- References
In mathematical analysis, Glaeser's continuity theorem, is a characterization of the continuity of the derivative of the square roots of functions of class 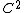 . It was introduced in 1963 by Georges Glaeser,[1] and was later simplified by Jean Dieudonné.[2]
. It was introduced in 1963 by Georges Glaeser,[1] and was later simplified by Jean Dieudonné.[2]
The theorem states: Let 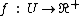 be a function of class
be a function of class 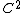 in an open set U contained in
in an open set U contained in  , then
, then 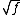 is of class
is of class  in U if and only if its partial derivatives of first and second order vanish in the zeros of f.
in U if and only if its partial derivatives of first and second order vanish in the zeros of f.
References
1. ^G. Glaeser, "Racine carrée d'une fonction différentiable", Annales de l'Institut Fourier 13, no 2 (1963), 203–210 : article
2. ^J. Dieudonné, "Sur un théorème de Glaeser", J. Analyse math. 23 (1970), 85–88 : Résumé Zbl, article p.85, article p.86, article p.87 (the p. 88, not shown on the free preview contains the reference to Glaeser)
2. ^J. Dieudonné, "Sur un théorème de Glaeser", J. Analyse math. 23 (1970), 85–88 : Résumé Zbl, article p.85, article p.86, article p.87 (the p. 88, not shown on the free preview contains the reference to Glaeser)
2 : Mathematical analysis|Theorems
- Corporate (film)
- Corporate Finance Institute
- Corporate Flight Management
- Corporate form
- Corporate forms
- Corporate Information Factory
- Corporate integrity agreement
- Corporate interests
- Corporate Knights (magazine)
- Corporate Knights Magazine
- Corporate Knights magazine
- Corporate ladder
- Corporate library
- Corporate lobbying in the United States
- Corporate Number
- Corporate Number (Japan)
- Corporate parent
- Corporate political donations
- Corporate promoters
- Corporate publishing
- Corporate Real Estate
- Corporate Representatives for Ethical Wikipedia Engagement
- Corporate ResourceNet
- Corporate secrecy
- Corporate Slave