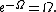- Properties Fixed point representation Computation Integral representations
- Transcendence
- See also
- References
- External links
The omega constant is a mathematical constant defined as the unique real number that satisfies the equation
It is the value of {{math|W(1)}}, where {{mvar|W}} is Lambert's {{mvar|W}} function. The name is derived{{cn|date=September 2018}} from the alternate name for Lambert's {{mvar|W}} function, the omega function. The numerical value of {{math|Ω}} is given by
{{math|1=Ω = {{gaps|0.56714|32904|09783|87299|99686|62210|...}}}} {{OEIS|id=A030178}}.
{{math|1=1/Ω = {{gaps|1.76322|28343|51896|71022|52017|76951|...}}}} {{OEIS|id=A030797}}.
Properties
Fixed point representation
The defining identity can be expressed, for example, as
or
or
Computation
One can calculate {{math|Ω}} iteratively, by starting with an initial guess {{math|Ω0}}, and considering the sequence
This sequence will converge to {{math|Ω}} as {{mvar|n}} approaches infinity. This is because {{math|Ω}} is an attractive fixed point of the function {{math|e−x}}.
It is much more efficient to use the iteration
because the function
in addition to having the same fixed point, also has a derivative that vanishes there. This guarantees quadratic convergence; that is, the number of correct digits is roughly doubled with each iteration.
Using Halley's method, {{math|Ω}} can be approximated with cubic convergence (the number of correct digits is roughly tripled with each iteration): (see also {{section link|Lambert W function|Numerical evaluation}}).
Integral representations
An identity due to Victor Adamchik{{cn|date=September 2018}} is given by the relationship
Another relation due to Mező is[1]
The latter identity can be extended to other values of the {{mvar|W}} function (see also {{section link|Lambert W function|Representations}}).
Transcendence
The constant {{math|Ω}} is transcendental. This can be seen as a direct consequence of the Lindemann–Weierstrass theorem. For a contradiction, suppose that {{math|Ω}} is algebraic. By the theorem, {{math|e−Ω}} is transcendental, but {{math|1=Ω = e−Ω}}, which is a contradiction. Therefore, it must be transcendental.
See also
- Lambert {{mvar|W}} function
References
External links
- {{MathWorld|urlname=OmegaConstant|title=Omega Constant}}
- {{citation|title=Omega constant (1,000,000 digits)|url=http://ankokudan.org/d/d.htm?mathlistindex-e.html|work=Darkside communication group (in Japan) |accessdate=2017-12-25}}
- J. Agric. Sci. Food Res.
- J Agric Sci Food Res
- Jag ringer pa fredag
- Jagrit Anand
- Jagriti Hindu Vidyamandir
- Jagruti Nagar
- Jags
- Jag Singh
- JAGS McCartney (airport)
- JAGS McCartney International
- JAGS McCartney (international airport)
- JAGS McCartney International (airport)
- Jagson (airline)
- Jagstzell station
- Jagtaj, Murshidabad
- Jagtar
- Jagtar Singh Johal
- Jagtial (Assembly constituency)
- Jagtial District
- Jagtial district
- Jagtiāl
- Jag trivs bäst i öppna landskap
- Jag trodde änglarna fanns
- Jag tror pa sommaren
- Jagtvej