农田防护林带小气候nongtian fanghulindai xiaoqihoumicroclimate in farm shelterbeits
在林带的影响下所产生的特有的农田小气候环境。农田防护林(包括林带、林岛、林农间作等形式)可改善农田小气候条件, 防止或减轻自然灾害(风沙、大风、台风、干热风、干旱、霜冻等),形成有利于农作物生长、发育的优良的小气候环境。林带保护下的谷类作物产量, 一般较无林带保护的农田高10%~30%;在自然灾害特别严重的情况下, 农田防护林的作用更为明显。
农田防护林小气候的研究始于19世纪下半叶。1872年丹麦学者曾观测了林带对空气温度和湿度的影响; 1882年俄国A.A.贝奇欣用风速表观测林带附近的风速, 研究了林带降低风速的作用, 以后苏联的В.А.博德罗夫、Т.И.马佳金、A.P.康斯坦丁诺夫,英国的J. M. 卡博恩, 丹麦的M.耶森, 美国的N. P.伍德拉夫、T. V.埃默恩等作了较为深入的研究。20世纪40年代中国在东北和西北地区曾作过观测和调查,50年代对华南橡胶园防护林、东北西部、内蒙古东部农田防护林, 相继开展了小气候的野外观测和林带模型的风洞实验研究。随着农田防护林建设范围扩大,全国大部分省、市、自治区相应的开展了防护林小气候的研究。
防护林带附近的小气候要素的分布特征和变化规律如后:
风速 防风效应是林带的主要作用, 林带向风面10H(H为林带平均高度)前后风速即开始减弱,最低风速出现在林带背风面0~10H之间,远离林带农田风速逐渐加大,到一定距离即恢复到无林带保护的田野上同一高度的风速——旷野风速。林带附近风速降低的程度、最低风速出现的位置、林后风速的分布特征以及恢复到旷野风速所达到的距离(称为防护距离)和林带的结构有关。防护距离不仅和林带结构有关,还受天气条件和下垫面状况的影响, 变化于20~55H之间。从Я.A.斯玛雷科在苏联进行野外观测的结果可以看出, 林带背风面和向风面存在弱风区。相对风速(即林带附近风速与旷野同一高度风速之百分比)小于100%。为林带的防护范围,在此范围内, 风速受到减弱的高度和林带结构、大气稳定度等有关, 一般大于林带的平均高度。在不稳定大气层结时甚至可达3.5H以上。在林带上面1.5~3.0H处有一增速区,相对风速大于100%, 其值随林带透风系数的减小而增大。在透风系数为0时可达130%以上;在透风系数为最适期(0.5~0.6)时约为115%。
辐射 由于林带遮荫,林网内日照时数减少, 使下垫面的总辐射收入降低, 以林缘附近最为明显。野外观测结果表明, 南林缘达85%以上,北林缘达29%左右。由于林带侧面的反射辐射可使地面的总辐射瞬时值比旷野大5%以上,林缘附近有效辐射可减少50%~60%。
温度 林带对辐射状况、风速、乱流交换和蒸发等的影响,使防护林附近的热量平衡各分量发生变化,影响到附近的空气温度、地面温度和土壤温度。这种影响和林带的结构有关,也和天气状况、气候条件等有关,一般在0~10H,尤其在0~2H范围内较明显,直到20H仍能观测到温度的差异。阴天和风速较大时,林带附近和旷野的温度差异极微,晴天无风或风速很小时,则较明显。林带附近向阳的一侧,地表温度高于旷野, 见表1。NE面(背阴面)地面温度只有1H(4米)处在上午7~9时以前较旷野高, SW面(向阳面) 11~17时较旷野高,最大(在1H)高5.8℃。其他时间由于林带遮蔽作用,温度较旷野低。夜间2H以内林带附近有效辐射减少,地表温度较旷野高。大量观测结果表明, 白天辐射差额为正值时,林带有增温效应,夜间辐射差额为负值时,林带有降温效应。据中国北方各农田防护林区的观测, 冬春季有林带防护的地区平均气温增加不到1℃;最高气温约增加1~2℃,个别的观测结果达4℃以上;最低温度既观测到提高1~2℃的纪录,也有降低的情况。在北方比较湿润的生长季节以及广东橡胶防护林的观测结果表明,有林带防护的地区平均气温降低0.5~2.5℃,在辐射型天气条件下甚至观测到降低4.0℃以上的例子。
