- Quantum information
- Relation to quantum mechanics
- Journals
- See also
- References
In physics and computer science, quantum information is the information of the state of a quantum system; it is the basic entity of study in quantum information theory, and can be manipulated using quantum information processing techniques. Quantum information, like classical information, can be processed using digital computers, transmitted from one location to another, manipulated with algorithms, and analyzed with the computer science mathematics. While the fundamental unit of classical information is the bit, the most basic unit of quantum information is the qubit.
Quantum information
Quantum information differs strongly from classical information, epitomized by the bit, in many striking and unfamiliar ways. Among these are the following:
- A unit of quantum information is the qubit. Unlike classical digital states (which are discrete), a qubit is continuous-valued, describable by a direction on the Bloch sphere. Despite being continuously valued in this way, a qubit is the smallest possible unit of quantum information, as despite the qubit state being continuously-valued, it is impossible to measure the value precisely.
- A qubit cannot be (wholly) converted into classical bits; that is, it cannot be "read". This is the no-teleportation theorem.
- Despite the awkwardly-named no-teleportation theorem, qubits can be moved from one physical particle to another, by means of quantum teleportation. That is, qubits can be transported, independently of the underlying physical particle.
- An arbitrary qubit can neither be copied, nor destroyed. This is the content of the no cloning theorem and the no-deleting theorem.
- Although a single qubit can be transported from place to place (e.g. via quantum teleportation), it cannot be delivered to multiple recipients; this is the no-broadcast theorem, and is essentially implied by the no-cloning theorem.
- Qubits can be changed, by applying linear transformations or quantum gates to them, to alter their state. While classical gates correspond to the familiar operations of Boolean logic, quantum gates are physical unitary operators that in the case of qubits correspond to rotations of the Bloch sphere.
- Due to the volatility of quantum systems and the impossibility of copying states, the storing of quantum information is much more difficult than storing classical information. Nevertheless, with the use of quantum error correction quantum information can still be reliably stored in principle. The existence of quantum error correcting codes has also led to the possibility of fault tolerant quantum computation.
- Classical bits can be encoded into and subsequently retrieved from configurations of qubits, through the use of quantum gates. By itself, a single qubit can convey no more than one bit of accessible classical information about its preparation. This is Holevo's theorem. However, in superdense coding a sender, by acting on one of two entangled qubits, can convey two bits of accessible information about their joint state to a receiver.
- Quantum information can be moved about, in a quantum channel, analogous to the concept of a classical communications channel. Quantum messages have a finite size, measured in qubits; quantum channels have a finite channel capacity, measured in qubits per second.
- Quantum information, and changes in quantum information, can be quantitatively measured by using an analogue of Shannon entropy, called the von Neumann entropy. Given a statistical ensemble of quantum mechanical systems with the density matrix
 , it is given by
, it is given by 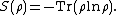 Many of the same entropy measures in classical information theory can also be generalized to the quantum case, such as Holevo entropy[1] and the conditional quantum entropy.
Many of the same entropy measures in classical information theory can also be generalized to the quantum case, such as Holevo entropy[1] and the conditional quantum entropy. - In some cases quantum algorithms can be used to perform computations faster than in any known classical algorithm. The most famous example of this is Shor's algorithm that can factor numbers in polynomial time, compared to the best classical algorithms that take sub-exponential time. As factorization is an important part of the safety of RSA encryption, Shor's algorithm sparked the new field of post-quantum cryptography that tries to find encryption schemes that remain safe even when quantum computers are in play. Other examples of algorithms that demonstrate quantum supremacy include Grover's search algorithm, where the quantum algorithm gives a quadratic speed-up over the best possible classical algorithm. The complexity class of problems efficiently solvable by a quantum computer is known as BQP.
- Quantum key distribution (QKD) allows unconditionally secure transmission of classical information, unlike classical encryption, which can always be broken in principle, if not in practice. Do note that certain subtle points regarding the safety of QKD are still hotly debated.
The study of all of the above topics and differences comprises quantum information theory.
