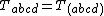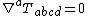- References
In general relativity and differential geometry, the Bel–Robinson tensor is a tensor defined in the abstract index notation by:
Alternatively,
where 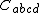 is the Weyl tensor. It was introduced by Lluís Bel in 1959.[1][2] The Bel–Robinson tensor is constructed from the Weyl tensor in a manner analogous to the way the electromagnetic stress–energy tensor is built from the electromagnetic tensor. Like the electromagnetic stress–energy tensor, the Bel–Robinson tensor is totally symmetric and traceless:
is the Weyl tensor. It was introduced by Lluís Bel in 1959.[1][2] The Bel–Robinson tensor is constructed from the Weyl tensor in a manner analogous to the way the electromagnetic stress–energy tensor is built from the electromagnetic tensor. Like the electromagnetic stress–energy tensor, the Bel–Robinson tensor is totally symmetric and traceless:
In general relativity, there is no unique definition of the local energy of the gravitational field. The Bel–Robinson tensor is a possible definition for local energy, since it can be shown that whenever the Ricci tensor vanishes (i.e. in vacuum), the Bel–Robinson tensor is divergence-free:
References
2. ^{{citation|first1=J. M. M.|last1=Senovilla|title=Editor's Note: Radiation States and the Problem of Energy in General Relativity by Louis Bel|journal=General Relativity and Gravitation|volume=32|page=2043|year=2000|doi=10.1023/A:1001906821162|bibcode=2000GReGr..32.2043S}}
- Docus femoratus
- Docus granulatus
- Docus griseolineatus
- Docus griseus
- Doc Walker (disambiguation)
- Doc Watkins
- DOC (website)
- Doc Williams (American football)
- Doc World
- Docwra, Thomas
- Docxing
- D.O.D
- DODAB
- Doda Conrad
- Doda Dome (Yosemite)
- Dodai Stewart
- Doda Kamman
- Doda Lake
- Dodamarg
- Dodam-dong
- Dodamthale Raja Maha Vihara
- Dodan
- Dodanthale Raja Maha Vihara
- Doda Sodagar
- Dodavah