表1 林带两侧地表温(℃)的日变化
| 时间 位置(H) | 5 | 7 | 9 | 11 | 13 | 15 | 17 | 平 均 | 振 幅 | |
| SW ⌢ 向 阳 面 ⌣ | 林缘 1 2 3 | 5.9 3.9 3.8 4.2 | 8.4 6.7 7.4 7.6 | 12. 6 22.1 20.0 18.7 | 26.3 28.6 28.6 24.9 | 34.8 33.9 32.7 28.0 | 29.7 28.0 26.1 23.8 | 20.3 17.0 15.7 16.2 | 20.5 21.3 19.7 18.4 | 28.9 29.0 28.9 23.8 |
| NE ⌢ 背 阴 面 ⌣ | 林缘 1 2 3 | 4.6 3.0 3.1 3.3 | 8.0 9.4 8.3 8.7 | 19.3 22.1 20.4 20.8 | 15.4 26.5 26.5 26.5 | 15.2 22.5 28.6 29.7 | 14.4 17.7 21.8 24.3 | 12.4 13.0 13.9 15.1 | 13.4 17.1 17.8 19.2 | 14.8 23.6 25.8 26.4 |
| 对 照 | 1.7 | 8.7 | 22.1 | 26.4 | 31.2 | 22.2 | 14.9 | 19.5 | 29.5 | |
在有风天气林带背风面温度的分布规律和风速分布规律相似,据詹森的观测,风速小于0.5米/秒时,林网内和旷野夜间最低气温相差不大; 风速在0.5~1.5米/秒时,林网内由于林带的防护作用风速极小,上层暖空气和低层冷空气的热交换微弱,空气温度较旷野低0.5~1.5℃; 当风速大于1.5米/秒时,林网内外的热交换均不太小,空气温度差异又趋于消失。林带的热效应使林网内的温度分布不均, 可引起林网内的局地环流,产生一定的局地风速,这对空气温度可产生反馈作用,使林带附近与旷野的温度差异减小。
林带的动力效应和水文效应可改变防护区内土壤的物理性质,使土壤含水量增大, 导致土壤导热率和热容量的增大,从而影响到土壤温度的改变。0~20厘米土壤温度提高0.5~1.0℃,在个别情况下5~10厘米层土温度可比旷野高3℃以上。
降水 林带明显地影响降水的再分配。苏联长明草原的观测表明,林网内比无林带保护的农田可增加10~20%的积雪。林带结构愈紧密,林带内及其附近保存的积雪也愈多,通风结构窄林带内的积雪虽少,但林网内积雪的分布较均匀,总积雪量大。
土壤湿度 林网内的土壤湿度与旷野相比略有增加。林缘附近由于林带树木根系的吸收、土壤湿度较小; 在2H前达最大; 更远离林带处逐渐减小到旷野值。
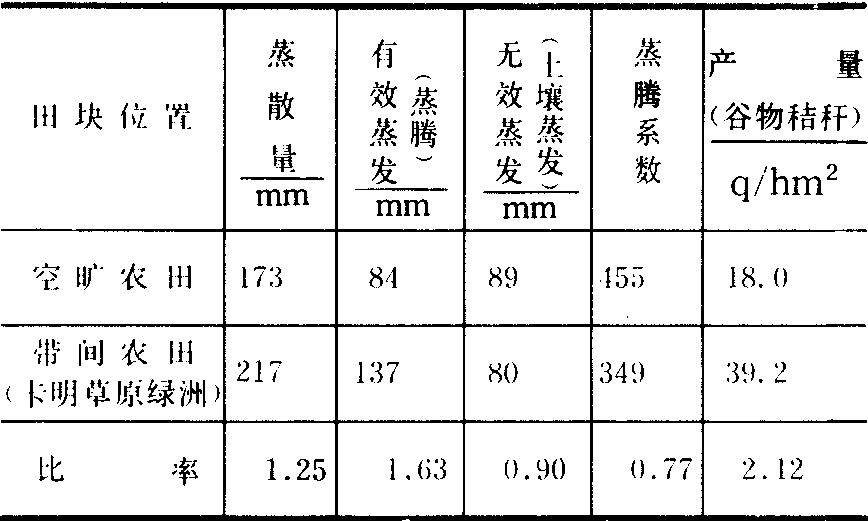
蒸散 由蒸发器测得林带附近的蒸发能力比无林带保护的农田明显减小, 中国北方各防护林区的观测结果表明, 网格内的蒸发能力平均约降低10%~25%,最小值与风速最低值出现的位置相一致, 当风速大、湿度小时,在5H处甚至可减少40%以上。林带影响蒸发能力的范围和影响风速的范围相一致。苏联的观测结果表明,林网内平均蒸发能力比旷野减低10%~20%。林带防护下的农田实际蒸散量与蒸发能力并不一致。林网内土壤较湿润, 总蒸散量有时反而较旷野高。表2是康斯坦丁诺夫的观测结果, 带内农田蒸散量为空旷农田的125%, 蒸腾量为163%, 土壤蒸发为90%。林网内的农田不仅降低了无效蒸发(土壤蒸发), 蒸腾系数也降低了23%, 他认为这种降低是农业森林土壤改良综合措施的结果。一般林带可使蒸腾系数降低15%左右。
表2 春小麦地的有效蒸发和无效蒸发的比较
空气湿度 林带附近的空气湿度一般比旷野略高。中国北方各防护林区的观测结果表明, 林网内相对湿度较旷野约高2~10%; 个别情况下更大。