- Definition
- Uses Calculating the order of magnitude Order-of-magnitude estimate Order of magnitude difference
- Non-decimal orders of magnitude Extremely large numbers
- See also
- References
- Further reading
- External links
An order of magnitude is an approximate measure of the number of digits that a number has in the commonly-used base-ten number system. It is equal to the whole number floor of logarithm (base 10). For example, the order of magnitude of 1500 is 3, because 1500 = 1.5 × 103.
Differences in order of magnitude can be measured on a base-10 logarithmic scale in “decades” (i.e., factors of ten).[1] Examples of numbers of different magnitudes can be found at Orders of magnitude (numbers).
Definition
Generally, the order of magnitude of a number is the smallest power of 10 used to represent that number.[2] To work out the order of magnitude of a number  , the number is first expressed in the following form:
, the number is first expressed in the following form:
where 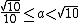 . Then,
. Then,  represents the order of magnitude of the number. The order of magnitude can be any integer. The table below enumerates the order of magnitude of some numbers in light of this definition:
represents the order of magnitude of the number. The order of magnitude can be any integer. The table below enumerates the order of magnitude of some numbers in light of this definition:
Number  | Expression in  | Order of magnitude  |
|---|---|---|
| 0.2 | 2 × 10−1 | −1 |
| 1 | 1 × 100 | 0 |
| 5 | 0.5 × 101 | 1 |
| 6 | 0.6 × 101 | 1 |
| 31 | 3.1 × 101 | 1 |
| 32 | 0.32 × 102 | 2 |
| 999 | 0.999 × 103 | 3 |
| 1000 | 1 × 103 | 3 |
The geometric mean of  and
and 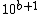 is
is 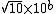 , meaning that a value of exactly
, meaning that a value of exactly  (i.e.,
(i.e.,  ) represents a geometric "halfway point" within the range of possible values of
) represents a geometric "halfway point" within the range of possible values of  .
.
Some use a simpler definition where  , perhaps because the arithmetic mean of
, perhaps because the arithmetic mean of  and
and 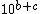 approaches
approaches 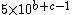 for increasing
for increasing  . This definition has the effect of lowering the values of
. This definition has the effect of lowering the values of  slightly:
slightly:
Number  | Expression in  | Order of magnitude  |
|---|---|---|
| 0.2 | 2 × 10−1 | −1 |
| 1 | 1 × 100 | 0 |
| 5 | 5 × 100 | 0 |
| 6 | 0.6 × 101 | 1 |
| 31 | 3.1 × 101 | 1 |
| 32 | 3.2 × 101 | 1 |
| 999 | 0.999 × 103 | 3 |
| 1000 | 1 × 103 | 3 |
Yet others restrict  to values where
to values where 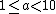 , making the order of magnitude of a number exactly equal to its exponent part in scientific notation.
, making the order of magnitude of a number exactly equal to its exponent part in scientific notation.
Uses
Orders of magnitude are used to make approximate comparisons. If numbers differ by one order of magnitude, x is about ten times different in quantity than y. If values differ by two orders of magnitude, they differ by a factor of about 100. Two numbers of the same order of magnitude have roughly the same scale: the larger value is less than ten times the smaller value.
