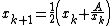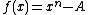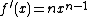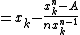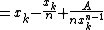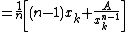- Derivation from Newton's method
- See also
- References
The principal nth root  of a positive real number A, is the positive real solution of the equation
of a positive real number A, is the positive real solution of the equation
.
(For a positive integer n there are n distinct complex solutions to this equation if 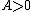 , but only one is positive and real).
, but only one is positive and real).
There is a very fast-converging nth root algorithm for finding  :
:
- Make an initial guess

- Set
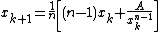 . In practice we do
. In practice we do 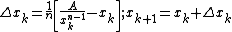 .
. - Repeat step 2 until the desired precision is reached, i.e.
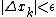 .
.
A special case is the familiar square-root algorithm. By setting n = 2, the iteration rule in step 2 becomes the square root iteration rule:
Several different derivations of this algorithm are possible. One derivation shows it is a special case of Newton's method (also called the Newton-Raphson method) for finding zeros of a function  beginning with an initial guess. Although Newton's method is iterative, meaning it approaches the solution through a series of increasingly accurate guesses, it converges very quickly. The rate of convergence is quadratic, meaning roughly that the number of bits of accuracy doubles on each iteration (so improving a guess from 1 bit to 64 bits of precision requires only 6 iterations). For this reason, this algorithm is often used in computers as a very fast method to calculate square roots.
beginning with an initial guess. Although Newton's method is iterative, meaning it approaches the solution through a series of increasingly accurate guesses, it converges very quickly. The rate of convergence is quadratic, meaning roughly that the number of bits of accuracy doubles on each iteration (so improving a guess from 1 bit to 64 bits of precision requires only 6 iterations). For this reason, this algorithm is often used in computers as a very fast method to calculate square roots.
For large n, the nth root algorithm is somewhat less efficient since it requires the computation of  at each step, but can be efficiently implemented with a good exponentiation algorithm.
at each step, but can be efficiently implemented with a good exponentiation algorithm.
Derivation from Newton's method
Newton's method is a method for finding a zero of a function f(x). The general iteration scheme is:
- Make an initial guess

- Set
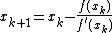
- Repeat step 2 until the desired precision is reached.
The nth root problem can be viewed as searching for a zero of the function
So the derivative is
and the iteration rule is
leading to the general nth root algorithm.
See also
- Recurrence relation
- Shifting nth root algorithm
References
- {{Citation |first=Kendall E. |last=Atkinson |title=An introduction to numerical analysis |location=New York |publisher=Wiley |year=1989 |edition=2nd |isbn=0-471-62489-6 }}.
- El Rey Theater
- El Rey (The Wedding Present album)
- El Rey Tiburon
- El Rey Tiburón
- Elrhaz Formation
- Elrhazosaurus
- Elrhazosaurus nigeriensis
- Elric (disambiguation)
- Elrick Irastorza
- Elric: Making of a Sorcerer
- Elric (role-playing game)
- Elric: The Making of a Sorcerer
- Elrig
- El Rincon
- El Rincon Light
- El Rincón Lighthouse
- El Rincón, Mexico
- ElringKlinger
- Elrington Halt railway station
- El Rinihuazo
- El rinihuazo
- El Rio Corte
- El Rio de Nuestra Senora La Reina de Los Angeles de Porciuncula
- El Rio de Nuestra Senora la Reina de los Angeles de Porciuncula
- El Rio Rey