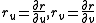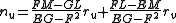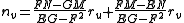- Statement in classical differential geometry
- Notes
- References
Statement in classical differential geometry
Let S be a surface in three-dimensional Euclidean space that is parametrized by position vector r(u, v) of the surface. Let P = P(u, v) be a fixed point on this surface. Then
are two tangent vectors at point P.
Let n be the unit normal vector and let (E, F, G) and (L, M, N) be the coefficients of the first and second fundamental forms of this surface, respectively. The Weingarten equation gives the first derivative of the unit normal vector n at point P in terms of tangent vectors ru and rv:
This can be expressed compactly in index notation as
,
where Kab are the components of the surface's curvature tensor.
Notes
1. ^{{cite journal|author=J. Weingarten|journal=Journal für die Reine und Angewandte Mathematik |title=Ueber eine Klasse auf einander abwickelbarer Flächen|volume=59|year=1861|pages=382–393}}
References
- {{MathWorld|urlname=WeingartenEquations|title=Weingarten Equations}}
- Springer Encyclopedia of Mathematics, Weingarten derivational formulas
- {{citation|last1 = Struik|first1=Dirk J.|title=Lectures on Classical Differential Geometry|year = 1988|publisher = Dover Publications|page=108|isbn=0-486-65609-8}}
- Erwin Kreyszig, Differential Geometry, Dover Publications, 1991, {{isbn|0-486-66721-9}}, section 45.
1 : Differential geometry of surfaces
- Burghausen Castle
- Burghausen (disambiguation)
- Burghauser number
- Burg, Hautes-Pyrenees
- Burg, Hautes-Pyrénées
- Burgh by sands
- Burghclere railway station
- Burghead Bull
- Burghead, Moray
- Burghead Thistle F. C.
- Burghead Thistle F C
- Burghead Thistle FC
- Burghead United F.C.
- Burgheard (disambiguation)
- Burgheard of lichfield
- Burgheard of Lichfield
- Burg Heidenreichstein
- Burg Heinfels
- Burg Heinrichsberg
- Burghelea
- Burg Helfenstein
- Burgher (disambiguation)
- Burgher Oath
- Burgher (people)
- Burgher's daughter