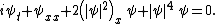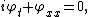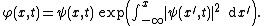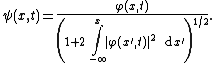- Linearization
- Notes
- References
In mathematical physics, the Eckhaus equation – or the Kundu–Eckhaus equation – is a nonlinear partial differential equations within the nonlinear Schrödinger class:[1]
The equation was independently introduced by Wiktor Eckhaus and by Anjan Kundu to model the propagation of waves in dispersive media.[2][3] The Kundu–Eckhaus equation admits many different types of analytical solutions – just like the nonlinear Schrödinger equation – including but not limited to rational rogue wave solutions.[4] Behavior of its stochastic rogue wave solutions and their spectra may be used for early detection purposes.[5]
Linearization
The Eckhaus equation can be linearized to the linear Schrödinger equation:[6]
through the non-linear transformation:[7]
The inverse transformation is:
This linearization also implies that the Eckhaus equation is integrable.
Notes
2. ^{{harvtxt|Eckhaus|1985}}
3. ^{{harvtxt|Kundu|1984}}
4. ^{{harvtxt|Bayindir|2016a}}
5. ^{{harvtxt|Bayindir|2016b}}
6. ^{{harvtxt|Calogero|De Lillo|1987}}
7. ^{{harvtxt|Ablowitz|Ahrens|De Lillo|2005}}
References
- {{citation |first1=M.J. |last1=Ablowitz |author1-link=Mark J. Ablowitz|first2=C.D. |last2=Ahrens |first3=S. |last3=De Lillo |year=2005 |title=On a "quasi" integrable discrete Eckhaus equation |journal=Journal of Nonlinear Mathematical Physics |volume=12 |issue=Supplement 1 |pages=1–12 |doi=10.2991/jnmp.2005.12.s1.1 |bibcode = 2005JNMP...12S...1A }}
- {{citation |first1=F. |last1=Calogero |author1-link=Francesco Calogero |first2=S. |last2=De Lillo |title=The Eckhaus PDE iψt + ψxx+ 2(|ψ|2)x ψ + |ψ|4 ψ = 0 |journal=Inverse Problems |volume=3 |issue=4 |pages=633–682 |year=1987 |doi=10.1088/0266-5611/3/4/012 |bibcode = 1987InvPr...3..633C }}
- {{citation |first=W. |last=Eckhaus |title=The long-time behaviour for perturbed wave-equations and related problems |id=Preprint no. 404 |publisher=Department of Mathematics, University of Utrecht |year=1985 }}.
Published in part in: {{citation |year=1986 |isbn=978-3-540-16467-8 |title=Trends in applications of pure mathematics to mechanics |volume=249 |series=Lecture Notes in Physics |editor1-last=Kröner |editor1-first=E. |editor2-last=Kirchgässner |editor2-first=K. |doi=10.1007/BFb0016391 |contribution=The long-time behaviour for perturbed wave-equations and related problems |publisher=Springer |location=Berlin |last=Eckhaus |first=W. |pages=168–194 }} - {{citation | first=C. |last=Bayindir |title=Rogue waves of the Kundu–Eckhaus equation in a chaotic wavefield | journal=Physical Review E | volume=93 | number=032201 | year=2016a |doi=10.1103/PhysRevE.93.032201|arxiv=1601.00209 |bibcode=2016PhRvE..93c2201B }}
- {{citation | first=C. |last=Bayindir |title=Rogue wave spectra of the Kundu–Eckhaus equation | journal=Physical Review E | volume=93 | number=062215 | year=2016b |doi=10.1103/PhysRevE.93.062215|arxiv=1604.08035 |bibcode=2016PhRvE..93f2215B }}
- {{citation | first=A. |last=Kundu |title=Landau–Lifshitz and higher-order nonlinear systems gauge generated from nonlinear Schrödinger-type equations | journal=Journal of Mathematical Physics | volume=25 | year=1984 |pages=3433–3438 |doi=10.1063/1.526113|bibcode = 1984JMP....25.3433K }}
- {{citation | title = The first-integral method applied to the Eckhaus equation |journal = Applied Mathematics Letters |volume = 25 |number = 5 |pages = 798–802 |year = 2012 |doi = 10.1016/j.aml.2011.10.021 |first1=N. |last1=Taghizadeh |first2=M. |last2=Mirzazadeh |first3=F. |last3=Tascan }}
- {{citation | title=Handbook of differential equations |first=D. |last=Zwillinger |edition=3rd |publisher=Academic Press |year=1998 | isbn=978 0 12 784396 4 }}
- George Byng (politician)
- George B. Știrbei
- George Cables at Maybeck
- George Cabot (senator)
- George Cadigan
- George Cadle
- George Cakobau, Jr.
- George Calboreanu
- George Caldwell (disambiguation)
- George Caledon Alexander
- George Calhern
- George Callender
- George Calvert Clarke
- George Cameron (priest)
- George Camocke
- George Campbell (1824-92)
- George Campbell (1824–1892)
- George Campbell (1824–92)
- George Campbell (Army Officer)
- George Campbell Gordon
- George Campbell (soccer)
- George Campion
- George Caner
- George canning
- George Canyon discography