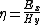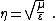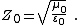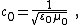- Types of optical mediums
- Notes and references
- See also
An optical medium is material through which electromagnetic waves propagate. It is a form of transmission medium. The permittivity and permeability of the medium define how electromagnetic waves propagate in it. The medium has an intrinsic impedance, given by
where  and
and 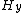 are the electric field and magnetic field, respectively.
are the electric field and magnetic field, respectively.
In a region with no electrical conductivity, the expression simplifies to:
For example, in free space the intrinsic impedance is called the characteristic impedance of vacuum, denoted Z0, and
Waves propagate through a medium with velocity 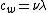 , where
, where  is the frequency and
is the frequency and  is the wavelength of the electromagnetic waves. This equation also may be put in the form
is the wavelength of the electromagnetic waves. This equation also may be put in the form
where 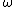 is the angular frequency of the wave and
is the angular frequency of the wave and  is the wavenumber of the wave. In electrical engineering, the symbol
is the wavenumber of the wave. In electrical engineering, the symbol 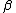 , called the phase constant, is often used instead of
, called the phase constant, is often used instead of  .
.
The propagation velocity of electromagnetic waves in free space, an idealized standard reference state (like absolute zero for temperature), is conventionally denoted by c0:[1]
whereis the electric constant and
is the magnetic constant.
For a general introduction, see Serway[2] For a discussion of synthetic media, see Joannopoulus.[3]
Types of optical mediums
- Homogeneous medium
- Heterogeneous medium
- Transparent medium
- Translucent medium
- Opaque body
Notes and references
2. ^{{cite book |author1=Raymond Serway |author2=Jewett J |lastauthoramp=yes |title=Physics for scientists and engineers|edition=6th|year= 2003|publisher=Thomson-Brooks/Cole|location=Belmont CA|isbn=0-534-40842-7|url=http://worldcat.org/isbn/0-534-40842-7}}
3. ^{{cite book |author1=John D Joannopouluos |author2=Johnson SG |author3=Winn JN |author4=Meade RD |title=Photonic crystals : molding the flow of light|edition=2nd|year= 2008|publisher=Princeton University Press|location=Princeton NJ|isbn=978-0-691-12456-8|url=http://ab-initio.mit.edu/book/}}
See also
- Čerenkov radiation
- Electromagnetic spectrum
- Electromagnetic radiation
- Optics
- SI units
- Free space
- Metamaterial
- Photonic crystal
- Photonic crystal fiber
- Sahajanpur Upazila
- Sahaj marg
- Sahak
- Sahakanuysh
- Sahakanuysh Sevada
- Sahak (disambiguation)
- Sahakduxt
- Sahak-e Abd ol Nabi
- Sahak-e Parih-e Yek
- Sahak-e Yareyeh
- Sahak II
- Sahak II Bagratuni
- Sahak II (disambiguation)
- Sahak III of Armenia
- Sahak of Armenia
- Sahak Parparyan
- Sahak VII Bagratuni
- Sahakyants, Robert
- Sahalan
- Saha-Langmuir equation
- Sahale Glacier
- Sahali, Iran
- Sa-Hali Secondary
- Sa-Hali Secondary School
- Sahal Mahfudz