| In words (long scale) | In words (short scale) | Prefix (Symbol) | Decimal | Power of ten | Order of magnitude |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| quadrillionth | septillionth | yocto- (y) | 0.000000000000000000000001}} | 10−24 | −24 |
| trilliardth | sextillionth | zepto- (z) | 0.000000000000000000001}} | 10−21 | −21 |
| trillionth | quintillionth | atto- (a) | 0.000000000000000001}} | 10−18 | −18 |
| billiardth | quadrillionth | femto- (f) | 0.000000000000001}} | 10−15 | −15 |
| billionth | trillionth | pico- (p) | 0.000000000001}} | 10−12 | −12 |
| milliardth | billionth | nano- (n) | 0.000000001}} | 10−9 | −9 |
| millionth | millionth | micro- (µ) (lowercase Mu symbol) | 0.000001}} | 10−6 | −6 |
| thousandth | thousandth | milli- (m) | 0.001 | 10−3 | −3 |
| hundredth | hundredth | centi- (c) | 0.01 | 10−2 | −2 |
| tenth | tenth | deci- (d) | 0.1 | 10−1 | −1 |
| one | one | 1 | 100 | 0 | |
| ten | ten | deca- (da) U+3372 (㍲) | 10 | 101 | 1 |
| hundred | hundred | hecto- (h) | 100 | 102 | 2 |
| thousand | thousand | kilo- (k) | {{val|1000|fmt=none}} | 103 | 3 |
| million | million | mega- (M) | {{val|1000000}} | 106 | 6 |
| milliard | billion | giga- (G) | {{val|1000000000}} | 109 | 9 |
| billion | trillion | tera- (T) | {{val|1000000000000}} | 1012 | 12 |
| billiard | quadrillion | peta- (P) | {{val|1000000000000000}} | 1015 | 15 |
| trillion | quintillion | exa- (E) | {{val|1000000000000000000}} | 1018 | 18 |
| trilliard | sextillion | zetta- (Z) | {{val|1000000000000000000000}} | 1021 | 21 |
| quadrillion | septillion | yotta- (Y) | {{val|1000000000000000000000000}} | 1024 | 24 |
| In words (long scale) | In words (short scale) | Prefix (Symbol) | Decimal | Power of ten | Order of magnitude |
Calculating the order of magnitude
The order of magnitude of a number is, intuitively speaking, the number of powers of 10 contained in the number. More precisely, the order of magnitude of a number can be defined in terms of the common logarithm, usually as the integer part of the logarithm, obtained by truncation. For example, the number {{val|4000000}} has a logarithm (in base 10) of 6.602; its order of magnitude is 6. When truncating, a number of this order of magnitude is between 106 and 107. In a similar example, with the phrase "He had a seven-figure income", the order of magnitude is the number of figures minus one, so it is very easily determined without a calculator to 6. An order of magnitude is an approximate position on a logarithmic scale.
Order-of-magnitude estimate
An order-of-magnitude estimate of a variable, whose precise value is unknown, is an estimate rounded to the nearest power of ten. For example, an order-of-magnitude estimate for a variable between about 3 billion and 30 billion (such as the human population of the Earth) is 10 billion. To round a number to its nearest order of magnitude, one rounds its logarithm to the nearest integer. Thus {{val|4000000}}, which has a logarithm (in base 10) of 6.602, has 7 as its nearest order of magnitude, because "nearest" implies rounding rather than truncation. For a number written in scientific notation, this logarithmic rounding scale requires rounding up to the next power of ten when the multiplier is greater than the square root of ten (about 3.162). For example, the nearest order of magnitude for {{val|1.7|e=8}} is 8, whereas the nearest order of magnitude for {{val|3.7|e=8}} is 9. An order-of-magnitude estimate is sometimes also called a zeroth order approximation.
Order of magnitude difference
An order-of-magnitude difference between two values is a factor of 10. For example, the mass of the planet Saturn is 95 times that of Earth, so Saturn is two orders of magnitude more massive than Earth. Order-of-magnitude differences are called decades when measured on a logarithmic scale.
Non-decimal orders of magnitude
{{see also|Logarithmic scale}}Other orders of magnitude may be calculated using bases other than 10. The ancient Greeks ranked the nighttime brightness of celestial bodies by 6 levels in which each level was the fifth root of one hundred (about 2.512) as bright as the nearest weaker level of brightness, and thus the brightest level being 5 orders of magnitude brighter than the weakest indicates that it is (1001/5)5 or a factor of 100 times brighter.
The different decimal numeral systems of the world use a larger base to better envision the size of the number, and have created names for the powers of this larger base. The table shows what number the order of magnitude aim at for base 10 and for base {{val|1000000}}. It can be seen that the order of magnitude is included in the number name in this example, because bi- means 2 and tri- means 3 (these make sense in the long scale only), and the suffix -illion tells that the base is {{val|1000000}}. But the number names billion, trillion themselves (here with other meaning than in the first chapter) are not names of the orders of magnitudes, they are names of "magnitudes", that is the numbers {{val|1000000000000}} etc.
| Order of magnitude | Is log10 of | {{val>1000000 of | Short scale | Long scale |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | {{val|10}} | {{val|1000000}} | million | million |
| 2 | {{val|100}} | {{val|1000000000000}} | trillion | billion |
| 3 | {{val|1000|fmt=none}} | {{val|1000000000000000000}} | quintillion | trillion |
SI units in the table at right are used together with SI prefixes, which were devised with mainly base 1000 magnitudes in mind. The IEC standard prefixes with base 1024 were invented for use in electronic technology.
