- Mathematical definition
- Physical interpretation
- Einstein tensor
- Examples
- See also
- References
In mathematical physics, a null dust solution (sometimes called a null fluid) is a Lorentzian manifold in which the Einstein tensor is null. Such a spacetime can be interpreted as an exact solution of Einstein's field equation, in which the only mass-energy present in the spacetime is due to some kind of massless radiation.
Mathematical definition
By definition, the Einstein tensor of a null dust solution has the form

where 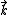 is a null vector field. This definition makes sense purely geometrically, but if we place a stress–energy tensor on our spacetime of the form
is a null vector field. This definition makes sense purely geometrically, but if we place a stress–energy tensor on our spacetime of the form
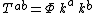 ,
,
then Einstein's field equation is satisfied, and such a stress–energy tensor has a clear physical interpretation in terms of massless radiation. The vector field specifies the direction in which the radiation is moving; the scalar multiplier specifies its intensity.
Physical interpretation
Physically speaking, a null dust describes either gravitational radiation, or some kind of nongravitational radiation which is described by a relativistic classical field theory (such as electromagnetic radiation), or a combination of these two. Null dusts include vacuum solutions as a special case.
Phenomena which can be modeled by null dust solutions include:
- a beam of neutrinos assumed for simplicity to be massless (treated according to classical physics),
- a very high-frequency electromagnetic wave,
- a beam of incoherent electromagnetic radiation.
In particular, a plane wave of incoherent electromagnetic radiation is a linear superposition of plane waves, all moving in the same direction but having randomly chosen phases and frequencies. (Even though the Einstein field equation is nonlinear, a linear superposition of comoving plane waves is possible.)
Here, each electromagnetic plane wave has a well defined frequency and phase, but the superposition does not. Individual electromagnetic plane waves are modeled by null electrovacuum solutions, while an incoherent mixture can be modeled by a null dust.
Einstein tensor
The components of a tensor computed with respect to a frame field rather than the coordinate basis are often called physical components, because these are the components which can (in principle) be measured by an observer.
In the case of a null dust solution, an adapted frame
(a timelike unit vector field and three spacelike unit vector fields, respectively) can always be found in which the Einstein tensor has a particularly simple appearance:
Here,  is everywhere tangent to the world lines of our adapted observers, and these observers measure the energy density of the incoherent radiation to be
is everywhere tangent to the world lines of our adapted observers, and these observers measure the energy density of the incoherent radiation to be  .
.
From the form of the general coordinate basis expression given above, it is apparent that the stress–energy tensor has precisely the same isotropy group as the null vector field 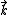 . It is generated by two parabolic Lorentz transformations (pointing in the
. It is generated by two parabolic Lorentz transformations (pointing in the  direction) and one rotation (about the
direction) and one rotation (about the  axis), and it is isometric to the three-dimensional Lie group
axis), and it is isometric to the three-dimensional Lie group  , the isometry group of the euclidean plane.
, the isometry group of the euclidean plane.
Examples
Null dust solutions include two large and important families of exact solutions:
- pp-wave spacetimes (which model generalizations of the plane waves familiar from electromagnetism),
- Robinson–Trautman null dusts (which model radiation expanding from a radiating object).
The pp-waves include the gravitational plane waves and the monochromatic electromagnetic plane wave. A specific example of considerable interest is
- the Bonnor beam, an exact solution modeling an infinitely long beam of light surrounded by a vacuum region.
Robinson–Trautman null dusts include the Kinnersley–Walker photon rocket solutions, which include the Vaidya null dust, which includes the Schwarzschild vacuum.
See also
- Vaidya metric
- Lorentz group
References
- {{cite book |author1=Stephani, Hans |author2=Kramer, Dietrich |author3=Maccallum, Malcolm |author4=Hoenselaers, Cornelius |author5=Herlt, Eduard |last-author-amp=yes | title=Exact Solutions of Einstein's Field Equations| location=Cambridge | publisher=Cambridge University Press | year=2003 | isbn=0-521-46136-7}}. This standard monograph gives many examples of null dust solutions.
- The Nightgowns
- The Night Has a Thousand Eyes (disambiguation)
- The Night Has A Way
- The Night has Eyes
- The Night Has Eyes
- The night he came home
- The Night Holds Terror
- The Night I Called the Old Man Out
- The Nightingale: A Conversation Poem
- The nightingale and the rose
- The Nightingale and the Rose (ballet)
- The Nightingale (Coleridge)
- The Nightingale Company
- The Nightingale's Song
- The Nightingale (Turnbull novel)
- The Night Invader
- The Night Is for Hunting
- The Night Is Ours
- The Night Is Still Young
- The Night is Still Young
- The Night Is Still Young (Sandra and Thomas Anders song)
- The Night Is Still Young (Sandra Feat. Thomas Anders song)
- The Night Is Still Young (Sandra feat. Thomas Anders song)
- The Night Is Still Young (Sandra song)
- The Night Lands

