- Expander codes
- Definition
- Rate
- Distance Proof Lemma 1 Proof Corollary Lemma 2 Proof Corollary
- Encoding
- Decoding Proof Correctness Lemma 3 Proof Lemma 4 Proof Complexity
- See also
- Notes
- References
| name = Expander codes
| image =
| image_caption = bipartite expander graph
| namesake =
| type = Linear block code
| block_length =

| message_length =

| rate =
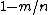
| distance =
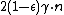
| alphabet_size =

| notation =
 -code
-code}}
In coding theory, expander codes form a class of error-correcting codes that are constructed from bipartite expander graphs.
Along with Justesen codes, expander codes are of particular interest since they have a constant positive rate, a constant positive relative distance, and a constant alphabet size.
In fact, the alphabet contains only two elements, so expander codes belong to the class of binary codes.
Furthermore, expander codes can be both encoded and decoded in time proportional to the block length of the code.
Expander codes
In coding theory, an expander code is a 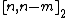 linear block code whose parity check matrix is the adjacency matrix of a bipartite expander graph. These codes have good relative distance
linear block code whose parity check matrix is the adjacency matrix of a bipartite expander graph. These codes have good relative distance  , where
, where  and
and 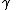 are properties of the expander graph as defined later), rate
are properties of the expander graph as defined later), rate  , and decodability (algorithms of running time
, and decodability (algorithms of running time 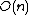 exist).
exist).
Definition
Consider a bipartite graph  , where
, where 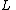 and
and 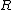 are the vertex sets and
are the vertex sets and  is the set of edges connecting vertices in
is the set of edges connecting vertices in 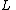 to vertices of
to vertices of 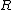 . Suppose every vertex in
. Suppose every vertex in 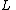 has degree
has degree  (the graph is
(the graph is  -regular),
-regular), 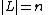 , and
, and  ,
,  . Then
. Then  is a
is a 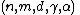 expander graph if every small enough subset
expander graph if every small enough subset 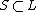 ,
, 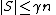 has the property that
has the property that  has at least
has at least  distinct neighbors in
distinct neighbors in 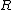 . Note that this holds trivially for
. Note that this holds trivially for  . When
. When 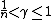 and
and 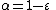 for a constant
for a constant  , we say that
, we say that  is a lossless expander.
is a lossless expander.
Since  is a bipartite graph, we may consider its
is a bipartite graph, we may consider its 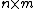 adjacency matrix. Then the linear code
adjacency matrix. Then the linear code 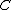 generated by viewing the transpose of this matrix as a parity check matrix is an expander code.
generated by viewing the transpose of this matrix as a parity check matrix is an expander code.
It has been shown that nontrivial lossless expander graphs exist. Moreover, we can explicitly construct them.[1]
Rate
The rate of 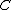 is its dimension divided by its block length. In this case, the parity check matrix has size
is its dimension divided by its block length. In this case, the parity check matrix has size 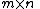 , and hence
, and hence 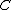 has dimension at least
has dimension at least  .
.
Distance
Suppose 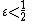 . Then the distance of a
. Then the distance of a  expander code
expander code 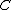 is at least
is at least 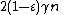 .
.
Proof
Note that we can consider every codeword  in
in 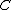 as a subset of vertices
as a subset of vertices 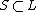 , by saying that vertex
, by saying that vertex 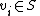 if and only if the
if and only if the  th index of the codeword is a 1. Then
th index of the codeword is a 1. Then  is a codeword iff every vertex
is a codeword iff every vertex 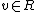 is adjacent to an even number of vertices in
is adjacent to an even number of vertices in  . (In order to be a codeword,
. (In order to be a codeword, 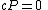 , where
, where  is the parity check matrix. Then, each vertex in
is the parity check matrix. Then, each vertex in 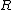 corresponds to each column of
corresponds to each column of  . Matrix multiplication over
. Matrix multiplication over 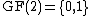 then gives the desired result.) So, if a vertex
then gives the desired result.) So, if a vertex 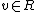 is adjacent to a single vertex in
is adjacent to a single vertex in  , we know immediately that
, we know immediately that  is not a codeword. Let
is not a codeword. Let 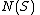 denote the neighbors in
denote the neighbors in 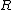 of
of  , and
, and  denote those neighbors of
denote those neighbors of  which are unique, i.e., adjacent to a single vertex of
which are unique, i.e., adjacent to a single vertex of  .
.
Lemma 1
For every 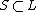 of size
of size 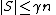 ,
,  .
.
Proof
Trivially,  , since
, since  implies
implies  .
.  follows since the degree of every vertex in
follows since the degree of every vertex in  is
is  . By the expansion property of the graph, there must be a set of
. By the expansion property of the graph, there must be a set of  edges which go to distinct vertices. The remaining
edges which go to distinct vertices. The remaining 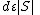 edges make at most
edges make at most 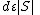 neighbors not unique, so
neighbors not unique, so 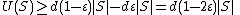 .
