- Example
- See also
- References
- External links
The Data processing inequality is an information theoretic concept which states that the information content of a signal cannot be increased via a local physical operation. This can be expressed concisely as 'post-processing cannot increase information'.[1] As explained by Kinney and Atwal, the DPI means that information is generally lost (never gained) when transmitted through a noisy channel.[2]
Example
Let 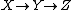 be a Markov chain; then,
be a Markov chain; then,
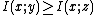 with
with  if and only if
if and only if 
where 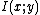 is the mutual information.
is the mutual information.
See also
- Garbage in, garbage out
References
1. ^{{citation |journal=Quantum Information & Computation |volume=12 |issue=5–6 |pages=432–441 |last1=Beaudry |first1=Normand |title=An intuitive proof of the data processing inequality |date=2012 |arxiv=1107.0740|bibcode=2011arXiv1107.0740B }}
2. ^{{cite journal|pmid=24550517 | doi=10.1073/pnas.1309933111 | last1=Kinney | last2=Atwal | volume=111 | issue=9 | title=Equitability, mutual information, and the maximal information coefficient. | date=Mar 2014 | journal=Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A | pages=3354–9 | pmc=3948249| arxiv=1301.7745 | bibcode=2014PNAS..111.3354K }}
2. ^{{cite journal|pmid=24550517 | doi=10.1073/pnas.1309933111 | last1=Kinney | last2=Atwal | volume=111 | issue=9 | title=Equitability, mutual information, and the maximal information coefficient. | date=Mar 2014 | journal=Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A | pages=3354–9 | pmc=3948249| arxiv=1301.7745 | bibcode=2014PNAS..111.3354K }}
External links
- http://www.scholarpedia.org/article/Mutual_information
1 : Data processing
- Aumann's Agreement Theorem
- Aumann-Shapley value
- Aumann–Shapley value
- Auma Obama
- Aumar Alsorani
- Aumar Lake
- Aumar lake
- Aumatre
- A um bum
- AUM (disambiguation)
- Aum doomsday cult
- Aumeisteri Manor
- Aumelas
- Aumenancourt
- Aumerus
- Aumes
- Aumetz
- Aumeville-Lestre
- Aumi
- Aumi, American Samoa
- Aumic House
- Aumism
- Aum (Korean name)
- Aum Namah Shivaya
- Au (mobile phone operator)