- References
Time-inhomogeneous hidden Bernoulli model (TI-HBM) is an alternative to hidden Markov model (HMM) for automatic speech recognition. Contrary to HMM, the state transition process in TI-HBM is not a Markov-dependent process, rather it is a generalized Bernoulli (an independent) process. This difference leads to elimination of dynamic programming at state-level in TI-HBM decoding process. Thus, the computational complexity of TI-HBM for probability evaluation and state estimation is 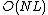 (instead of
(instead of 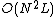 in the HMM case, where
in the HMM case, where  and
and  are number of states and observation sequence length respectively). The TI-HBM is able to model acoustic-unit duration (e.g. phone/word duration) by using a built-in parameter named survival probability. The TI-HBM is simpler and faster than HMM in a phoneme recognition task, but its performance is comparable to HMM.
are number of states and observation sequence length respectively). The TI-HBM is able to model acoustic-unit duration (e.g. phone/word duration) by using a built-in parameter named survival probability. The TI-HBM is simpler and faster than HMM in a phoneme recognition task, but its performance is comparable to HMM.
For details, see [https://dx.doi.org/10.1016/j.sigpro.2008.09.004] or [https://dx.doi.org/10.1109/ICASSP.2008.4518556].
References
[1] Jahanshah Kabudian, M. Mehdi Homayounpour, S. Mohammad Ahadi, "Bernoulli versus Markov: Investigation of state transition regime in switching-state acoustic models," Signal Processing, vol. 89, no. 4, pp. 662–668, April 2009.
[2] Jahanshah Kabudian, M. Mehdi Homayounpour, S. Mohammad Ahadi, "Time-inhomogeneous hidden Bernoulli model: An alternative to hidden Markov model for automatic speech recognition," Proceedings of the IEEE International Conference on Acoustics, Speech and Signal Processing (ICASSP), pp. 4101–4104, Las Vegas, Nevada, USA, March 2008.
- Agishev
- Agisheva
- Agishin
- Agishina
- Agis of Elis
- Agis (play)
- Agistron
- Agis VI
- Agiswail
- Agis XIV
- Agi Szaloki
- Agit
- Agita language
- Agitando El Show
- Agitated emergence
- Agitations (album)
- Agitation (South Asia)
- Agites
- Agitococcus
- Agito (disambiguation)
- Agiton
- Agit Prop 1970-1977
- Agitprop (album)
- Agit-propin kvartetti laulaa työväenlauluja
- Agitprop (Kalahari Surfers)