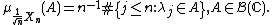- Precise statement
- History
- See also
- References
In probability theory, more specifically the study of random matrices, the circular law concerns the distribution of eigenvalues of an {{math|n × n}} random matrix with independent and identically distributed entries in the limit
{{math|n → ∞}}.It asserts that for any sequence of random {{math|n × n}} matrices whose entries are independent and identically distributed random variables, all with mean zero and variance equal to {{math|1/n}}, the limiting spectral distribution is the uniform distribution over the unit disc.
Precise statement
Let  be a sequence of {{math|n × n}} matrix ensembles whose entries are i.i.d. copies of a complex random variable {{math|x}} with mean 0 and variance 1. Let
be a sequence of {{math|n × n}} matrix ensembles whose entries are i.i.d. copies of a complex random variable {{math|x}} with mean 0 and variance 1. Let 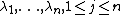 denote the eigenvalues of
denote the eigenvalues of 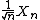 . Define the empirical spectral measure of
. Define the empirical spectral measure of  as
as
With these definitions in mind, the circular law asserts that almost surely (i.e. with probability one), the sequence of measures  converges in distribution to the uniform measure on the unit disk.
converges in distribution to the uniform measure on the unit disk.
History
For random matrices with Gaussian distribution of entries (the Ginibre ensembles), the circular law was established in the 1960s by Jean Ginibre.[1] In the 1980s, Vyacheslav Girko introduced[2] an approach which allowed to establish the circular law for more general distributions. Further progress was made[3] by Zhidong Bai, who established the circular law under certain smoothness assumptions on the distribution.
The assumptions were further relaxed in the works of Terence Tao and Van H. Vu,[4] Guangming Pan and Wang Zhou,[5] and Friedrich Götze and Alexander Tikhomirov.[6] Finally, in 2010 Tao and Vu proved[7] the circular law under the minimal assumptions stated above.
See also
- Wigner semicircle distribution
References
2. ^{{cite journal|last=Girko|first=V.L.|title=The circular law|journal=Teor. Veroyatnost. i Primenen.|year=1984|volume=29|issue=4|pages=669–679}}
3. ^{{cite journal|last=Bai|first=Z.D.|title=Circular law|journal=Annals of Probability|year=1997|volume=25|issue=1|pages=494–529|doi=10.1214/aop/1024404298|mr=1428519}}
4. ^{{cite journal|last=Tao|first=T.|last2=Vu|first2=V.H.|title=Random matrices: the circular law.|journal=Commun. Contemp. Math.|year=2008|volume=10|issue=2|pages=261–307|doi=10.1142/s0219199708002788|mr=2409368|arxiv=0708.2895}}
5. ^{{cite journal|last=Pan|first=G.|last2=Zhou|first2=W.|title=Circular law, extreme singular values and potential theory.|journal=J. Multivariate Anal.|year=2010|volume=101|issue=3|pages=645–656|doi=10.1016/j.jmva.2009.08.005}}
6. ^{{cite journal|last=Götze|first=F.|last2=Tikhomirov|first2=A.|title=The circular law for random matrices|journal=Annals of Probability|year=2010|volume=38|issue=4|pages=1444–1491|doi=10.1214/09-aop522|mr=2663633|arxiv=0709.3995}}
7. ^{{cite journal|last1=Tao|first1=Terence|author1-link=Terence Tao|last2=Vu|first2=Van|author2link=Van Vu|title=Random matrices: Universality of ESD and the Circular Law|others=appendix by Manjunath Krishnapur|journal=Annals of Probability|volume=38|issue=5|year=2010|pages=2023–2065|arxiv=0807.4898|doi=10.1214/10-AOP534|mr=2722794}}
- List of ships built at the Fore River Shipyard
- List of ships built by A. & J. Inglis
- List of ships built by Fincantieri
- List of Ships built by Fincantieri
- List of ships built by Hall, Russell & Company (1-200)
- List of ships built by Hall, Russell & Company (601-700)
- List of ships built by Hall, Russell & Company (801-900)
- List of ships built by Hall, Russell & Company (901-1000)
- List of ships built by Harland and Wolff
- List of ships built by the Fore River Shipyard
- List of ships built by William Denny and Brothers
- List of ships built in Alameda, California
- List of ships captured in the 18th century
- List of ships captured in the 19th century
- List of ships damaged by kamikaze attack
- List of ships in Battlestar Galactica (2004)
- List of ships in Battlestar Galactica (2004 TV series)
- List of ships in Gold Bombardment Group
- List of ships in Juno Bombardment Group
- List of ships in Omaha Bombardment Group
- List of ships in Sword Bombardment Group
- List of ships in the Culture
- List of ships involved in the Dunkirk evacuation
- List of ships named City of Benares
- List of ships named Fanny