the sample and
is the probability of being included in the sample and 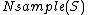 is the total number of elements in the sample
is the total number of elements in the sample  and
and 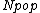 is the total number of elements in the population (before sampling commenced).
is the total number of elements in the population (before sampling commenced).
Sample design for managerial research
In business research, companies must often generate samples of customers, clients, employees, and so forth to gather their opinions. Sample design is also a critical component of marketing research and employee research for many organizations. During sample design, firms must answer questions such as:
- What is the relevant population, sampling frame, and sampling unit?- What is the appropriate margin of error that should be achieved?- How should sampling error and non-sampling error be assessed and balanced?These issues require very careful consideration, and good commentaries are provided in several sources.[1][2]
See also
- Bernoulli sampling
- Sampling probability
- Statistical sampling
Further reading
- Sarndal, Swenson, and Wretman (1992), Model Assisted Survey Sampling, Springer-Verlag, {{isbn|0-387-40620-4}}
References
2. ^Hansen, Morris H., William N. Hurwitz, and William G. Madow. "Sample Survey Methods and Theory." (1953).
- Alabama State Route 123
- Alabama State Route 124
- Alabama State Route 127
- Alabama State Route 133
- Alabama State Route 137
- Alabama State Route 139
- Alabama State Route 148
- Alabama State Route 153
- Alabama State Route 154
- Alabama State Route 156
- Alabama State Route 159
- Alabama State Route 162
- Alabama State Route 163
- Alabama State Route 169
- Alabama State Route 170
- Alabama State Route 171
- Alabama State Route 172
- Alabama State Route 173
- Alabama State Route 179
- Alabama State Route 182
- Alabama State Route 183
- Alabama State Route 184
- Alabama State Route 185
- Alabama State Route 187
- Alabama State Route 188