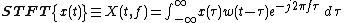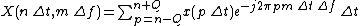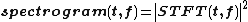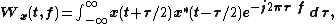- Knowledge about music signal
- Short-time Fourier transform Continuous STFT Discrete STFT
- STFT example
- Spectrogram
- Wigner distribution function Formula
- See also
- Sources
Time–frequency analysis for music signals is one of the applications of time–frequency analysis. Musical sound can be more complicated than human vocal sound, occupying a wider band of frequency. Music signals are time-varying signals; while the classic Fourier transform is not sufficient to analyze them, time–frequency analysis is an efficient tool for such use. Time–frequency analysis is extended from the classic Fourier approach. Short-time Fourier transform (STFT), Gabor transform (GT) and Wigner distribution function (WDF) are famous time–frequency methods, useful for analyzing music signals such as notes played on a piano, a flute or a guitar.
Knowledge about music signal
Music is a type of sound that has some stable frequencies in a time period. Music can be produced by several methods. For example, the sound of a piano is produced by striking strings, and the sound of a violin is produced by bowing. All musical sounds have their fundamental frequency and overtones. Fundamental frequency is the lowest frequency in harmonic series. In a periodic signal, the fundamental frequency is the inverse of the period length. Overtones are integer multiples of the fundamental frequency.
| Frequency | Order | ||
|---|---|---|---|
| f = 440 Hz | N = 1 | Fundamental frequency | 1st harmonic |
| f = 880 Hz | N = 2 | 1st overtone | 2nd harmonic |
| f = 1320 Hz | N = 3 | 2nd overtone | 3rd harmonic |
| f = 1760 Hz | N = 4 | 3rd overtone | 4th harmonic |
In musical theory, pitch represents the perceived fundamental frequency of a sound. However the actual fundamental frequency may differ from the perceived fundamental frequency because of overtones.
Short-time Fourier transform
Continuous STFT
Short-time Fourier transform is a basic type of time–frequency analysis. If there is a continuous signal x(t), we can compute the short-time Fourier transform by
where w(t) is a window function. When the w(t) is a rectangular function, the transform is called Rec-STFT. When the w(t) is a Gaussian function, the transform is called Gabor transform.
Discrete STFT
However, normally the musical signal we have is not a continuous signal. It is sampled in a sampling frequency. Therefore, we can’t use the formula to compute the Rec-short-time Fourier transform. We change the original form to
Let 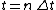 ,
, 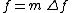 ,
, 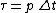 and
and 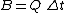 . There are some constraints of discrete short-time Fourier transform:
. There are some constraints of discrete short-time Fourier transform:
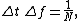 where N is an integer.
where N is an integer.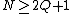
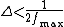 , where
, where 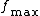 is the highest frequency in the signal.
is the highest frequency in the signal.
STFT example
Fig.1 shows the waveform of a piano music audio file with 44100 Hz sampling frequency. And Fig.2 shows the result of short-time Fourier transform (we use Gabor transform here) of the audio file. We can see from the time–frequency plot, from t = 0 to 0.5 second, there is a chord with three notes, and the chord changed at t = 0.5, and then changed again at t = 1. The fundamental frequency of each note in each chord is shown in the time–frequency plot.
Spectrogram
Figure 3 shows the spectrogram of the audio file shown in Figure 1. Spectrogram is the square of STFT, time-varying spectral representation. The spectrogram of a signal s(t) can be estimated by computing the squared magnitude of the STFT of the signal s(t), as shown below:
Although the spectrogram is profoundly useful, it still has one drawback. It displays frequencies on a uniform scale. However, musical scales are based on a logarithmic scale for frequencies. Therefore, we should describe the frequency in logarithmic scale related to human hearing.
Wigner distribution function
The Wigner distribution function can also be used to analyze music signals. The advantage of the Wigner distribution function is the high clarity of the output; however, it is computationally expensive and has a cross-term problem, so it's more suitable to analyze signals without more than one frequency at the same time.
Formula
The Wigner distribution function 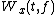 is:
is:
where x(t) is the signal, and x*(t) is the conjugate of the signal.
See also
- Musical acoustics
- Harmonic pitch class profiles (HPCP)
- cone-shape distribution function (ZAM)
Sources
- Joan Serra, Emilia Gomez, Perfecto Herrera, and Xavier Serra, "Chroma Binary Similarity and Local Alignment Applied to Cover Song Identification," August, 2008
- William J. Pielemeier, Gregory H. Wakefield, and Mary H. Simoni, "Time–frequency Analysis of Musical Signals," September,1996
- Jeremy F. Alm and James S. Walker, "Time–Frequency Analysis of Musical Instruments," 2002
- Monika Dorfler, "What Time–Frequency Analysis Can Do To Music Signals," April,2004
- EnShuo Tsau, Namgook Cho and C.-C. Jay Kuo, "Fundamental Frequency Estimation For Music Signals with Modified Hilbert–Huang transform" IEEE International Conference on Multimedia and Expo, 2009.
- Lamb, Joseph Quinton
- Lamb-kill
- Lamb Leer
- Lambley, Nottinghamshire
- Lambliasis
- Lamb Lies Down on Broadway
- Lamb (Liturgy)
- Lamb (liturgy)
- Lamb marking
- Lambmarking
- Lamb meal
- Lamb meat
- Lamb (meat)
- Lambo
- Lambo (album)
- Lambo doors
- Lamb Of God
- Lamb of god band
- Lamb of god (band)
- Lamb of God (disambiguation)
- Lamb of God Discography
- Lamb of God discography
- Lambo Gran Turismo
- Lambo gran turismo
- Lambo GT