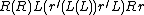- Definition Syntax Semantics
- Relation to other programming languages
- Example program
- References
| name = P′′
| paradigm = Imperative, structured
| released = 1964
| designer = Corrado Böhm
| typing = untyped
| dialects = Brainfuck
| influenced = Brainfuck
}}
P′′ (P double prime[1]) is a primitive computer programming language created by Corrado Böhm[2][3] in 1964 to describe a family of Turing machines.
Definition
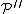 (hereinafter written P′′) is formally defined as a set of words on the four-instruction alphabet
(hereinafter written P′′) is formally defined as a set of words on the four-instruction alphabet 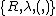 , as follows:
, as follows:
Syntax
-
 and
and  are words in P′′.
are words in P′′. - If
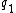 and
and  are words in P′′, then
are words in P′′, then 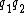 is a word in P′′.
is a word in P′′. - If
 is a word in P′′, then
is a word in P′′, then 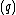 is a word in P′′.
is a word in P′′. - Only words derivable from the previous three rules are words in P′′.
Semantics
-
 is the tape-alphabet of a Turing machine with left-infinite tape,
is the tape-alphabet of a Turing machine with left-infinite tape,  being the blank symbol, equivalent to
being the blank symbol, equivalent to  .
. - All instructions in P′′ are permutations of the set
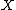 of all possible tape configurations; that is, all possible configurations of both the contents of the tape and the position of the tape-head.
of all possible tape configurations; that is, all possible configurations of both the contents of the tape and the position of the tape-head. -
 is a predicate saying that the current symbol is not
is a predicate saying that the current symbol is not  . It is not an instruction and is not used in programs, but is instead used to help define the language.
. It is not an instruction and is not used in programs, but is instead used to help define the language. -
 means move the tape-head rightward one cell (if possible).
means move the tape-head rightward one cell (if possible). -
 means replace the current symbol
means replace the current symbol  with
with 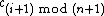 , and then move the tape-head leftward one cell.
, and then move the tape-head leftward one cell. -
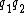 means the function composition
means the function composition 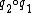 . In other words, the instruction
. In other words, the instruction 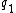 is performed before
is performed before  .
. -
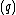 means iterate
means iterate  in a while loop, with the condition
in a while loop, with the condition  .
.
Relation to other programming languages
- P′′ was the first "GOTO-less" imperative structured programming language to be proven Turing-complete[2][3]
- The Brainfuck language (apart from its I/O commands) is a minor informal variation of P′′. Böhm gives explicit P′′ programs for each of a set of basic functions sufficient to compute any computable function, using only
 ,
,  and the four words
and the four words 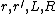 where
where 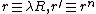 with
with 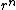 denoting the
denoting the  th iterate of
th iterate of  , and
, and 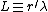 . These are the equivalents of the six respective Brainfuck commands [, ], +, -, <, >. Note that since
. These are the equivalents of the six respective Brainfuck commands [, ], +, -, <, >. Note that since 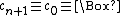 , incrementing the current symbol
, incrementing the current symbol  times will wrap around so that the result is to "decrement" the symbol in the current cell by one (
times will wrap around so that the result is to "decrement" the symbol in the current cell by one (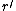 ).
).
Example program
Böhm[2] gives the following program to compute the predecessor (x-1) of an integer x > 0:
which translates directly to the equivalent Brainfuck program:
The program expects an integer to be represented in bijective base-k notation, with 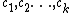 encoding the digits
encoding the digits 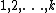 respectively, and to have
respectively, and to have  before and after the digit-string. (E.g., in bijective base-2, the number eight would be encoded as
before and after the digit-string. (E.g., in bijective base-2, the number eight would be encoded as 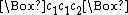 , because 8 in bijective base-2 is 112.) At the beginning and end of the computation, the tape-head is on the
, because 8 in bijective base-2 is 112.) At the beginning and end of the computation, the tape-head is on the  preceding the digit-string.
preceding the digit-string.
References
2. ^1 2 Böhm, C.: "On a family of Turing machines and the related programming language", ICC Bull. 3, 185-194, July 1964.
3. ^1 Böhm, C. and Jacopini, G.: "Flow diagrams, Turing machines and languages with only two formation rules", CACM 9(5), 1966. (Note: This is the most-cited paper on the structured program theorem.)
- Banded Sunbird
- Banded Supple Skink
- Banded Surili
- Banded Tiger Moth
- Banded tilapia
- Banded Tilapia
- Banded toadfish
- Banded Toed Gecko
- Banded Triplefin
- Banded triplefin
- Banded tulip
- Banded Uromastyx
- Banded warbler
- Banded Warbler
- Banded water cobra
- Banded Wattle-eye
- Banded wedge shell
- Banded white-eye
- Banded Whiteface
- Banded-winged Stenopsis
- Banded-wing whitefly
- Banded Woodpecker
- Banded Wren
- Banded Yellow Robin
- Bandee Sardi Dam