- Derivation
- See also
- References
The Shunt equation quantifies the extent that venous blood bypasses oxygenation in the capillaries of the lung.
Shunt and dead space are terms used to describe conditions where either blood flow or ventilation does not meet the other in the lung as it should for gas exchange to take place. They can also be used to describe areas or effects where blood flow and ventilation are not properly matched though both may be present to varying extents. Some refer to shunt-effect or dead space-effect to designate the ventilation/perfusion mismatch states that are less extreme than absolute shunt or dead space.
The following equation relates the percentage of blood flow that is not exposed to inhaled gas, called the shunt fraction 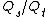 , to the content of oxygen in venous, arterial, and pulmonary capillary blood.
, to the content of oxygen in venous, arterial, and pulmonary capillary blood.
[1][2]
Where:
Qs = Pulmonary Physiologic Shunt (mL/min)
Qt = Cardiac Output (mL/min)
CCO2 = End-pulmonary-capillary Oxygen Content
CaO2 = Arterial oxygen content
CVO2 = Mixed Venous Oxygen Content
Derivation
The blood entering the pulmonary system will have oxygen flux 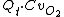 , where
, where 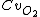 is oxygen content of the venous blood and
is oxygen content of the venous blood and 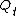 is the total cardiac output.
is the total cardiac output.
Similarly, the blood emerging from the pulmonary system will have oxygen flux 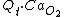 , where
, where 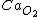 is oxygen content of the arterial blood.
is oxygen content of the arterial blood.
This will be made up of blood that bypassed the lungs (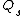 ) and that which went through the pulmonary capillaries (
) and that which went through the pulmonary capillaries (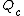 ).
).
We can express this as
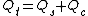 .
.
We can solve for 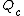 :
:
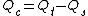 .
.
If we add the oxygen content of Qs to Qc we get the oxygen content of Qt:
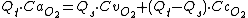
Substitute Qc as above, CcO2 is the oxygen content of pulmonary (alveolar) capillary blood.
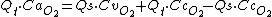
Multiply out the brackets.
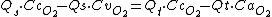
Get the Qs terms and the Qt terms on the same side.
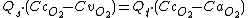
Factor out the Q terms.
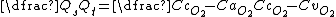
Divide by Qt and by (CcO2 - CvO2).
See also
- Pulmonary shunt
- Ventilation/perfusion ratio
- Pulmonary contusion
References
2. ^{{Cite journal|last=Leigh|first=J. M.|last2=Tikrell|first2=M. F.|last3=Stricklaxd|first3=D. a. P.|date=1969-04-01|title=Simplified Versions of the Shunt and Oxygen Consumption Equations|url=http://anesthesiology.pubs.asahq.org/article.aspx?articleid=1964340|journal=Anesthesiology|language=en|volume=30|issue=4|pages=468–470|issn=0003-3022}}
- Smolniki, Lubusz Voivodeship
- Smolniki Mostkowskie
- Smolniki, Naklo County
- Smolniki, Nakło County
- Smolniki Osieckie
- Smolniki, Ostrzeszow County
- Smolniki, Ostrzeszów County
- Smolniki, Podlaskie Voivodeship
- Smolniki Polskie
- Smolniki, Pomeranian Voivodeship
- Smolniki Powidzkie
- Smolniki Racieckie
- Smolniki, Starogard County
- Smolniki, Warmian-Masurian Voivodeship
- Smolniki, West Pomeranian Voivodeship
- Smolnik, Kuyavian-Pomeranian Voivodeship
- Smolnik, Ruše
- Smolnik, Sanok County
- Smolnik, Warmian-Masurian Voivodeship
- Smolnitsa
- Smolnitsa, Estonia
- Smolno
- Smolno (disambiguation)
- Smolno, Greater Poland Voivodeship
- Smolno, Kuyavian-Pomeranian Voivodeship