- Example
- See also
- References
In probability theory, conditional dependence is a relationship between two or more events that are dependent when a third event occurs.[1][2] For example, if A and B are two events that individually increase the probability of a third event C, and do not directly affect each other, then initially (when it has not been observed whether or not the event C occurs)
[3][4] (A and B are independent).
But suppose that now C is observed to occur. If event B occurs the probability of occurrence of the event A will decrease because its positive relation to C is less necessary as an explanation for the occurrence of C (similarly, event A occurring will decrease the probability of occurrence of B). Hence, now the two events A and B are conditionally negatively dependent on each other because the probability of occurrence of each is negatively dependent on whether the other occurs. We have
[5]
Conditional dependence is different from conditional independence. In conditional independence two events (which may be dependent or not) become independent given the occurrence of a third event.[6]
Example
In essence probability is influenced by a person's information about the possible occurrence of an event. For example, let the event A be 'I have a new phone'; event B be 'I have a new watch'; and event C be 'I am happy'; and suppose that having either a new phone or a new watch increases the probability of my being happy. Let us assume that the event C has occurred – meaning 'I am happy'. Now if another person sees my new watch, he/she will reason that my likelihood of being happy was increased by my new watch, so there is less need to attribute my happiness to a new phone.
To make the example more numerically specific, suppose that there are four possible states, given in the four columns of the following table, in which the occurrence of event A is signified by a 1 in row A and its non-occurrence is signified by a 0 (and likewise for B and C):
| probability | 1/4 | 1/4 | 1/4 | 1/4 |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| A | 0 | 1 | 0 | 1 |
| B | 0 | 0 | 1 | 1 |
| C | 0 | 1 | 1 | 1 |
In this example, C occurs if and only if at least one of A, B occurs. Unconditionally (i.e., without reference to C), A and B are independent of each other because P(A)—the sum of the probabilities associated with a 1 in row A—is  while P(A|B) = P(A and B) / P(B) =
while P(A|B) = P(A and B) / P(B) = 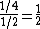 = P(A). But conditional on C having occurred (the last three columns in the table), we have P(A|C) = P(A and C) / P(C) =
= P(A). But conditional on C having occurred (the last three columns in the table), we have P(A|C) = P(A and C) / P(C) = 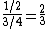 while P(A|C and B) = P(A and C and B) / P(C and B) =
while P(A|C and B) = P(A and C and B) / P(C and B) = 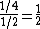 < P(A|C). Since in the presence of C the probability of A is affected by the presence or absence of B, A and B are mutually dependent conditional on C.
< P(A|C). Since in the presence of C the probability of A is affected by the presence or absence of B, A and B are mutually dependent conditional on C.
See also
- Conditional independence
- de Finetti's theorem
- Conditional expectation
References
2. ^Introduction to learning Bayesian Networks from Data by Dirk Husmeier "Introduction to Learning Bayesian Networks from Data -Dirk Husmeier"
3. ^Conditional Independence in Statistical theory "Conditional Independence in Statistical Theory", A. P. Dawid" {{webarchive|url=https://web.archive.org/web/20131227164541/http://edlab-www.cs.umass.edu/cs589/2010-lectures/conditional%20independence%20in%20statistical%20theory.pdf |date=2013-12-27 }}
4. ^Probabilistic independence on Britannica "Probability->Applications of conditional probability->independence (equation 7) "
5. ^Introduction to Artificial Intelligence by Sebastian Thrun and Peter Norvig, 2011 [https://www.ai-class.com/course/video/quizquestion/60 "Unit 3: Explaining Away"]
6. ^Conditional Independence in Statistical theory "Conditional Independence in Statistical Theory", A. P. Dawid {{webarchive|url=https://web.archive.org/web/20131227164541/http://edlab-www.cs.umass.edu/cs589/2010-lectures/conditional%20independence%20in%20statistical%20theory.pdf |date=2013-12-27 }}
- Monticello Bypass
- Monticello College
- Monticello Commercial Historic District
- Monticello Confederate Monument
- Monticello Courthouse Square Historic District
- Monticello Crossroads Scenic Byway
- Monticello Female Seminary
- Monticello (fictional)
- Monticello High School (Arkansas)
- Monticello High School (Illinois)
- Monticello High School (Monticello, Georgia)
- Monticello Historic District (Monticello, Georgia)
- Monticello Hotel
- Monticello, Miss.
- Monticello, New Mexico
- Monticello North Main Street Historic District
- Monticello Old Jail Museum
- Monticello Post Office
- Monticello School District
- Monticello School District (Arkansas)
- Monticello School District (disambiguation)
- Monticello Seminary
- Monticello Store and Post Office
- Monticello Township, Iowa
- Monticello, Virginia