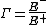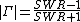- Telecommunications
- Seismology
- Optics and microwaves
- Acoustics
- See also
- References
- External links
In physics and electrical engineering the reflection coefficient is a parameter that describes how much of an electromagnetic wave is reflected by an impedance discontinuity in the transmission medium. It is equal to the ratio of the amplitude of the reflected wave to the incident wave, with each expressed as phasors. For example, it is used in optics to calculate the amount of light that is reflected from a surface with a different index of refraction, such as a glass surface, or in an electrical transmission line to calculate how much of the electromagnetic wave is reflected by an impedance. The reflection coefficient is closely related to the transmission coefficient. The reflectance of a system is also sometimes called a "reflection coefficient".
Different specialties have different applications for the term.
Telecommunications
{{see also|Reflections of signals on conducting lines|Signal reflection}}In telecommunications, the reflection coefficient is the ratio of the complex amplitude of the reflected wave to that of the incident wave. In particular, at a discontinuity in a transmission line, it is the complex ratio of the electric field strength of the reflected wave ( ) to that of the incident wave (
) to that of the incident wave (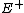 ). This is typically represented with a
). This is typically represented with a  (capital gamma) and can be written as:
(capital gamma) and can be written as:
The reflection coefficient may also be established using other field or circuit quantities.
The reflection coefficient of a load is determined by its impedance 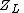 (load impedance) and the impedance toward the source
(load impedance) and the impedance toward the source 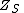 (source impedance).
(source impedance).

Notice that a negative reflection coefficient means that the reflected wave receives a 180°, or  , phase shift.
, phase shift.
The magnitude (designated by vertical bars) of the reflection coefficient can be calculated from the standing wave ratio, 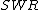 :
:
The reflection coefficient is displayed graphically using a Smith chart.
Seismology
{{main|Reflection seismology}}Reflection coefficient is used in feeder testing for reliability of medium.
Optics and microwaves
{{main|Fresnel equations}}In optics and electromagnetics in general, "reflection coefficient" can refer to either the amplitude reflection coefficient described here, or the reflectance, depending on context. Typically, the reflectance is represented by a capital R, while the amplitude reflection coefficient is represented by a lower-case r.These related concepts are covered by Fresnel equations in classical optics.
Acoustics
{{main|Acoustic wave#Reflection}}Acousticians use reflection coefficients to understand the effect of different materials on their acoustic environments.
See also
- Microwave
- Mismatch loss
- Scattering parameters
- Transmission coefficient
- Target strength
- Hagen-Rubens relation
References
- {{FS1037C MS188}}
- {{cite book | last = Bogatin | first = Eric | title = Signal Integrity - Simplified | year = 2004 | publisher = Pearson Education, Inc. | location = Upper Saddle River, New Jersey | isbn = 0-13-066946-6}} Figure 8-2 and Eqn. 8-1 Pg. 279
External links
{{commons category|Smith charts}}- Flash tutorial for understanding reflection A flash program that shows how a reflected wave is generated, the reflection coefficient and VSWR
- [https://poynting.herokuapp.com Application for drawing standing wave diagrams including the reflection coefficient, input impedance, SWR, etc.]