.
Corollary
Every sufficiently small  has a unique neighbor. This follows since
has a unique neighbor. This follows since 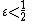 .
.
Lemma 2
Every subset 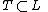 with
with  has a unique neighbor.
has a unique neighbor.
Proof
Lemma 1 proves the case 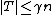 , so suppose
, so suppose  . Let
. Let  such that
such that 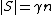 . By Lemma 1, we know that
. By Lemma 1, we know that  . Then a vertex
. Then a vertex  is in
is in 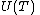 iff
iff 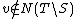 , and we know that
, and we know that 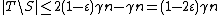 , so by the first part of Lemma 1, we know
, so by the first part of Lemma 1, we know 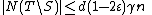 . Since
. Since 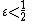 ,
, 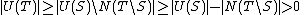 , and hence
, and hence 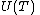 is not empty.
is not empty.
Corollary
Note that if a 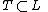 has at least 1 unique neighbor, i.e.
has at least 1 unique neighbor, i.e. 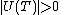 , then the corresponding word
, then the corresponding word  corresponding to
corresponding to  cannot be a codeword, as it will not multiply to the all zeros vector by the parity check matrix. By the previous argument,
cannot be a codeword, as it will not multiply to the all zeros vector by the parity check matrix. By the previous argument, 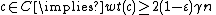 . Since
. Since 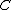 is linear, we conclude that
is linear, we conclude that 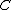 has distance at least
has distance at least 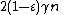 .
.
Encoding
The encoding time for an expander code is upper bounded by that of a general linear code -  by matrix multiplication. A result due to Spielman shows that encoding is possible in
by matrix multiplication. A result due to Spielman shows that encoding is possible in 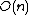 time.[2]
time.[2]
Decoding
Decoding of expander codes is possible in 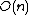 time when
time when 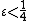 using the following algorithm.
using the following algorithm.
Let 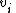 be the vertex of
be the vertex of 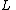 that corresponds to the
that corresponds to the  th index in the codewords of
th index in the codewords of 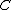 . Let
. Let  be a received word, and
be a received word, and 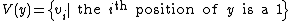 . Let
. Let 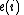 be
be 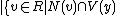 is even
is even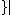 , and
, and 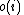 be
be  is odd
is odd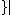 . Then consider the greedy algorithm:
. Then consider the greedy algorithm:
Input: received codeword  .
.
initialize y' to y while there is a v in R adjacent to an odd number of vertices in V(y') if there is an i such that o(i) > e(i) flip entry i in y' else fail
Output: fail, or modified codeword  .
.
Proof
We show first the correctness of the algorithm, and then examine its running time.
Correctness
We must show that the algorithm terminates with the correct codeword when the received codeword is within half the code's distance of the original codeword. Let the set of corrupt variables be  ,
, 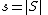 , and the set of unsatisfied (adjacent to an odd number of vertices) vertices in
, and the set of unsatisfied (adjacent to an odd number of vertices) vertices in 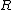 be
be  . The following lemma will prove useful.
. The following lemma will prove useful.
Lemma 3
If 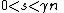 , then there is a
, then there is a 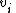 with
with 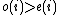 .
.
Proof
By Lemma 1, we know that 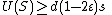 . So an average vertex has at least
. So an average vertex has at least 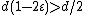 unique neighbors (recall unique neighbors are unsatisfied and hence contribute to
unique neighbors (recall unique neighbors are unsatisfied and hence contribute to 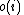 ), since
), since 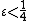 , and thus there is a vertex
, and thus there is a vertex 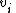 with
with 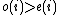 .
.
So, if we have not yet reached a codeword, then there will always be some vertex to flip. Next, we show that the number of errors can never increase beyond 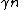 .
.
Lemma 4
If we start with  , then we never reach
, then we never reach  at any point in the algorithm.
at any point in the algorithm.
Proof
When we flip a vertex 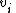 ,
, 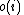 and
and 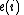 are interchanged, and since we had
are interchanged, and since we had 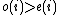 , this means the number of unsatisfied vertices on the right decreases by at least one after each flip. Since
, this means the number of unsatisfied vertices on the right decreases by at least one after each flip. Since  , the initial number of unsatisfied vertices is at most
, the initial number of unsatisfied vertices is at most 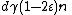 , by the graph's
, by the graph's  -regularity. If we reached a string with
-regularity. If we reached a string with 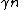 errors, then by Lemma 1, there would be at least
errors, then by Lemma 1, there would be at least 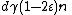 unique neighbors, which means there would be at least
unique neighbors, which means there would be at least 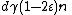 unsatisfied vertices, a contradiction.
unsatisfied vertices, a contradiction.
