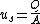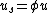- See also
Superficial velocity (or superficial flow velocity), in engineering of multiphase flows and flows in porous media, is a hypothetical (artificial) flow velocity calculated as if the given phase or fluid were the only one flowing or present in a given cross sectional area. Other phases, particles, the skeleton of the porous medium, etc. present in the channel are disregarded.
Superficial velocity is used in many engineering equations because it is the value which is usually readily known and unambiguous, whereas real velocity is often variable from place to place, its mean not readily available in complex flow systems, and subject to assumptions.
Superficial velocity can be expressed as:
where:
- us - superficial velocity of a given phase, m/s
- Q - volume flow rate of the phase, m3/s
- A - cross sectional area, m2
Using the concept of porosity, the dependence between the advection velocity and the superficial velocity can be expressed as (for one-dimensional flow):
where:
 is porosity, dimensionless
is porosity, dimensionless- u is the average fluid velocity (excluding the other phase, solids, etc.), m/s.
The local physical velocity can still be different than the average fluid velocity because the vector of the local fluid flow does not have to be parallel to that of average flow. Also, there may be local constriction in the flow channel.
See also
- Volumetric flux
- UN/LOCODE:USWSR
- UN/LOCODE:USWSS
- UN/LOCODE:USWSV
- UN/LOCODE:USWSW
- UN/LOCODE:USWSY
- UN/LOCODE:USWSZ
- UN/LOCODE:USWTA
- UN/LOCODE:USWTB
- UN/LOCODE:USWTG
- UN/LOCODE:USWTH
- UN/LOCODE:USWTI
- UN/LOCODE:USWTK
- UN/LOCODE:USWTL
- UN/LOCODE:USWTO
- UN/LOCODE:USWTQ
- UN/LOCODE:USWTS
- UN/LOCODE:USWTU
- UN/LOCODE:USWTW
- UN/LOCODE:USWTY
- UN/LOCODE:USWUB
- UN/LOCODE:USWUF
- UN/LOCODE:USWUI
- UN/LOCODE:USWUL
- UN/LOCODE:USWUN
- UN/LOCODE:USWUR