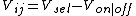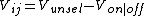- See also
- References
Passive matrix addressing is an addressing scheme used in early LCDs. This is a matrix addressing scheme meaning that only m + n control signals are required to address an m × n display. A pixel in a passive matrix must maintain its state without active driving circuitry until it can be refreshed again.
The signal is divided into a row or select signal and a column or video signal. The select voltage determines the row that is being addressed and all n pixels on a row are addressed simultaneously. When pixels on a row are being addressed, a Vsel potential is applied, and all other rows are unselected with a Vunsel potential. The video signal or column potential is then applied with a potential for each m columns individually. An on-lighted pixel corresponds to a Von, an off-switched corresponds to a Voff potential.[1]
The potential across pixel at selected row i and column j is
and
for the unselected rows.[2]
Passive matrix addressed displays such as Ferro Liquid Display do not need the switch component of an active matrix display because they have built-in bistability. Technology for electronic paper also has a form of bistability. Displays with bistable pixel elements are addressed with a passive matrix addressing scheme, whereas TFT LCD displays are addressed using active addressing.
See also
- Active matrix addressing
- Pixel geometry
- Liquid crystal display
References
2. ^P. M. Alt, P. Pleshko Scanning limitations of liquid-crystal displays, IEEE Trans. Electron Devices, vol. ED-21, pp. 146–155, Feb. 1974.
- ShopStyle
- Shop Until You Drop
- Shopurka
- Shop Your Way
- Shoqeda
- Shor and Shorshor
- Shor Bible
- Shor, Charles
- Shorchi
- Shordyn
- Shore
- Shore Action
- Shore, Andrew
- Shore Boulevard Mall
- Shore butter-cup
- Shore buttercup
- Shore, Charles
- Shore, David
- Shoreditch and Finsbury by-election, 1954
- Shoreditch and Finsbury by-election, 1958
- Shoreditch and Finsbury (London County Council constituency)
- Shoreditch Borough Council
- Shoreditch Hoppa
- Shoreditch-on-Sea
- Shore dotterel