The ancient apparent magnitudes for the brightness of stars uses the base 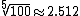 and is reversed. The modernized version has however turned into a logarithmic scale with non-integer values.
and is reversed. The modernized version has however turned into a logarithmic scale with non-integer values.
Extremely large numbers
For extremely large numbers, a generalized order of magnitude can be based on their double logarithm or super-logarithm. Rounding these downward to an integer gives categories between very "round numbers", rounding them to the nearest integer and applying the inverse function gives the "nearest" round number.
The double logarithm yields the categories:
..., 1.0023–1.023, 1.023–1.26, 1.26–10, 10–1010, 1010–10100, 10100–10{{val|1000|fmt=none}}, ...
(the first two mentioned, and the extension to the left, may not be very useful, they merely demonstrate how the sequence mathematically continues to the left).
The super-logarithm yields the categories:
0–1, 1–10, 10–1010, 1010–101010, 101010–10101010, ... or
0–010, 010–110, 110–210, 210–310, 310–410, ...
The "midpoints" which determine which round number is nearer are in the first case:
1.076, 2.071, 1453, {{val|4.20|e=31}}, {{val|1.69|e=316}},...
and, depending on the interpolation method, in the second case
−0.301, 0.5, 3.162, {{val|1453|fmt=none}}, {{val|1|e=1453|fmt=none}},,
,... (see notation of extremely large numbers)
For extremely small numbers (in the sense of close to zero) neither method is suitable directly, but the generalized order of magnitude of the reciprocal can be considered.
Similar to the logarithmic scale one can have a double logarithmic scale (example provided here) and super-logarithmic scale. The intervals above all have the same length on them, with the "midpoints" actually midway. More generally, a point midway between two points corresponds to the generalised f-mean with f(x) the corresponding function log log x or slog x. In the case of log log x, this mean of two numbers (e.g. 2 and 16 giving 4) does not depend on the base of the logarithm, just like in the case of log x (geometric mean, 2 and 8 giving 4), but unlike in the case of log log log x (4 and {{val|65536}} giving 16 if the base is 2, but not otherwise).
See also
- Big O notation
- Decibel
- Names of large numbers
- Names of small numbers
- Number sense
- Orders of magnitude (numbers)
- Scientific notation
- Valuation (algebra), an algebraic generalization of "order of magnitude"
- Unicode symbols for CJK Compatibility includes SI Unit symbols
- Mathematical operators and symbols in Unicode
References
2. ^{{cite web|title=Order of Magnitude|url=http://mathworld.wolfram.com/OrderofMagnitude.html|website=Wolfram MathWorld|accessdate=3 January 2017|quote=Physicists and engineers use the phrase "order of magnitude" to refer to the smallest power of ten needed to represent a quantity.}}
Further reading
- Asimov, Isaac The Measure of the Universe (1983)
External links
- The Scale of the Universe 2 Interactive tool from Planck length 10−35 meters to universe size 1027
- [https://web.archive.org/web/20080412094332/http://www.shekpvar.net/~dna/Publications/Cosmos/cosmos.html Cosmos – an Illustrated Dimensional Journey from microcosmos to macrocosmos] – from Digital Nature Agency
- Powers of 10, a graphic animated illustration that starts with a view of the Milky Way at 1023 meters and ends with subatomic particles at 10−16 meters.
- What is Order of Magnitude?
- William Watts Biggers
- William Watts (disambiguation)
- William Watts (engraver)
- William Watts (governor)
- William Watts Hart Davis
- William Watts Sherman
- William Watts (translator)
- William Wauer
- William Waugh
- William Waugh (disambiguation)
- William W. Axe School
- William Wayne Frazier
- William Wayne Frazier, Sr.
- William W. Bain Jr
- William W. Bennett (educator)
- William W. "Bill" Kirtley
- William W. Blanton
- William W. Brien
- William W. Brien, MD
- William W. Brown (Wisconsin politician)
- William W. Burritt
- William W. Campbell (New York state senator)
- William W. Cargill
- William W. Cate
- William W. Christmas