Lemmas 3 and 4 show us that if we start with  (half the distance of
(half the distance of 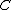 ), then we will always find a vertex
), then we will always find a vertex 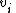 to flip. Each flip reduces the number of unsatisfied vertices in
to flip. Each flip reduces the number of unsatisfied vertices in 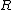 by at least 1, and hence the algorithm terminates in at most
by at least 1, and hence the algorithm terminates in at most  steps, and it terminates at some codeword, by Lemma 3. (Were it not at a codeword, there would be some vertex to flip). Lemma 4 shows us that we can never be farther than
steps, and it terminates at some codeword, by Lemma 3. (Were it not at a codeword, there would be some vertex to flip). Lemma 4 shows us that we can never be farther than 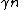 away from the correct codeword. Since the code has distance
away from the correct codeword. Since the code has distance 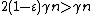 (since
(since 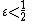 ), the codeword it terminates on must be the correct codeword, since the number of bit flips is less than half the distance (so we couldn't have traveled far enough to reach any other codeword).
), the codeword it terminates on must be the correct codeword, since the number of bit flips is less than half the distance (so we couldn't have traveled far enough to reach any other codeword).
Complexity
We now show that the algorithm can achieve linear time decoding. Let 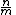 be constant, and
be constant, and  be the maximum degree of any vertex in
be the maximum degree of any vertex in 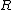 . Note that
. Note that  is also constant for known constructions.
is also constant for known constructions.
- Pre-processing: It takes
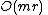 time to compute whether each vertex in
time to compute whether each vertex in 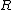 has an odd or even number of neighbors.
has an odd or even number of neighbors. - Pre-processing 2: We take
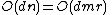 time to compute a list of vertices
time to compute a list of vertices 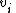 in
in 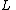 which have
which have 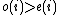 .
. - Each Iteration: We simply remove the first list element. To update the list of odd / even vertices in
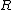 , we need only update
, we need only update 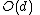 entries, inserting / removing as necessary. We then update
entries, inserting / removing as necessary. We then update  entries in the list of vertices in
entries in the list of vertices in 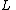 with more odd than even neighbors, inserting / removing as necessary. Thus each iteration takes
with more odd than even neighbors, inserting / removing as necessary. Thus each iteration takes  time.
time. - As argued above, the total number of iterations is at most
 .
.
This gives a total runtime of  time, where
time, where  and
and  are constants.
are constants.
See also
- Expander graph
- Low-density parity-check code
- Linear time encoding and decoding of error-correcting codes
- ABNNR and AEL codes
Notes
This article is based on Dr. Venkatesan Guruswami's course notes.[3]
References
2. ^{{cite journal |first=D. |last=Spielman |title=Linear-time encodable and decodable error-correcting codes |journal=IEEE Transactions on Information Theory |volume=42 |issue=6 |pages=1723–31 |year=1996 |doi=10.1109/18.556668 |url=|citeseerx=10.1.1.47.2736 }}
3. ^{{cite web |first=V. |last=Guruswami |title=Lecture 13: Expander Codes |date=15 November 2006 |work=CSE 533: Error-Correcting |publisher=University of Washington |url=http://www.cs.washington.edu/education/courses/cse533/06au/lecnotes/lecture13.pdf }}
{{cite web |first=V. |last=Guruswami |title=Notes 8: Expander Codes and their decoding |date=March 2010 |work=Introduction to Coding Theory |publisher=Carnegie Mellon University |url=http://www.cs.cmu.edu/~venkatg/teaching/codingtheory/notes/notes8.pdf }}
{{cite journal |first=V. |last=Guruswami |title=Guest column: error-correcting codes and expander graphs |journal=ACM SIGACT News |volume=35 |issue=3 |pages=25–41 |date=September 2004 |doi=10.1145/1027914.1027924 |url=http://dl.acm.org/citation.cfm?id=1027924}}
- Fellow of the (Royal) Statistical Society
- Fellow of the Scottish Society of Arts
- Fellow of the Society of Antiquaries of London
- Fellow of the Society of Antiquaries of Scotland
- Fellow of the Statistical Society
- Fellow Passengers
- Fellows
- Fellows Auctioneers
- Fellows Gear Shaper Company
- Fellowship (album)
- Fellowship Christian School
- Fellowship Deaconry
- Fellowship Examination of the Royal College of Pathologists
- Fellowship Farm
- Fellowship Farm Cooperative Association
- Fellowship Farm (New Jersey)
- Fellowship Farms
- Fellowship group
- Fellowship in Manufacturing Management
- Fellowship of Brethren Homes
- Fellowship of Christian Peace Officers
- Fellowship of Churches of Christ in Nigeria
- Fellowship of Confessing Anglicans
- Fellowship of Confessing Churches
- Fellowship offering