Relation to quantum mechanics
{{expert needed|1=Physics|2=section|talk=Relation to quantum mechanics|reason=QM does not study|date=December 2018}}Quantum mechanics studies how microscopic physical systems change dynamically in nature. In the field of quantum information theory, the quantum systems studied are abstracted away from any real world counterpart. A qubit might for instance physically be a photon in a linear optical quantum computer, an ion in a trapped ion quantum computer, or it might be a large collection of atoms as in a superconducting quantum computer. Regardless of the physical implementation, the limits and features of qubits implied by quantum information theory hold as all these systems are all mathematically described by the same apparatus of density matrices over the complex number
Journals
Many journals publish research in quantum information science, although only a few are dedicated to this area. Among these are
- International Journal of Quantum Information
- Quantum Information & Computation
- Quantum Information Processing
- npj Quantum Information[2]
- Quantum[3]
- Quantum Science and Technology[4]
See also
- Categorical quantum mechanics
- Einstein's thought experiments
- Interpretations of quantum mechanics
- POVM (positive operator valued measure)
- Quantum clock
- Quantum cognition
- Quantum foundations
- Quantum information science
- Quantum statistical mechanics
- Qutrit
- Typical subspace
References
2. ^{{cite web|url=http://www.nature.com/npjqi/|title=npj Quantum Information|website=Nature.com|accessdate=4 December 2018}}
3. ^{{cite web|url=http://quantum-journal.org/|title=Quantum Homepage|website=Quantum-journal.org|accessdate=4 December 2018}}
4. ^{{cite web|url=http://iopscience.iop.org/journal/2058-9565|title=Quantum Science and Technology|website=IOP Publishing|accessdate=12 January 2019}}
- Charles H. Bennett and Peter W. Shor, "Quantum Information Theory," IEEE Transactions on Information Theory, Vol 44, pp 2724–2742, Oct 1998|
- [https://www.springer.com/east/home?SGWID=5-102-22-173664707-0&changeHeader=true Gregg Jaeger's book on Quantum Information](published by Springer, New York, 2007, {{ISBN|0-387-35725-4}})
- [https://web.archive.org/web/20160303183533/http://www.quantware.ups-tlse.fr/IHP2006/ Lectures at the Institut Henri Poincaré (slides and videos)]
- International Journal of Quantum Information World Scientific
- [https://www.springer.com/new+%26+forthcoming+titles+%28default%29/journal/11128 Quantum Information Processing] Springer
- Michael A. Nielsen, Isaac L. Chuang, "Quantum Computation and Quantum Information"
- {{citation|first=Mark M.|last=Wilde|arxiv=1106.1445|title=Quantum Information Theory|year=2017|publisher=Cambridge University Press|bibcode = 2011arXiv1106.1445W |doi=10.1017/9781316809976.001}}
- John Preskill, Course Information for Physics 219/Computer Science 219 Quantum Computation, Caltech
- Charles H. Bennett, Peter W. Shor, "Quantum Information Theory" [https://www.researchgate.net/profile/Fabio_Benatti/publication/226219951_Quantum_Information_Theory/links/0deec517fd717b0130000000.pdf]
- Vlatko Vedral, [https://global.oup.com/academic/product/introduction-to-quantum-information-science-9780199215706?cc=gb&lang=en& "Introduction to Quantum Information Science"]
- Masahito Hayashi, [https://www.springer.com/in/book/9783642067693 "Quantum Information: An Introduction"]
- Masahito Hayashi, [https://www.springer.com/gb/book/9783662497234 "Quantum Information Theory: Mathematical Foundation"]
- Christian Weedbrook, Stefano Pirandola, Raul Garcia-Patron, Nicolas J. Cerf, Timothy C. Ralph, Jeffrey H. Shapiro, Seth Lloyd [https://arxiv.org/abs/1110.3234 "Gaussian Quantum Information", arXiv:1110.3234]
- Stand by Your Man (EP)
- Stand by Your Van
- Stand By Your Van
- Stand Cricket Club
- Stand down
- Standedge Canal Tunnel
- Standedge tunnel
- Standedge Tunnels
- Standen
- Standerbred
- Standerton
- Standesamt
- Standesamt Adelnau
- Standesamt Budsin
- Standesamt Dziembowo
- Standesamt Kolmar
- Standesamt Margonin
- Standesamt Podanin
- Standesamt Podstolitz
- Standesamt Rawitsch
- Standesamt Samotschin
- Standesamt Schneidemühl
- Standesamt Tremessen
- Standesamt Usch
- Standesamt Wongrowitz