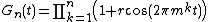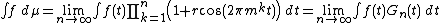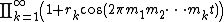- History
- References
- External links
In mathematics, a G-measure is a measure  that can be represented as the weak-∗ limit of a sequence of measurable functions
that can be represented as the weak-∗ limit of a sequence of measurable functions 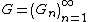 . A classic example is the Riesz product
. A classic example is the Riesz product
where 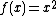 . The weak-∗ limit of this product is a measure on the circle
. The weak-∗ limit of this product is a measure on the circle 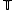 , in the sense that for
, in the sense that for 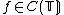 :
:
where 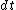 represents Haar measure.
represents Haar measure.
History
It was Keane[1] who first showed that Riesz products can be regarded as strong mixing invariant measure under the shift operator 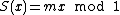 . These were later generalized by Brown and Dooley [2] to Riesz products of the form
. These were later generalized by Brown and Dooley [2] to Riesz products of the form
where 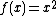 .
.
References
1. ^{{cite journal | last1=Keane | first1=M. | title=Strongly mixing g-measures | year=1972 | journal= Invent. Math. | volume=16 | issue=4 | pages=309–324 | doi=10.1007/bf01425715}}
2. ^{{cite journal | first1=G. | last1=Brown | first2=A. H. |last2=Dooley | title=Odometer actions on G-measures.| journal=Ergodic Theory and Dynamical Systems |volume=11 | issue=2 | year = 1991 | pages=279–307 | doi=10.1017/s0143385700006155}}
2. ^{{cite journal | first1=G. | last1=Brown | first2=A. H. |last2=Dooley | title=Odometer actions on G-measures.| journal=Ergodic Theory and Dynamical Systems |volume=11 | issue=2 | year = 1991 | pages=279–307 | doi=10.1017/s0143385700006155}}
External links
- Riesz Product at Encyclopedia of Mathematics
2 : Measures (measure theory)|Dimension theory
- Sat.1 Comedy
- Sat.1 Emotions
- Sat.1 emotions
- Sat.1 Gold Österreich
- Sat.1 Schweiz
- Sat.1 Österreich
- SATA 2.5
- SATA 2.6
- SATA Air Acores Flight SP530M
- SATA Air Açores destinations
- SATA Air Açores Flight 530
- SATA Air Açores Flight SP530M
- Satadhanvan
- SATADOM
- Satadra chola
- Satadra lazula
- Satafi
- Satafis
- SATA Flight 530
- SATA flight 530
- Sata (Hemsedal)
- SATA International
- SATA International destinations
- SAT Airport
- Satakarni I