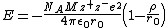- See also
- References
The Born–Mayer equation is an equation that is used to calculate the lattice energy of a crystalline ionic compound. It is a refinement of the Born–Landé equation by using an improved repulsion term.[1]
where:
- NA = Avogadro constant;
- M = Madelung constant, relating to the geometry of the crystal;
- z+ = charge number of cation
- z− = charge number of anion
- e = elementary charge, 1.6022{{e|−19}} C
- ε0 = permittivity of free space
4{{pi}}ε0 = 1.112{{e|−10}} C2/(J·m)
- r0 = distance to closest ion
- ρ = a constant dependant on the compressibility of the crystal; 30 pm works well for all alkali metal halides
See also
- Born–Landé equation
- Kapustinskii equation
References
1. ^{{cite web|url=http://alpha.chem.umb.edu/chemistry/ch370/CH370_Lectures/Lecture%20Documents/Ch07_2_LatticeEnergy.pdf|title=Lattice Energy}}
{{DEFAULTSORT:Born-Mayer Equation}} 2 : Solid-state chemistry|Ions
- Geology of dorset
- Geology of England
- Geology of england
- Geology of europe
- Geology of Europe
- Geology of Georgia
- Geology of Georgia (U.S. state)
- Geology of Georgia (U.S. State)
- Geology of Georgia (U. S. State)
- Geology of Gloucestershire
- Geology of gloucestershire
- Geology of hampshire
- Geology of hertfordshire
- Geology of hong kong
- Geology of Hong Kong
- Geology of Iberia
- Geology of iceland
- Geology of Iceland
- Geology of Idaho
- Geology of idaho
- Geology of illinois
- Geology of Illinois
- Geology of indonesia
- Geology of Indonesia
- Geology of Ireland